Mentors
-
Aman Raj
-
Vartika T Rao
Members
-
Bhuvanesh Singla
-
Chirag S
-
Krishna Tulsyan
-
Smruthi Bhat
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the IEEE organization for conducting envision, providing a platform for knowledge exchange. We would like to express our gratitude to the deep learning community and the creators of the FER 2013 dataset for their invaluable contributions to facial recognition and classification. We also thank the dataset participants, researchers, and the open-source community for their support
Aim
This deep learning project essentially aims to use a convolutional neural network architecture to recognize facial expressions and those expressions.
Introduction
Images can both express and affect people’s emotions. It is intriguing and important to understand what emotions are conveyed and how they are implied by the visual content of images. Inspired by advancements in computer vision deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) in visual recognition, we will classify the images into the following categories: 0:angry 1:disgust 2:fear 3:happy 4:sad 5:surprise 6:natural
We will use the Keras library to build the deep learning model and the FER2013 dataset (facial expression recognition) to train and test our model.
The implementation of the model is done using a GUI interface and a web app using Streamlit.
Libraries Used
- Pandas
- Numpy
- Matplotlib
- Tensorflow->Keras
- cv2
- PIL
- Streamlit
Datasets
Facial Expression Recognition 2013
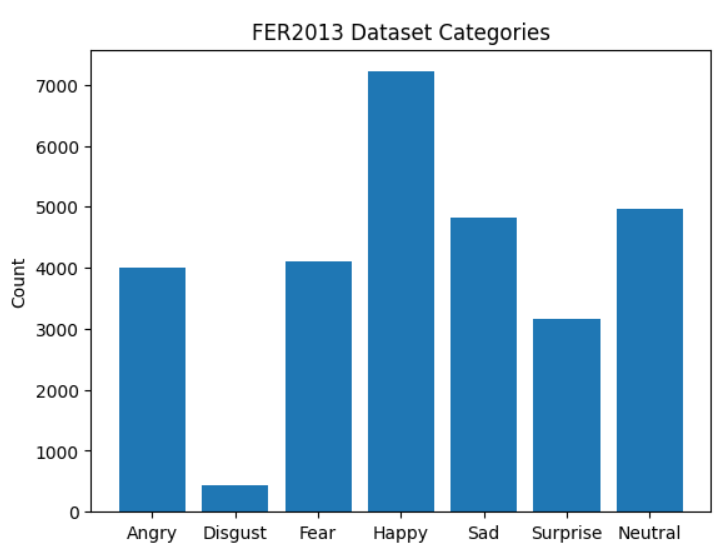
The data consists of 48x48 pixel grayscale images of faces. There are a total of 28,709 images.
Bar graph representing the number of images of each emotion:
Convolutional Neural Network
Convolutional Neural Network or CNN is a type of artificial neural network which has capability to analyse images and video. They apply a special type of mathematical operation called Convolution.
Due to large number of paramters, these networks can learn very complex patterns and are Shift invariant. Owing to this power of CNN, they are widely used in image classification algorithms.
Our project involves use of a CNN architecture to classify input image into 7 classes of emotion. The network learns pattern from images training images and uses the knowledge to classify real time human expressions
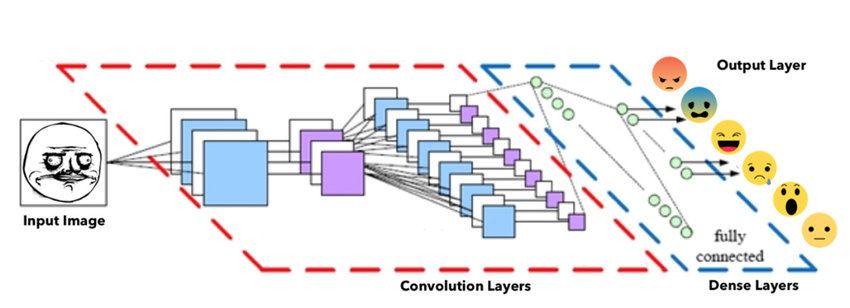
Model Architecture
Our CNN model is inspired by VGG-16 which is one of the popular algorithms for image classification.
We have 4 convolution layers each followed by a Dropout and MaxPooling layer with a stride of 2 and each layer having few sub-layers.
A kernel size of 3 and same padding was utilised.
It is followed by a Flattening layer and a Dense network of 3 fully connected layers and at the end an output layer for performing the final classification.
While compiling the model, Adam optimizer was deployed with an optimum leraning rate to perform the training effectively.
The activation function used in layers is ReLU and at the end Softmax is used in output layer.
Several techniques to prevent overfitting and ease training had been used.
-
- Dropout Layers: These randomly turns off certain neurons from the model in order to reduce the over dependency of model over any particular node or feature.
-
- Batch Normalization : It makes training of neural network faster and more stable by performing some rescaling and recentering of layers’ inputs and help in decreasing number of epochs to train.
-
- Early Stopping : Early Stopping is a technique wherein the training of model is haulted forcefully once it starts to overfit.
-
- Reduce Learning Rate: When a metric stops improving for a longer time, the model is benefitted by reducing the learning rate by a certain factor.
Result
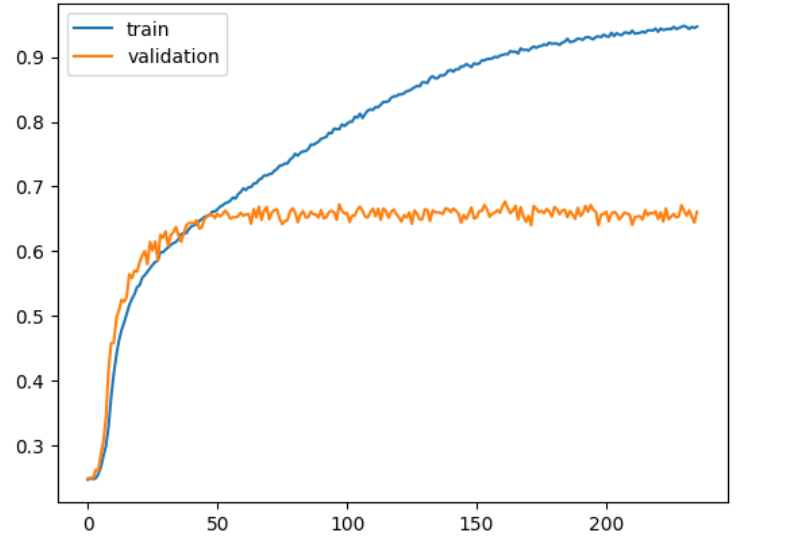
Training and validation accuracy
On the test set, we have achieved an accuracy of around 65% and an accuracy of around 68% on the validation set.
We are trying to improve the accuracy of our model.
The results are pretty good considering that as a kaggle challenge, the same task had a highest accuracy of about 68%.
References
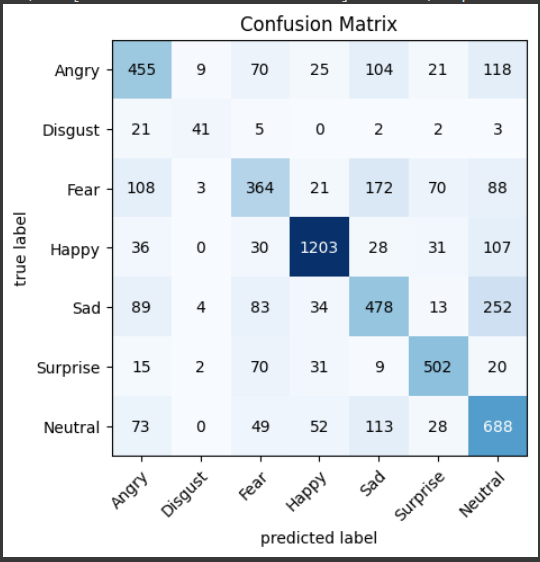
A Confusion matrix of the predicted output is shown below
Implementation
We have implemented our project by making a GUI based interface and a Web app using Streamlit.
WebApp using Streamlit
Instructions
1) clone the repo
2) switch to webapp branch
3) add the dl models h5 file with the name “FER2013new.h5”
4) create a virtual env
5) install requirements.txt
6) run this command in terminal “streamlit run webapp.py”
Webview
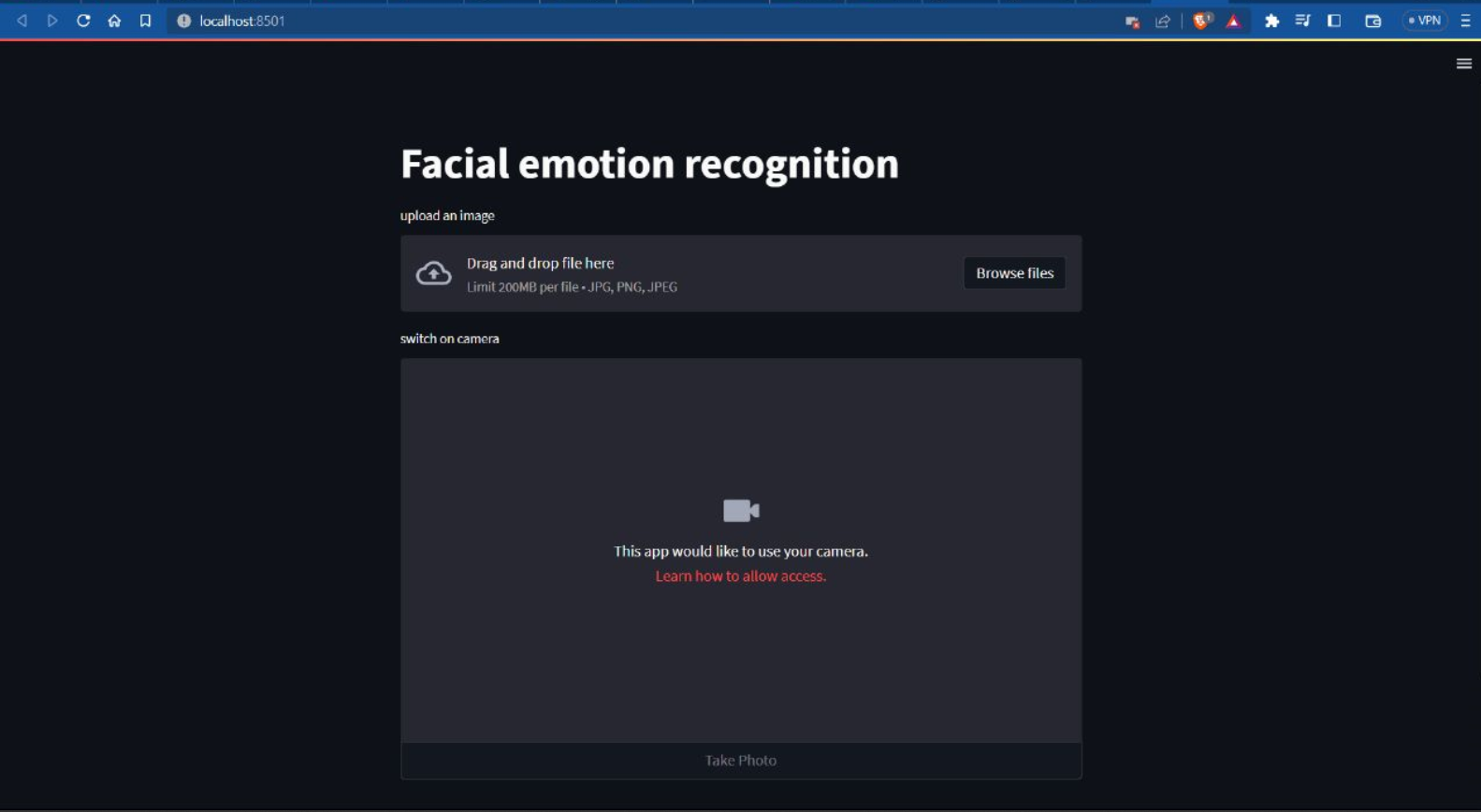
## Future ventures By leveraging the power of facial recognition algorithms, the application can unlock various capabilities to optimize the feedback process. Here are some key areas where facial recognition can contribute:
-
Personalized Feedback Delivery: Facial recognition algorithms can tailor feedback messages based on users’ emotional responses. By analyzing facial expressions, the application can deliver personalized feedback that addresses specific concerns or highlights positive aspects. This personalized approach enhances the user experience, making feedback more meaningful and impactful.
-
Gamification and Interactive Feedback: Facial recognition integration allows for interactive feedback mechanisms, such as gamified features or virtual avatars that mirror users’ facial expressions. This gamification approach adds a fun and engaging element to the feedback process, encouraging users to provide more detailed and expressive feedback.
Conclusion
This Project gave us an oppurtunity to learn image processing and classification of images based on emotions through deep learning implemented through Tensorflow Keras. It provided proper insight over feature extraction from images through CNNs. Understanding the CNN architecture to obtain optimum accuracy and minimum loss was exciting. Development of GUI using openCV and Tkinter which is able to classify the face and output the emotion was definetly a plus to knowledge learnt in the project.
References
-
https://in.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks-deep-learning
-
https://in.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-introduction#courses
-
https://github.com/marinavillaschi/ML-AndrewNg
-
https://github.com/amanchadha/coursera-deep-learning-specialization
-
https://deeplizard.com/resource/pavq7noze2.
-
https://deeplizard.com/resource/pavq7noze3
-
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/msambare/fer2013