Mentors
- Moha Mankad
- Sujay Chuttar
Members
- Dharaneedaran
- Nakul
- Nihar
- Saathwik
Abstract
Aim of this project was to generate music using an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). Like musical instruments, computers too can generate music using algorithms. In our project we used the Karplus Strong algorithm. To program an FPGA a class of programming languages called as hardware description languages (HDL) have to be used. In this project we have used the Verilog hardware description language. Since we do not have access to an FPGA board, we used a python script to play the generated music.
Karplus Strong algorithm
This is the simplest algorithm to generate music. Pick a positive number L. Then:
- The first L outputs y[0], y[1], …, y[L - 1] are random.
- For n larger than L, y[n] = (y[n - L] + y[n - (L + 1)])/2
A plucked string is initially highly energetic and the amplitudes of oscillation of all points on string is random. As the string loses energy, amplitudes reduce to zero gradually
The algorithm imitates the above procedure. We can understand this pictorially
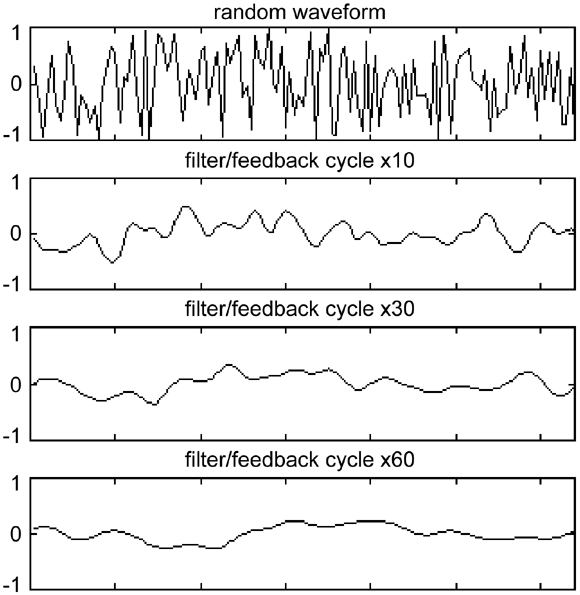
Initial outputs of the algorithm are random but they gradually become zero as can be seen in the picture
Frequency of resulting sound is governed by L and type of instrument being simulated is dependent on the distribution (for example gaussian) from which random values are obtained.
Methodology
In the first step, we tried to understand the Karplus Strong Algorithm and the way to implement it. We tried to approach the solution by understanding how to build a sound. Sound is often taken as a 1-dimensional array of decimal numbers, and music is also such. Coming to this conclusion, we tried to build a software implementation of this project using python to understand the process better and debug possible flaws in our approach to the final product.
Software Implementation
We used Numpy and Scipy library functions to generate sound. Numpy is used for working with arrays and provides more usability and processing speed as opposed to python lists. Scipy allows us to build a sound using Numpy arrays.
We tried building a white noise generator, which gives a random Numpy array of a certain length, mean and standard deviation as an input sound, we then proceeded to pass this noise through a low pass filter and append the output of the filter onto a new array. This was done by constantly providing the new input of the filter as its output, till we get a certain large length to the final output array. We then converted this said Numpy array (after manipulation to obtain a certain range of values to get desired sound in final output) to sound using the scipy library function to make it into a wavfile and then play it.
We then proceeded to the hardware implementation of the project using the hardware description language, Verilog.
Hardware Implementation
We tried to break down the entire program into two modules/functions: the delay line and filter and build them separately and integrate these two functions together to ensure the proper functioning of both the modules.
Delay Line: A digital delay line is a discrete element in digital filter theory, which allows a signal to be delayed by a number of samples. If the delay is an integer multiple of samples, digital delay lines are often implemented as circular buffers. In this project, the delay line delayed the signal input by 4 time periods of the clock.
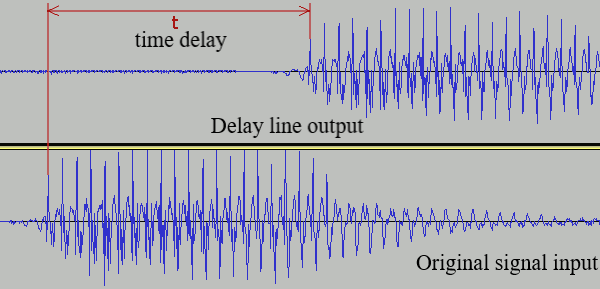
Filter Line: The filter line acts as a low pass filter that averages the delay line’s adjacent output samples. The filter characteristics determine the harmonic structure of sound.
The output of the filter is fed back to the delay line and passed through the output concurrently. The following is the waveform result of the filter module
After the completion of these two modules, the integration of both these modules was the next step. The integrated module was built to give a text file (.txt) that contains the entire output in binary format. This txt file was then processed with the help of a python program using the Numpy arrays and Ipython.display libraries to give an audio output. The text file is mounted in Google Drive and the file is read character by character to convert into an integer data type (8-bits of binary is considered as one value) and formed as an array which is played as audio using Ipython.Display.
Challenges of synchronizing parallel processes The process of integrating the filter and delay line module was the challenge we faced. These processes, although simple as individual components, were hard to implement simultaneously. This was mainly due to the intertwining relationship between the input and output of both the modules, where the output of one is the input to the other.
Results
Results of Python program we wrote to implement algorithm

Four different sounds with L as 15, 25, 50 and 100 respectively. Random values taken from gaussian distribution.
Results of Verilog codes we wrote
Output of the delay line
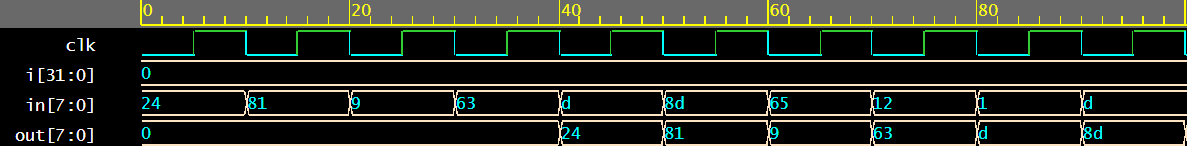
‘in’ is input, ‘out’ is output, the output can be seen lagging behind the input by 4 clock cycles
Output of the filter line

‘i_fil’ is the input of the filter and ‘o_fil’ is the output of the filter
THE FINAL OUTPUT
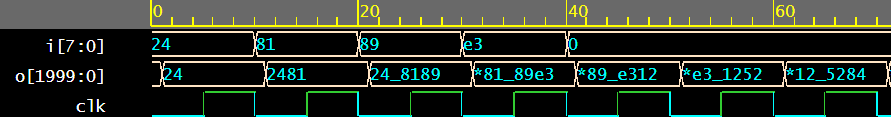
The parameter ‘i’ is the input, which represents the quick burst of signal sound ‘o’ is the output parameter which is a 2000 bit register to store a large enough sample
WAVEFORM OF FINAL OUTPUT SOUND
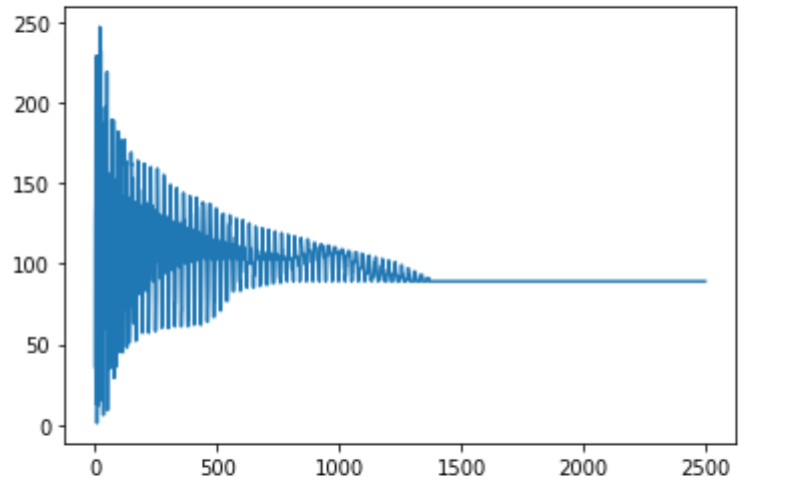
Four different sounds with L as 15, 25, 50 and 100 respectively
Future work
Creating a musical orchestra. Multiple musical instruments to be played together to produce a melodious song.
Here is a link to the Github repository of the programs we wrote. Thank you!!