Mentors
- A Shrikant
Members
- Garvin Pokhra
- Sujay Chuttar
HIDING IMAGES IN IMAGES
Steganography is the practice of hiding a secret message inside an image which acts as a carrier. The carrier can be an image, word document or even an excel sheet.
 Steganographical image of tree
Steganographical image of tree Recovered image of cat
Recovered image of catAdvantage of steganography over cryptography is that the intended secret message does not attract attention to itself. Cryptography is a science that enables privacy, steganography is a practice that enables secrecy.
DEMO
OUR PROJECT
Our project aims to hide images in images using 3 different approaches.
- K-LSB method
- DFT approach
- Deep learning
K- LSB METHOD
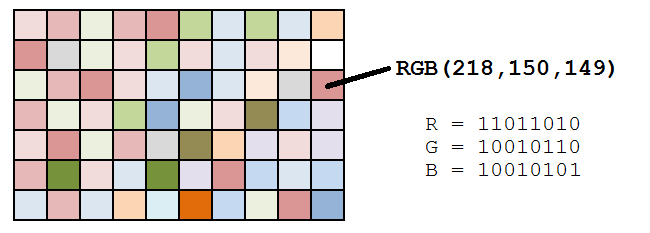
An image is a matrix of ‘pixels’. A pixel is a small block in the image which has a single color. This color of the pixel is effect of combination of red, green and blue components (abbreviated as RGB) of the pixel. Values of these components are generally represented by 8 bit binary numbers. For example, RGB components of the red color are 11111111, 00000000, 00000000 respectively. A black colored pixel will have RGB values 00000000, 00000000, and 00000000 respectively.
The K-LSB method of hiding images in images is based on the observation that a slight change in the RGB values of a color does not produce a visible change in the color.
For an example of the K-LSB method consider the 4 pixels below

The 8 bit representations of the pixels are respectively 01111000, 00001010, 10100000, 11110000
Suppose we want to hide the letter H in the image. ASCII code of H is 01000111. After hiding the pixel values will be 01111001, 00001000, 1010000001, 11110011. Constructing the image from new 4 pixels,

The new image is hardly distinguishable from older image!
To hide an RGB image in an RGB image former will have to be atleast 4 times smaller than the latter if we use the above method.
Similar appoach can be used to hide images within images. The below example shows K-LSB based hiding, where K=4.

DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM (DFT) METHOD
We perceive an image in terms of its brightness and colors. The Fourier transform is a tool which helps us to visualize an image in terms of its frequency contents.
The discrete Fourier transform can be obtained by sampling the Fourier transform of an image at certain frequencies. The discrete Fourier transform of an image has the same size as the image. Using the inverse discrete Fourier transform it is possible to recover the image from frequency domain.
 Image
Image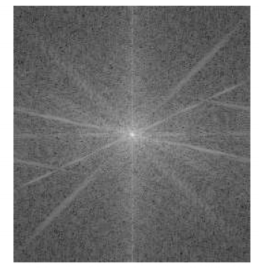 Magnitude of its DFT
Magnitude of its DFTThe DFT of an image results in a matrix of complex numbers. When plotting DFT we plot only the magnitude of the DFT.
In this approach we use the DFT to hide an image. To avoid complications due to complex numbers we will not use DFT of entire host image to hide an image. We will take DFT of 2x2 blocks in the image and add to it scaled pixel values of hidden image. Then taking the IDFT of the 2x2 block will give the corresponding 2x2 block in steganographic image.
DEEP LEARNING-BASED METHOD
In this approach, we train a set of three 2-D convolutional neural networks (2-D CNNs), which can be used for extracting features of the images, so as to hide them efficiently. These networks are
- Preparation Network
- Hiding Network
- Reveal Network
The Preparation Network takes input, the image to be hidden (S), and extracts useful features from it to be hidden. This is the preparation of the hiding image, ready to be fed to Hiding Network for hiding.
The Hiding Network takes two inputs:
- The Host image/ Cover Image (H)
- The prepared image
The Hiding Network then hides the prepared image inside the host H. The resulting output of the Hiding Network is called the Container Image (H’).
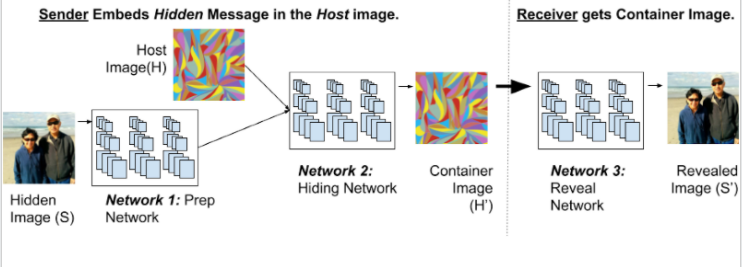
The Reveal Network is then used to recover the hidden image. It take the Container image (H’) as input, and outputs the Revealed Image (S’).
The important point to note here is that, all three models are actually trained as a single model.
This is to ensure that the Preparation Network, Hiding Network and Reveal Network work exclusively for each other, i.e., no other differently trained Reveal Network can be used to reveal the Container image (H’). This includes some privacy constraints, So that only the receiver with the appropriate Reveal Network can recover the image exactly.
RESULTS
The following images were obtained on training the CNNs for optimal performance.




ADVANTAGES OF CNN-BASED IMPLEMENTATION OVER OTHERS
The security of hiding process depends on a lot of factors. One of the important factors is distribution of pixel characteristics of Hidden image (S) over the the Host image (H). If the information of one pixel of S, is hidden in a single pixel of the host image, it can be recovered easily by training suitable AI based models. But if the information of a single pixel of S, is distributed over several pixels of H, the hiding process is more concrete.
Deep Learning based approach helps here a lot, as shown below, it is evident that the information of one pixel of S is roughly distributed over 7 pixels of H.
![]()
FUTURE IMPROVEMENTS ON THIS PROJECT
In this project, only one image is hidden inside the host. Further research evidences show that multiple images can be hidden inside an single host image, making the hising proces even more complex, yet secure, since adversaries now need to look for an arbitrary number of images to recover, which is practically not feasible.