Mentors
- Kavya Bhat
- Rakshith M
- Madhav Kumar
Members
- Abhishek Satpathy
- Hemant Kumar Bajaj
- Mayur K Nair
Aim
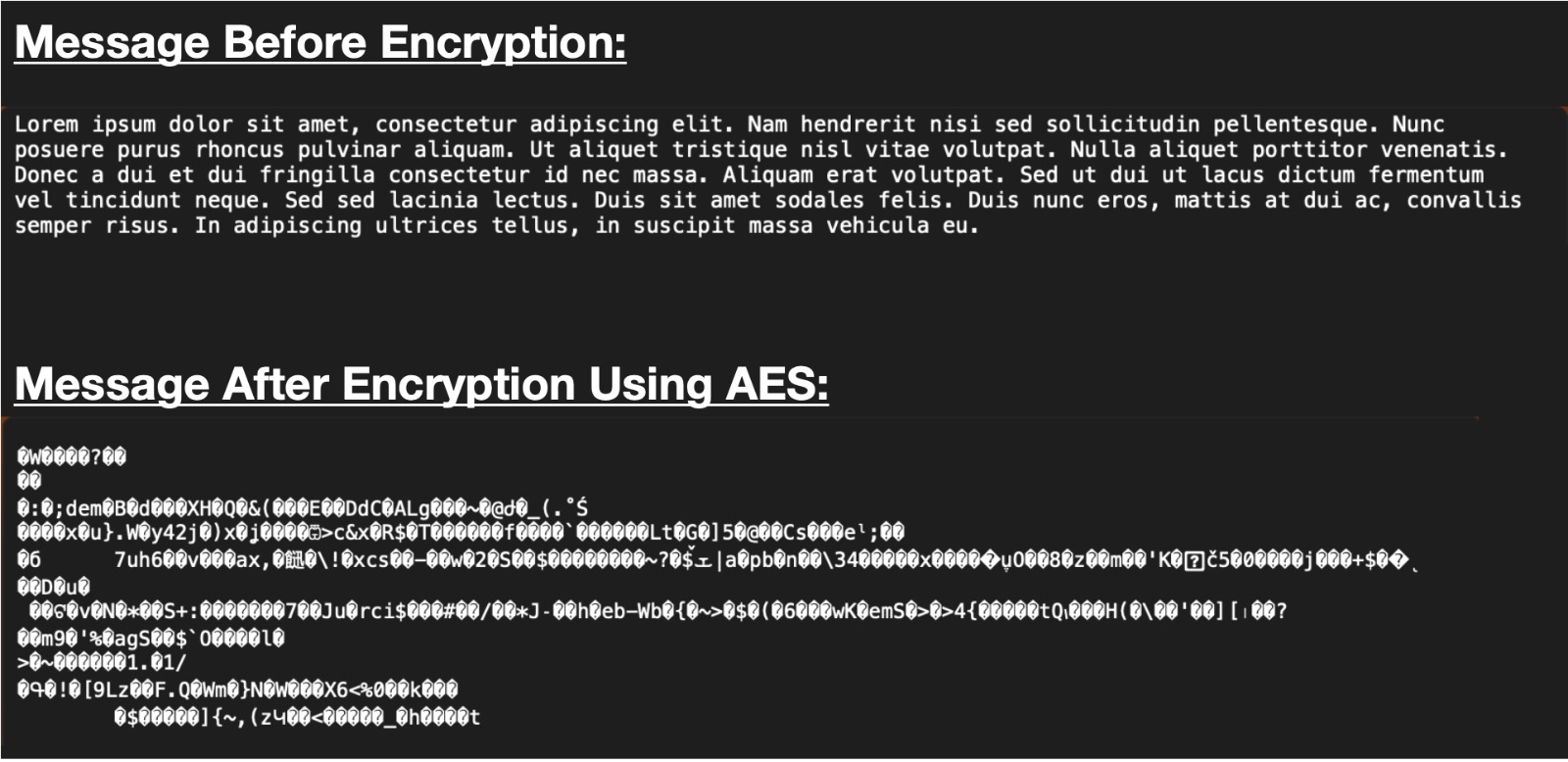
This project aims to provide end-to-end encryption, allow multiple file transfers and also resume interrupted transfers. It should also transfer files irrespective of the platform on which the computer is running like Windows, Mac or Linux. Also to build a fast, secure and easy tool for sharing files between two endpoints, without the use of a third-party server
Introduction
In today’s digital world, secure communication is becoming increasingly important to protect sensitive information from being intercepted by unauthorized parties. When transferring messages and files between two computers, one way to increase security is by using a relay, which acts as an intermediary between the two devices. In this scenario, the relay server facilitates the transfer of messages and files, ensuring that all data is encrypted and transmitted securely. By using a relay, the two computers do not have to directly communicate with each other, which can help to further protect against potential threats. To build a secure message and file transfer system using a relay, there are several steps that need to be taken. These include setting up the relay server, establishing a secure connection between the two computers and the relay, implementing encryption protocols, and configuring access controls to ensure that only authorized users can access the system. Overall, building a secure message and file transfer system using a relay requires careful planning and attention to detail, but it can provide an effective way to protect sensitive information during communication between two devices.
Methodology
Building a secure message and file transfer system between two computers using a relay requires a systematic approach that takes into account various security considerations. Below are the general steps to follow in developing a secure message and file transfer system between two computers using a relay:
A. Determine the requirements
The first step is to define the requirements of the message and file transfer system. This includes identifying the types of data that will be transferred, the number of users who will have access to the system, the desired level of security, and other specific needs.
B. Set up the relay server
The relay server should be set up with the appropriate hardware and software. The server should be located in a secure environment and protected with firewalls and other security measures.
C. Establish secure connections
All connections between the two computers and the relay server should be encrypted to ensure data security. This can be achieved by using SSL/TLS protocols or other encryption methods.
D. Implement encryption protocols
All messages and files should be encrypted using strong encryption protocols, such as AES or RSA, to protect them from unauthorized access.
E. Configure access controls
Access to the system should be controlled through authentication and authorization processes. This can include the use of username and password combinations, multi-factor authentication, or other methods.
F. Monitor and log activity
System activity should be monitored and logged to detect any suspicious activity or potential security breaches.
G. Test the system
Before deploying the system, it should be tested thoroughly to ensure that it meets all the security requirements and operates as expected.
H. Continuously review and update
The security of the system should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains effective against new threats and vulnerabilities
FTP server-client
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used for transferring files between a client and a server over a network. The client-server architecture of FTP allows multiple clients to connect to a server simultaneously, making it an ideal protocol for sharing files among a large group of users. The FTP server, installed on a computer or server, listens for incoming connections from client machines. Clients can connect to the server using an FTP client software that supports the FTP protocol. Once connected, clients can browse the files and directories on the server and upload or download files as needed.
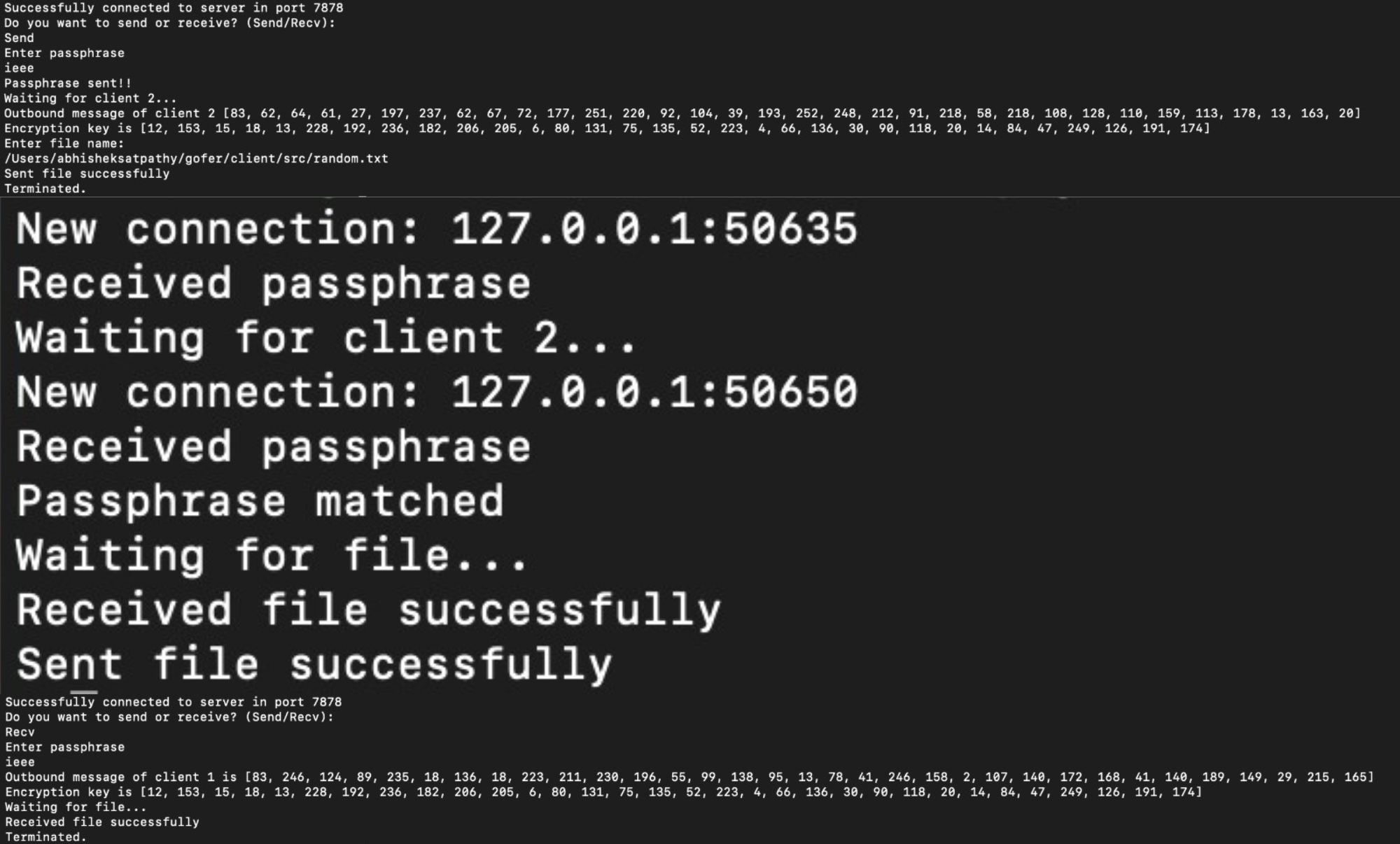
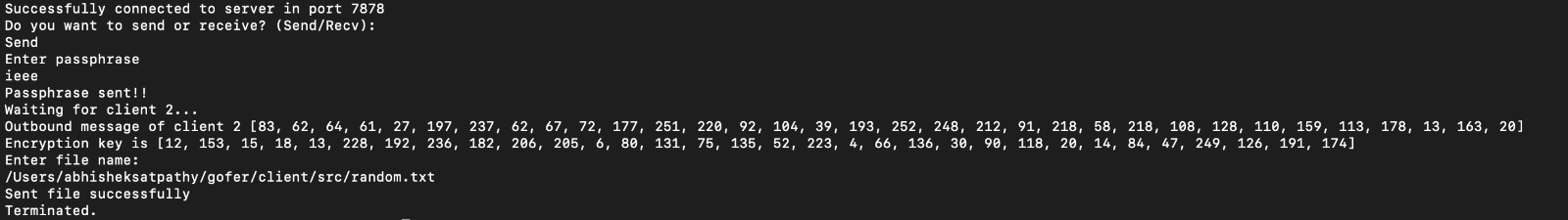
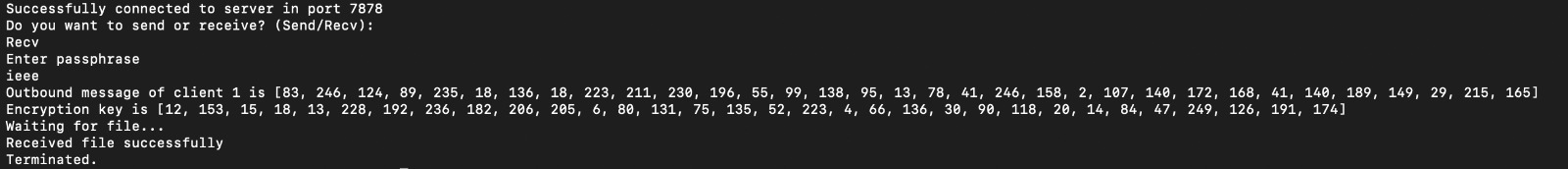
Multiple Client
File transfer involves the movement of files between two or more computers over a network. Multiple client file transfer refers to a scenario where multiple clients are transferring files to and from a central server. In this scenario, each client has an FTP client software that enables them to connect to the server and transfer files. The server, on the other hand, has an FTP server software that listens for incoming connections from clients and manages the file transfers. Multiple client file transfer is commonly used in scenarios where a large group of users needs to share files, such as in a corporate network or an online storage service. It allows users to access a central repository of files, making it easier to collaborate and share resources. One of the advantages of multiple client file transfer is that it reduces the need for users to physically transfer files using external storage devices, such as USB drives or CDs. This reduces the risk of data loss or corruption and simplifies the file transfer process. Another advantage is that it allows for centralized management of files, making it easier for administrators to control access to files and enforce security policies. For example, an administrator can set up different levels of access permissions for different users, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive files.
PAKE Usage
SPAKE2 (Simple Password-Based Augmented Key Exchange 2) is a password-authenticated key exchange (PAKE) protocol that can be used to establish a shared secret between two parties based on a password. It can be used in FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client-server applications to provide secure and password-protected file transfers. To use SPAKE2 in FTP client-server applications, the client and server need to agree on the protocol parameters, such as the underlying cryptographic primitives and the size of the password. The protocol parameters can be negotiated during the initial handshake between the client and server. Once the protocol parameters are agreed upon, SPAKE2 can be used to establish a shared secret between the client and server based on the password provided by the user. This shared secret can be used to encrypt and authenticate the file transfer, ensuring that the data is protected during transit. On the server-side, SPAKE2 can be used to securely authenticate the client by verifying that the password provided by the client matches the expected password. If the authentication is successful, the server can proceed with the file transfer. On the client-side, SPAKE2 can be used to securely establish a shared secret with the server based on the password provided by the user. This shared secret can be used to encrypt and authenticate the file transfer, ensuring that the data is protected during transit. SPAKE2 is a secure and efficient method for password-based authentication and key exchange. It provides strong security guarantees, even against attackers who have access to the network traffic and the protocol parameters. Overall, the use of SPAKE2 in FTP client-server applications provides an additional layer of security by allowing for password-based authentication and secure key exchange. However, it is important to note that SPAKE2 alone does not provide encryption or confidentiality, so additional measures may need to be taken to protect sensitive data during transit.
Conclusion
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client-server applications are widely used for transferring files over a network. However, these applications can be vulnerable to various security threats, such as unauthorized access, data tampering, and interception.
- To address these security threats, various cryptographic techniques can be used in FTP client-server applications. For example, SHA-256 can be used to verify the integrity of data during file transfers, while SPAKE2 can be used to establish a shared secret between the client and server based on a password, providing secure and password-protected file transfers.
- It is important to note that while cryptographic techniques can provide additional security for FTP client-server applications, they should not be relied upon as the sole means of protection. Additional security measures, such as access control, firewalls, and network monitoring, should also be implemented to ensure the security and integrity of data during file transfers.