Mentors:
- Ashish Bharath
- Aryan Amit Barsainyan
- Amandeep Singh
Members:
- Bharadwaja M Chittrapragada
- Karan Kumar Bhagat
- Mohammad Aadil Shabier
- Tejashree Chaudhari
Aim
To deploy a model based on the F-Gen framework to generate an FAQ from multiple similar sounding email queries.
Introduction
With overwhelming volumes of official emails being exchanged in enterprises every day, emails have become vital information storehouses. Automatic generation of FAQs from email systems helps in identifying important information. Our project solves this problem using an F-Gen framework. An F-Gen framework is a tool designed to convert emails into Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) by utilizing natural language processing techniques. The goal of the framework is to reduce the time and effort required to manage and respond to customer emails, while also improving the overall customer experience. The F-Gen framework includes three subsystems connected end to end. We have also developed a web application which provides a user - friendly interface to view the output of each subsystem.
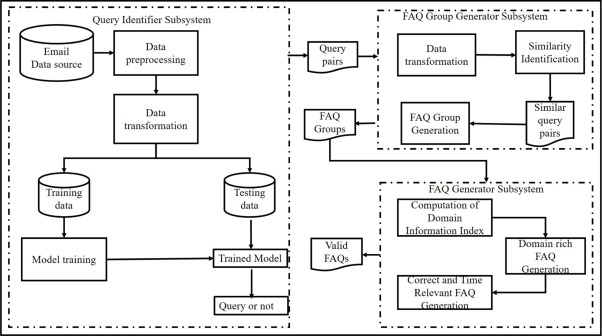
QC - Query Classifier Subsystem
Email sentences are taken as input and the data is cleaned and sentences are tokenized. Tokenization involves splitting paragraphs and sentences into smaller units that can be more easily assigned meaning. This preprocessed data is then fed into Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model which uses the Transformer encoder architecture to process each token of input text in the full context of all tokens before and after it in the sentence. This subsystem filters out queries from the email sentences and forwards them to the next subsystem.
FGG - FAQ Group Generator Subsystem
The second subsystem uses a Siamese LSTM network coupled with Manhattan distance metric to create clusters of similar queries from all the queries provided by the QC subsystem.
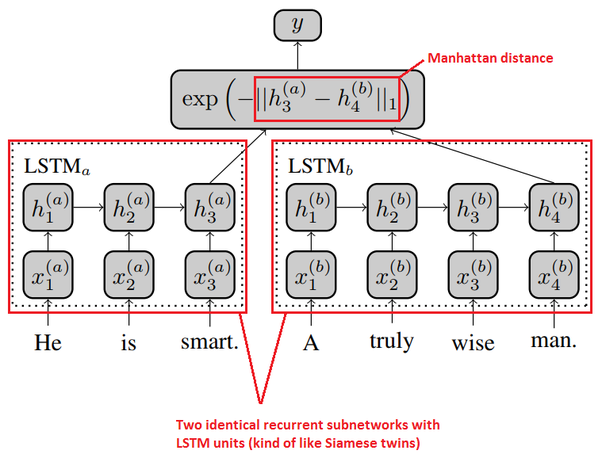
Siamese LSTM
Upon comparing accuracies of models like Cosine similarity, Jaccard, Levenshtein Distance and Transformer based techniques , Siamese LSTM model was chosen to compare semantic similarity as it has maximum accuracy. Siamese LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) network consists of two identical sub-networks that share the same weights and architecture wherein each sub-network is an LSTM network. To train the network, pairs of input sequences are fed into the two LSTMs that employ a Word2Vec pre-trained model to convert sentences into dense vector representations which capture the semantic and syntactic meaning of the words. These vectorial representations are then compared using Manhattan distance metric which provides a numerical score. The Manhattan distance technique measures the distance between two points in a two-dimensional space. Pairs of queries having a high similarity score are grouped together to form clusters. These clusters contain similar queries which are fed to the last subsystem.
Dataset used:
The Siamese LSTM model was trained on 10,000 questions .These questions were generated using a Chat-GPT based API script. The dataset contained queries pertaining to various industries like Laptop servicing, Tours and Travels, food delivery business, real estate builders ,etc.
FG - FAQ Generator Subsystem
A single FAQ is generated from multiple queries that had been grouped together by second subsystem. This is carried out by Pegasus summarizer . Pegasus is a language model developed by Google for text summarization. It is based on the transformer architecture, which allows it to analyze text and generate high-quality summaries. The Pegasus summarizer works by first encoding the input text using a multi-layer transformer network. This network processes the text at different levels of abstraction, allowing it to capture both the general meaning of the text and the specific details. Once the input text has been encoded, Pegasus generates a summary by decoding the encoded text into a shorter summary text. The decoding process is guided by a pre-trained language model that has learned to generate high-quality summaries based on the input text. Ultimately , one FAQ is generated using the summarized text.
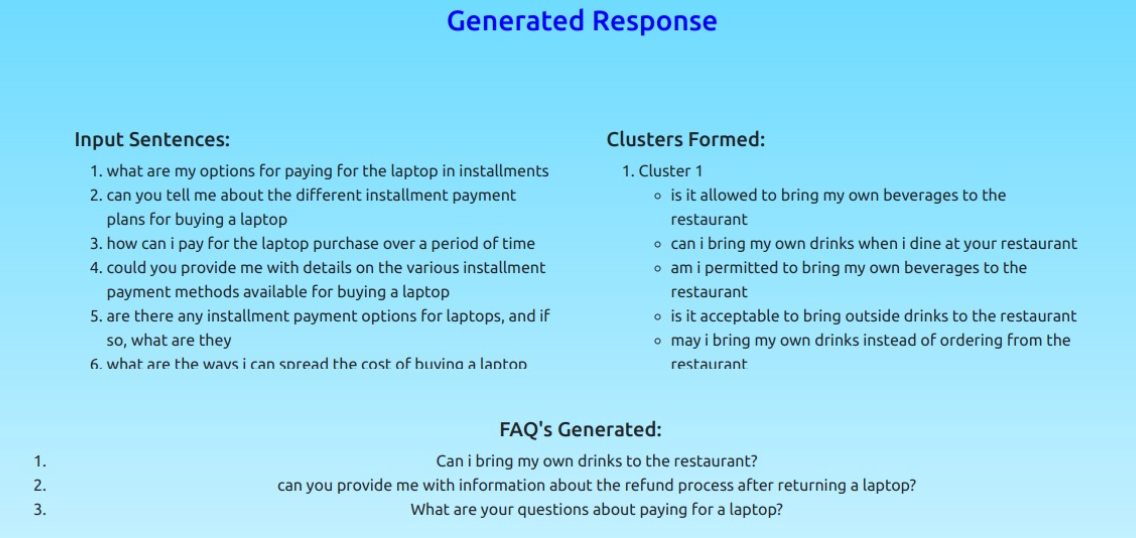
##Web Application
We developed a Flask based website application to display sentences after passing through each subsystem. Flask is a micro web framework written in Python which provides a lightweight and flexible way to create web applications. We also used Jinja as a templating engine to render HTML templates in Flask web applications. Our application initially displays all the input sentences fed to the QC subsystem, then the clusters of similar queries formed by FGG subsystem and also the final FAQs generated by FG subsystem. This application provides a user-friendly interface for end users to thoroughly understand the working of our subsystems.
Python Libraries and Modules used
For F-Gen Framework Datetime, datasets ,dataclasses ,data_loader , email , intertool, keras, logging, matplotlib, model, nltk, NumPy, os, pandas, re, seaborn, tensorflow ,time, torch, tqdm, transformers, typing, warnings For Web Application Framework - Flask Template Engine - Jinga
Conclusion
- Successfully implemented an F-Gen Framework model which converts email queries to a single FAQ.
- Accuracy of the Siamese LSTM model can be improved after training on larger datasets and feeding a Thesaurus-like vocabulary to replace synonyms.
References
- A deep learning based end-to-end system (F-Gen) for automated email FAQ generation - ScienceDirect
- A Framework for Automatic Generation of FAQs from Email Repositories IEEE Conference Publication IEEE Xplore
- Siamese Recurrent Architectures for Learning Sentence Similarity Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
- Domain Adapted word embeddings for improved sentiment classification
- Graph embedding techniques, applications, and performance: A survey - ScienceDirect