Team Members
- Rohit Kulkarni
- Prithvi Patil
- Adithya Kannan
- Shashank Holla
Abstract
The main aim of Sound Follower Bot is for the bot to recognise and localise the sound impulse source and move towards it. The initial aim was to identify impulse sound. The sound is recorded by the mic and classified as a sharp impulse. Then if it’s classified the source is localised(i.e. The x,y coordinates are found with respect to the microphone setup) and the bot is made to move towards the source.The approach used was of the relative delay of arrival between pairs of mics among four of them and an indigenous algorithm to obtain position of source based on four delays was written. Then the bot is turned in that direction and moves towards the source.
Objectives
To classify impulse sound source, localise the source and move the bot towards the source.
Methodology
The project is divided into two major parts.
Localization
Localization is done by using mic delays and obtaining the source direction. The individual time stamps with microsecond resolution were taken when mic output crosses a certain threshold to classify the sound as an impulse. The values were taken in by the microcontroller (Arduino Due) using function micros(). Arduino Due is used in this case because of the high sampling speed and the ADC pins available. The mic timestamps are taken and the relative delays between the microphone are calculated. These delays are then used to calculate the angle of the sound source wrt lines joining a pair of mics.
This is the link to the code which was used to obtain the delay and send it serially from Arduino to a computer for computation of direction of the source.
Using this set of delays from the microcontroller the x,y coordinate of the source can be obtained. The following method was used to do so. Based on the sign of the delay the quadrant of the source is obtained. Once the coordinate of the source is obtained the sign value of the x and y coordinate is set.
Then the tan angle of the source is found. Following that geometry is used to find the x and the y coordinate of the source by solving the four cone loci formed by 4 pairs among the mics and 4 relative delay values and the sign is appended to it so that the exact coordinate of the source can be found out with respect to the microphone arrangement.
All this computation is done using python. This is the link for the python code for the same
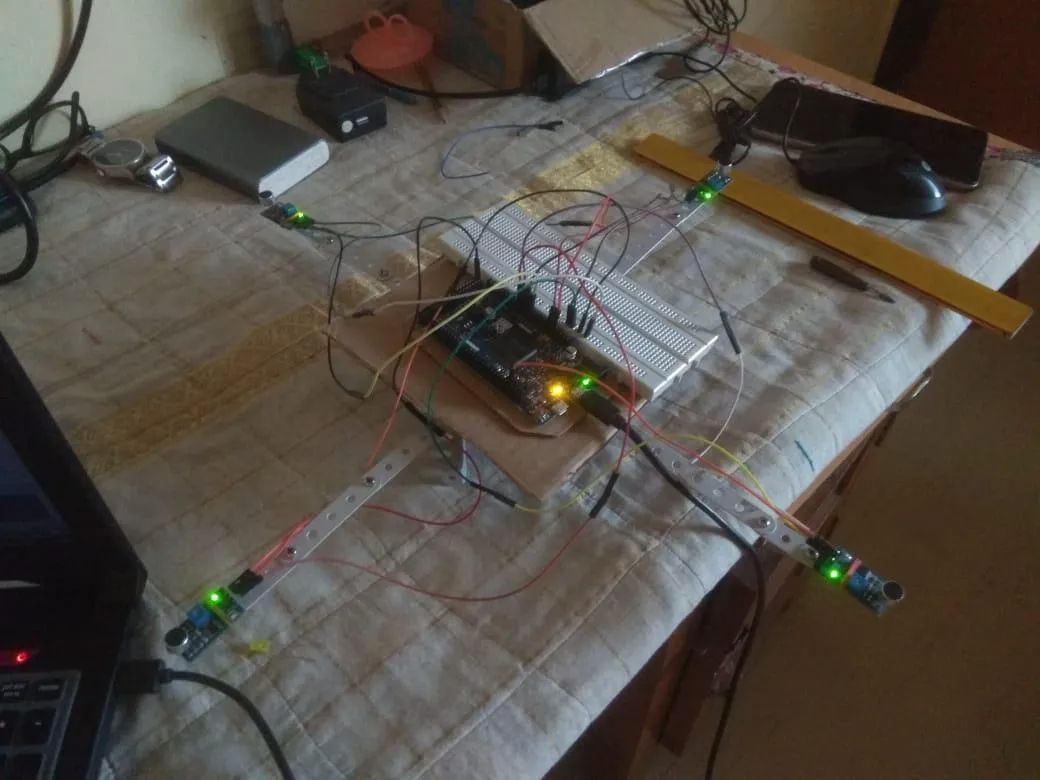

Distance between adjacent mics is set at 0.3 m
Motion of the Bot
Once the coordinates of the source have been obtained, the bot can be moved to that particular coordinate. The angle of the source is calculated with respect to North and a compass module is used to turn the bot and align itself to the line along the sound source. And the bot can be moved towards the sound source. This is done using the motor driver Monster Motor Shield VNH2SP30.
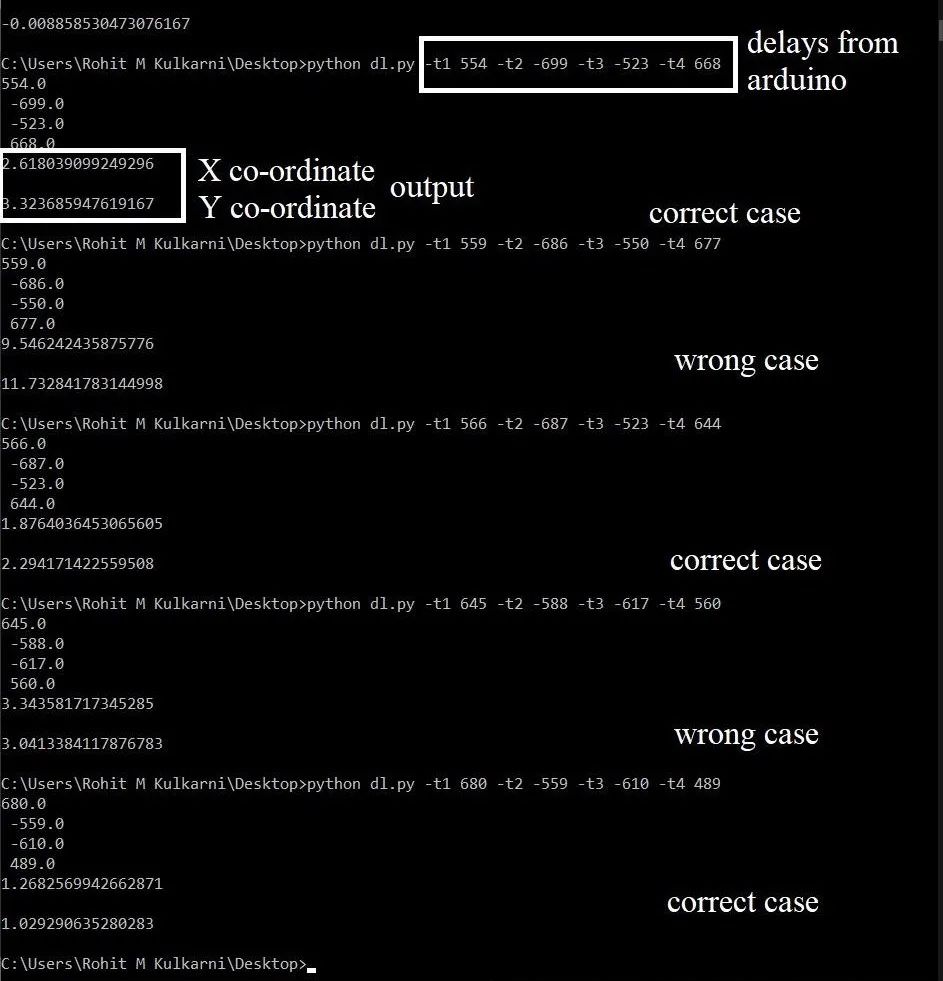
Results
After running the code for finding the x,y coordinate the following output is obtained. The image shown below is the actual testing screenshot.
Actual locations (m) :
- 2.4 , 1.2
- 2.4 , 1.2
- 1.8 , 2.4
- 1.8 , 2.4
- 1.2 , 1.2
Results given by the algorithm , once the relative delays were plugged in (in the same order) :
Application and Future Work
This project can be utilised to make smart robots. It can be used in carry carts where a cart can be summoned with an impulse sound. Various explorations to track predators can be performed without risking human life.
A PID controller can be introduced to improve accuracy. Obstacle avoidance softwares can be introduced. For now the bot follows a straight path to the source. But once the obstacle avoidance is added the bot can circumvent obstacles in its path.