Project Mentors:
- Shivani Chanda
- Spandan Patkar
- Sunaina Sunil
Project Members:
- Joel Jojo Painuthara
- Pooja M
- Sakshi Bothra
Table of Contents
Introduction
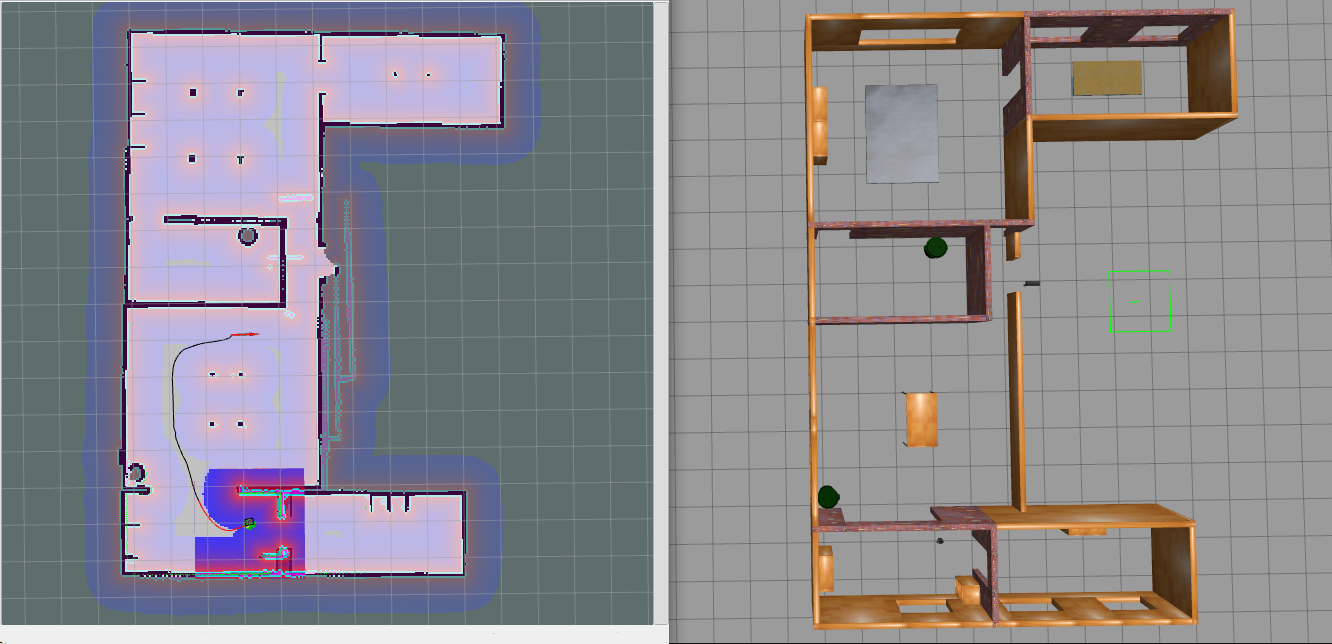
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) is an essential technology used in robotics that helps robots to estimate their position and orientation on a map while creating a map of the environment to carry out autonomous activities.
 Turtlebot using SLAM to navigate across a map
Turtlebot using SLAM to navigate across a map
This project aims to put together a mobile robot similar to a TurtleBot. A TurtleBot is a low-cost personal robot kit with open-source software.
 SLAMBot
SLAMBot
Technologies Used
Literature Survey
Robot Operating System (ROS)
ROS is an open-source, meta-operating system to operate robots. ROS provides the services of an operating system, such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly-used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management. ROS provides tools and libraries for obtaining, building, writing, and running code across multiple computers. ROS currently only runs on Unix-based platforms. Software for ROS is primarily tested on Ubuntu and Mac OS X systems, though the ROS community has been contributing support for Fedora, Gentoo, Arch Linux, and other Linux platforms.
Turtlebot:
TurtleBot3 is a small, affordable, programmable, ROS-based mobile robot for education, research, hobby, and product prototyping. The TurtleBot’s core technology is SLAM, Navigation, and Manipulation, making it suitable for home service robots.

Turtlebot3 Models - Burger and Waffle
LIDAR:
A LIDAR (LIght Detection And Ranging) is a sensor that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to calculate the relative distances of various objects. This 3D scanning system calculates how long it takes for beams of light to hit an object or surface and reflect back to the laser scanner using the velocity of light. The observed LIDAR data is then used to generate precise, three dimensional information about the environment of the robot and navigate smoothly while avoiding the obstacles.
Raspberry Pi:
The Raspberry Pi is an affordable single-board computer that can run Linux operating system such as Raspbian and Ubuntu. It is extensively used to develop programming skills or build hardware projects. It is a fast and versatile microprocessing board along with a set of GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins, allowing one to control electronic components for physical computing. This project uses a Raspberry Pi 3B.

Raspberry Pi Model B
Arduino Mega:
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software intended for applications in interactive projects. Arduino Mega is a microcontroller development board based on the ATmega2560 microcontroller IC. It can be interfaced with various hardware components such as sensors and actuators. Arduino can be programmed using Arduino C which is a language based on C++.
Arduino Mega
SLAM Algorithm
In this project we have used SLAM gmapping algorithm which is a very commonly used laser-based SLAM algorithm.
The SLAM process begins with the robot moving through its environment while collecting data from sensors such as LIDAR, cameras, and IMUs. This data is then processed using algorithms to create a map of the environment. The map can be a 2D or 3D representation of the area and includes details such as walls, obstacles, and other features.
At the same time, the robot is also localizing its position within the mapped environment. This is done by using the data from the IMU and encoders to determine the robot’s position relative to the known features of the environment. By comparing the data collected from the sensors with the map, the robot can determine its position with a high degree of accuracy.
As the robot continues to move through its environment, it updates its map and localization data in real-time thereby allowing the robot to navigate its surroundings and avoid obstacles.
The SLAM process relies heavily on sensors to provide accurate data about the environment. LIDAR sensors are commonly used because they provide highly accurate data about the distance and location of objects in the environment. Cameras and IMUs can also be used to provide additional data about the environment and the robot’s position.
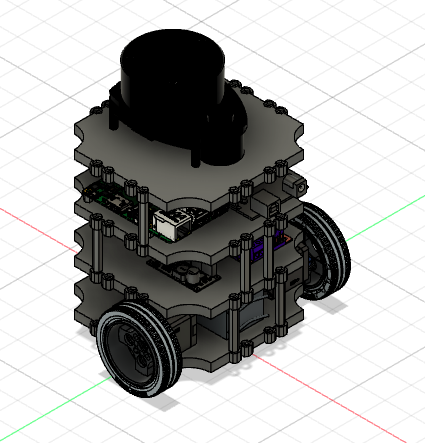
The Robot
The robot model used in this project is a simple differential drive comprising of 2 wheels mounted on their motor along with a roller castor for additional base support.
The robot consists of 4 layers:
- Bottom-most layer: The propulsion group comprising of battery and motors.
- Second layer: It consists of the power distribution board along with motor drivers.
- Third layer: This layer has an Raspberry Pi, which is a single board computer, along with an Arduino Mega microcontroller.
- Top-most layer: It comprises of the LIDAR
Design of SLAMBot in Fusion360
The above mentioned plates are 3D printed parts which are further assembled with the electronic hardware using screws and supports to ensure stability of the structure.
The design of the bot is created on Fusion 360, a commercial CAD and CAM software. It is then directly exported as a URDF (Unified Robotic Description Format) file, accompanied by a .stl file of the model alongside a .launch and .yaml file to simulate it on Gazebo. The URDF is an XML file format for specifying the geometry and organization of robots in ROS and can be generated using URDF_Exporter.
The robot is simulated in Gazebo, a powerful, open-source 3D robotics simulator with the ability to accurately and efficiently generate synthetic sensor data and offers realistic environments with high fidelity sensor streams to construct and interact with simulations. Within Gazebo, a physics engine is used to define realistic elements of an environment such as illumination, gravity and inertia.