Mentors
- Guddati Sri Sai Akhil
- Rayner Menezes
Members
- Bharat Patel
- Debargha Biswas
Aim
Analyzing the design of wind turbines with the help of computer-aided methods to establish efficient design types and find their efficiency based on certain given conditions, followed by simulating real-world conditions to see if they are feasible and if they will hold up.
Introduction
Wind turbines are one of the most commonly used renewable energy sources right now. Wind turbines come in various sizes and shapes, some being more efficient than others. There are various factors involved in the process of selection of a wind turbine to make it usable in the real world. Here we try to find the most efficient type of wind turbine followed by taking a particular case study with various real-world conditions to test our results.
The two main sub-divisions of wind turbines are HAWT and VAWT. Out of these, it is seen that HAWT is the more efficient variant. The maximum theoretical efficiency of a wind turbine is tested to be around 59.3%. To test these we are going to use ANSYS software and apply finite element analysis, meshing, and CFD to get the outputs based on certain input conditions. This process is followed by static structure testing also performed on ANSYS to find out if the wind turbine can sustain the loads on it and be functional.
Methodology
-
ANSYS: It is a CAE/Multiphysics engineering simulation software for product design, testing, and operation. Here we use the geometry function to import the blade design and create a desired flow domain around it, followed by using ANSYS Fluent for CFD analysis, and finally Static Structural testing by transferring loads from the cfd simlulation onto the blades itself to see if they can sustain it.
-
QBlade: Is a public source, cross-platform simulation software for wind turbine blade design and aerodynamic simulation.
We used the example of the GE1.5xle and set boundary conditions as follows: The radius of rotor: 44.2m Rotational speed: 2.22 rad/sec clockwise Average inlet velocity: 10m/s The system was solved using the turbulence model SST k-w The governing equations of the setup are the conservation of mass and the Navier-Stokes equation
For designing our own blade we chose the NACA 63-415 airfoil designed for windblades. We generated and optimised the twist of our blade along the length using Qblade and a cfd simulation was performed on it.
Validation
We achieved results comparable to the research paper referred under similar boundary conditions and velocity.
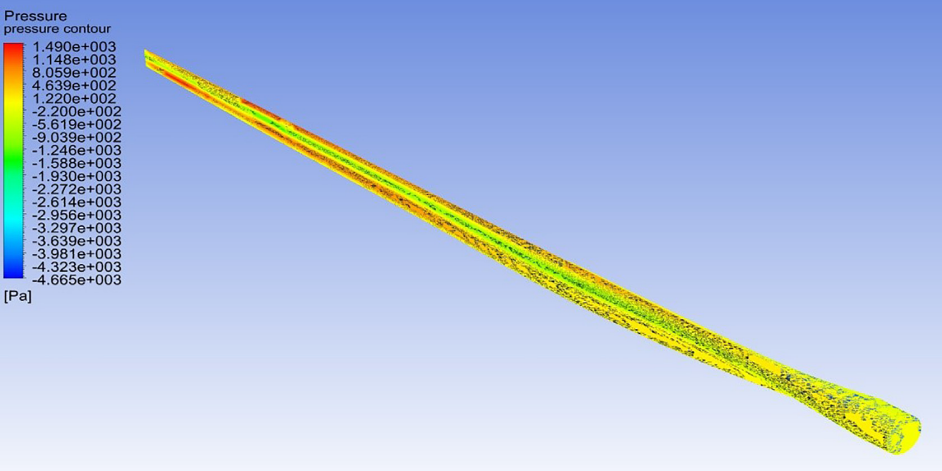
Pressure contours of GE 1.5xle Wind Turbine from Ref.
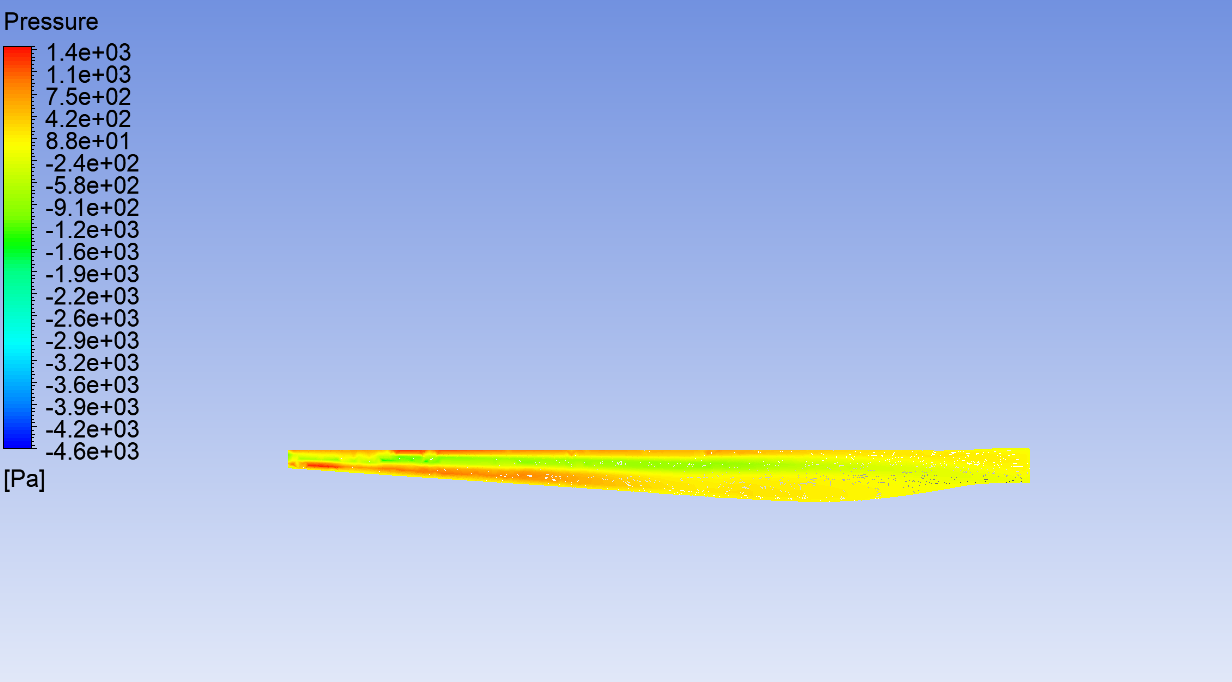
Pressure contours of GE 1.5xle Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
Result
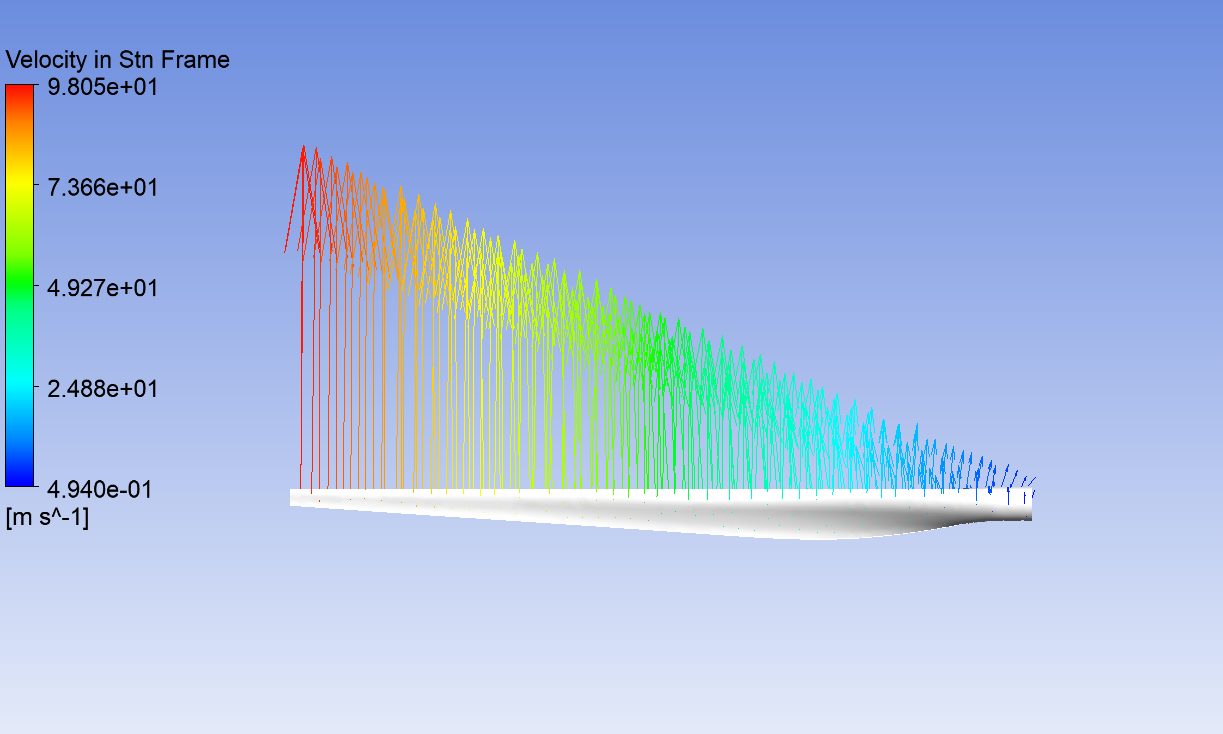
Velocity profile of GE 1.5xle Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
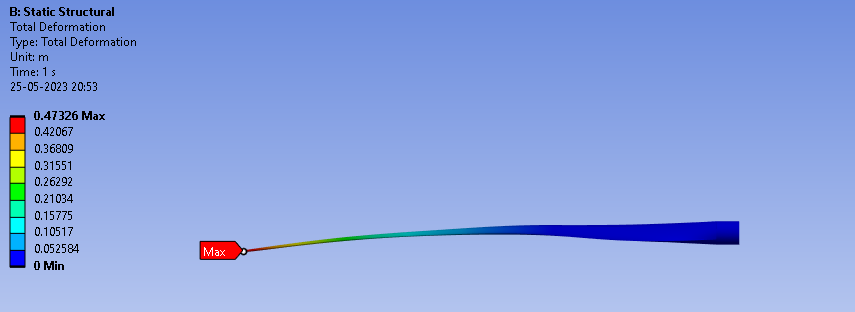
Total deformation of GE 1.5xle Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
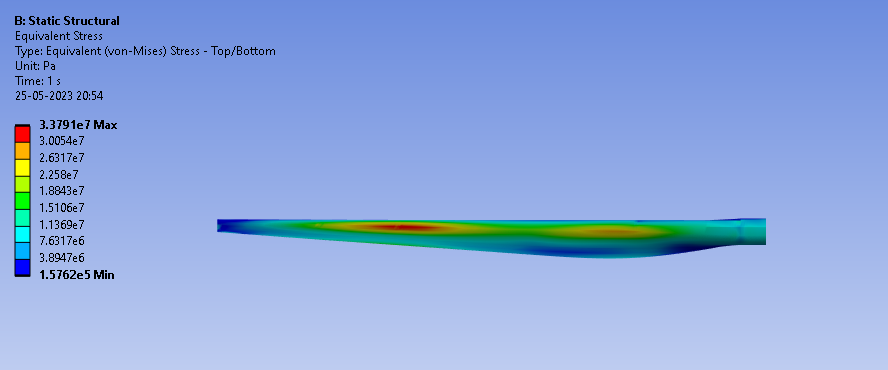
Equivalent stress of GE 1.5xle Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
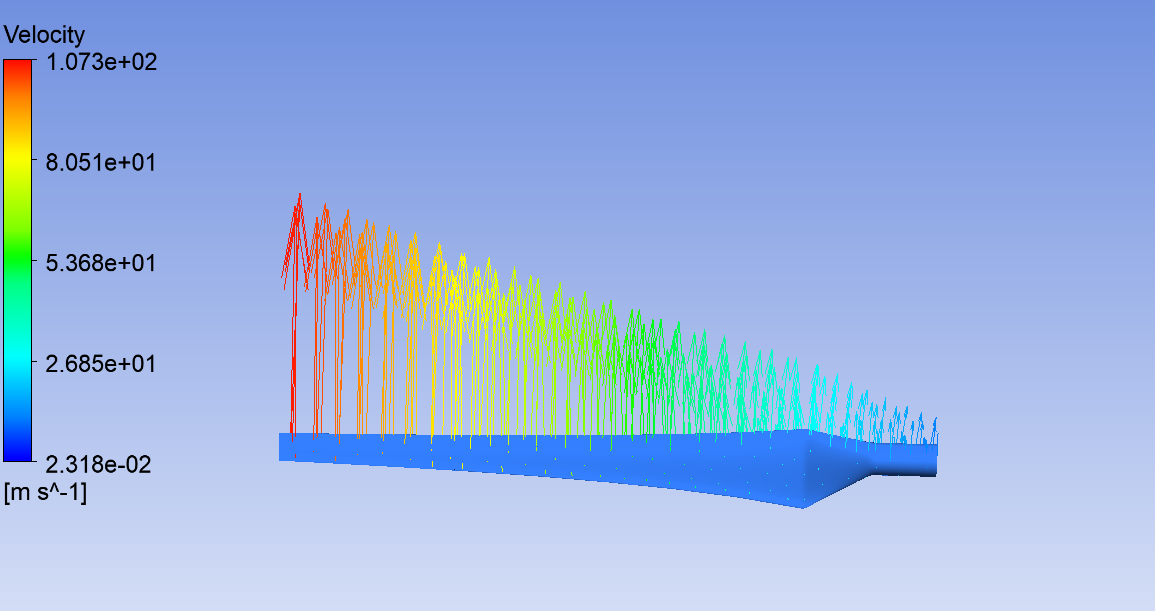
Velocity profile of Our Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
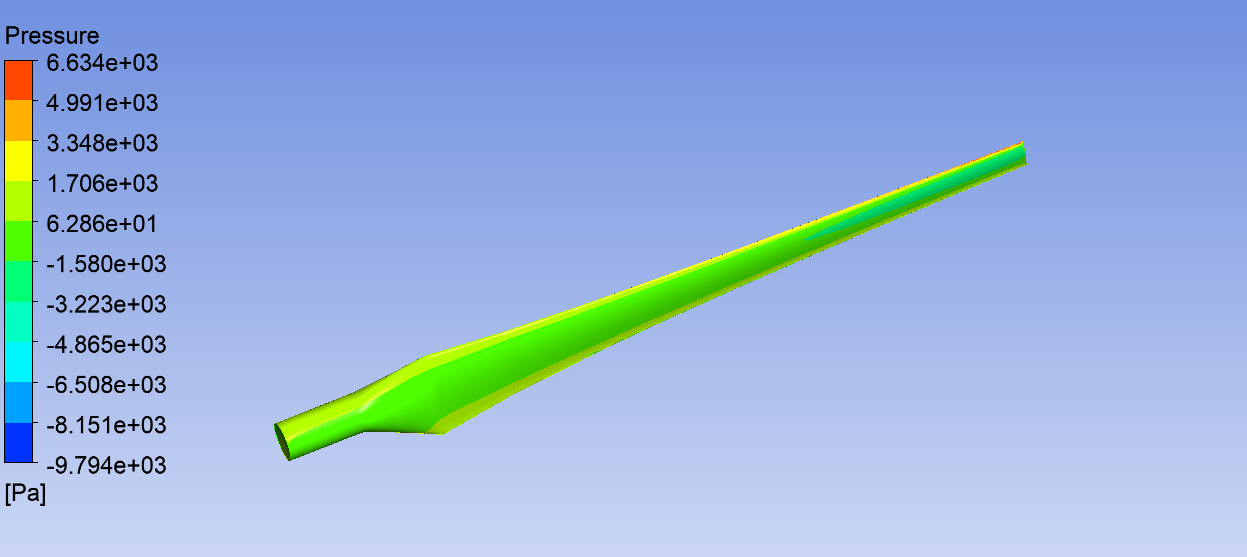
Pressure contours of Our Wind Turbine from Ansys simulation.
Conclusion
In this project, we acquired knowledge of wind turbine physics and Betz’s limit but also gained hands-on experience with industry-standard software tools. We employed Ansys Fluent to conduct computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis on both the original GE1.5xle and our designed wind turbine blade. The CFD simulations provided a comprehensive understanding of the flow characteristics, including velocity distribution, pressure distribution, and turbulence effects. These insights along with the static structural simulation were crucial in evaluating the performance of the blade and identifying areas for improvement.