Faculty Guide
- Krishnan C M C
Mentor
- Jeet R Shah
Members
- Akash S Bharadwaj
- Anirudh T
- Moha Mankad
Abstract
With doctors in high demand in these trying times, this project aims to supplement respiratory pre-diagnosis of a patient, through an IoT Stethoscope module. The module consists of two parts. The first is a convolutional neural network, trained to classify breathing patterns into four categories. The second part is an Android app, which interfaces audio recorded from the device microphone with the neural network. On deployment, users can diagnose two different breathing disorders, wheeze and crackle. Furthermore, past records of patients can be accessed to substantiate diagnosis.
Digital Signal Processing
1) Short Time Fourier Transform (STFT)
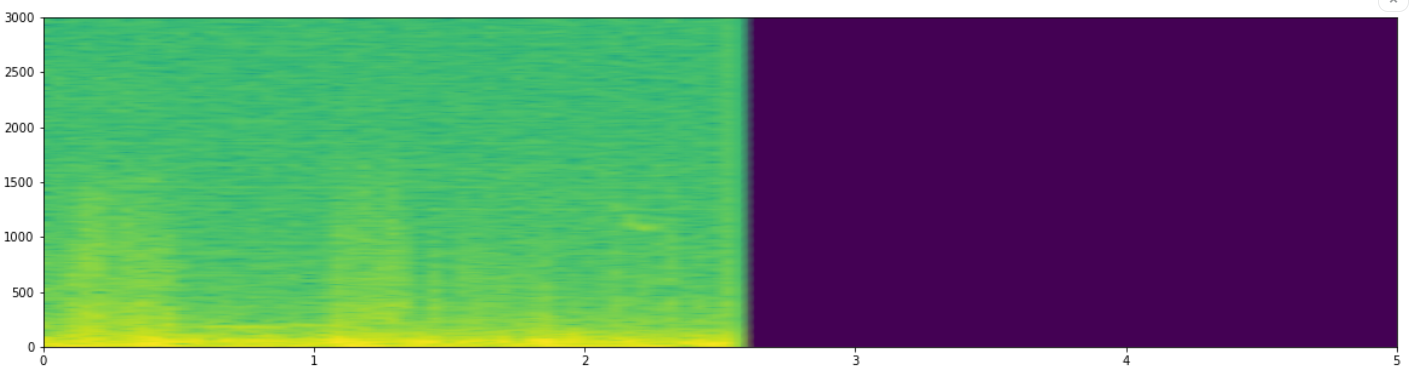
STFT is a DSP technique which has the knowledge of frequency components present in a wave at a given time. It is as simple as taking the Fourier transform of a segment of wave to analyze frequency distribution at that particular time instant. The X-axis represents the time, the Y-axis represents the frequency and the color coding represents magnitude of the frequency component. The wheezes can be detected by short horizontal patch at a frequency below 100 Hz on the spectrogram and crackles can be detected by a thin vertical patch of varying higher frequencies.
Example of a STFT spectrogram with both wheeze and crackle is given below -
2) Mel - Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC)
Just like the eyes of a human being can detect certain colors of light much better than other colors, the ears also follow the same concept and based on this, MFCC plots the frequency according to the sound which is perceived by the human ear. The MFCCs are plotted as coefficients in Mel Scale vs frequency. We have considered 13 coefficients here.
Here is an example of a spectrogram with both wheezes and crackles -

3) Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT)
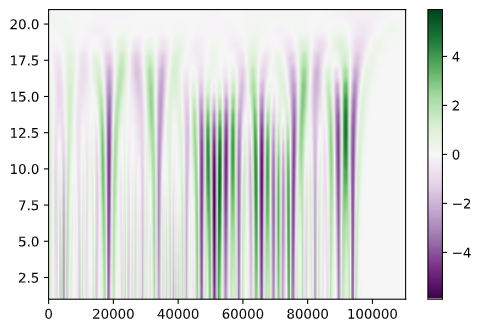
The Continuous Wavelet Transform is the decomposition of a signal into a set of basis functions consisting of contractions, expansions, and translations of a mother function ψ(t), called the wavelet. A wavelet is a rapidly decaying, wave-like oscillation that has zero mean. Unlike sinusoids, which extend to infinity, a wavelet exists for a finite duration. Wavelets come in different sizes and shapes and the availability of a wide range of wavelets is a key strength of wavelet analysis.
In the processing of our dataset, the Complex Morlet wavelet was used for analysis and 6 scales were taken for the same. Given below is a spectrogram for a sample with both wheezing and crackling -
Results
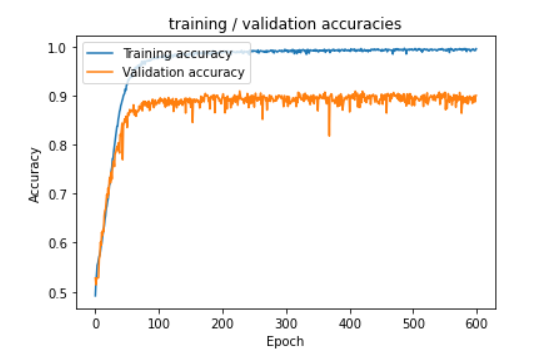
For the STFT, a CNN model with 1.7M parameters was trained and the validation accuracy achieved was 91%.
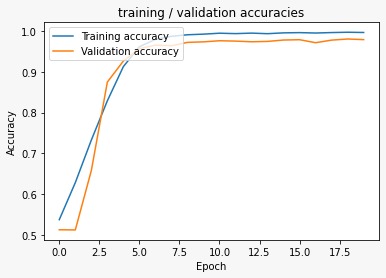
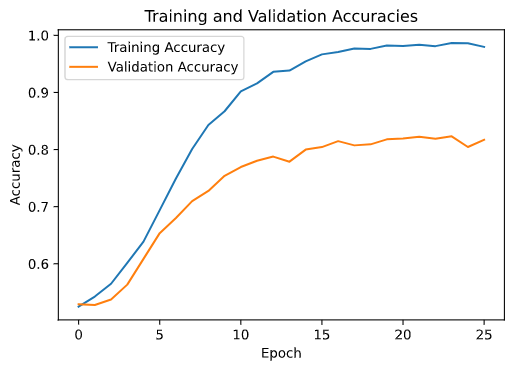
For MFCC, the model yielded a healthy result of 97% validation accuracy
For the CWT, a CNN model with 28M parameters was trained and the validation accuracy of 80% was obtained
Python libraries such as Librosa, Numpy, Pandas, SoundFile and an assortment of audio processing libraries were used to obtain the various spectrograms. Keras was used for deep learning.