Mentors
- Rohan Mallya
- Shreyas Rao
Members
- Abhinav Sai
- Aryan Agrawal
- Hrishikesh Kulkarni
- Malkangouda S Patil
- Nihal
OBJECTIVE
After the outbreak of the worldwide pandemic COVID-19, there arises a severe need to build computer vision frameworks to detect face masks and count the number of social distancing violations in videos. Image processing and Machine Learning have various applications in motion detection and allied fields such as Face detection, sports analysis, agriculture, and autonomous vehicles, etc. The project focuses on the concepts of image processing and deep learning using OpenCV and TensorFlow libraries and how it can be used in motion detection, face detection, and recognition. In the new world of coronavirus, computer vision can play a crucial role in monitoring the spread of the disease.
Motivation
To build your very own COVID-19 surveillance system which could be incorporated publicly, hence make a contribution to society. This COVID-19 pandemic has increased the demand for such useful surveillance systems. In this pandemic deploying such surveillance will reduce the chances of getting infected and can increase the check on the covid protocols issued by the government.
Project Approach
We plan to use the various image processing algorithms in the Open-CV documentation to implement object detection, edge detection etc. Also, using TensorFlow we intend to implement deep learning models using datasets available online to detect face masks and social distancing violations. We go through various steps like data visualization, building the CNN model, training the CNN model and test its efficacy as given below
Dataset
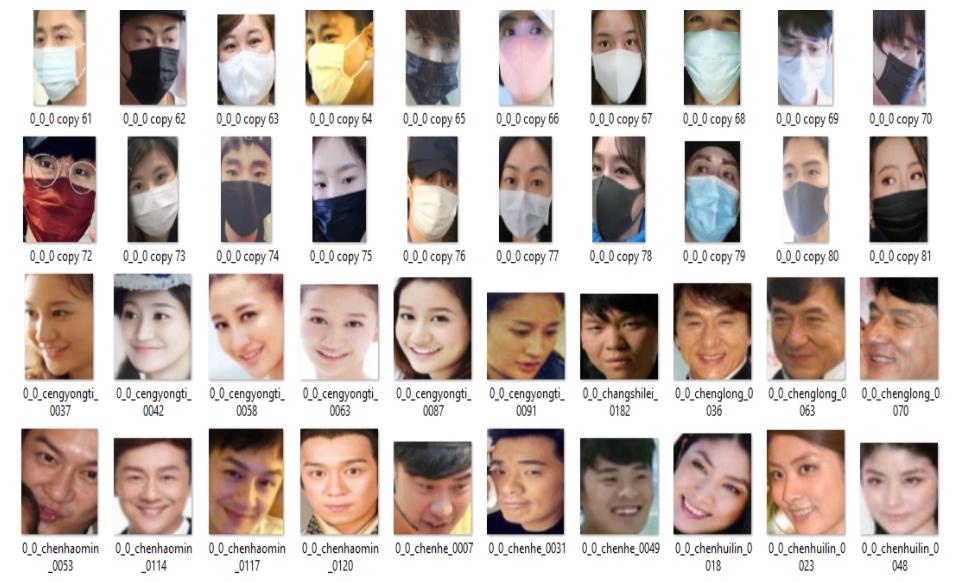
The dataset we have used consisted of 3919 which were labelled with mask and without mask. There were a total 1915 images under with mask category and 1924 images under without mask category. These datasets are taken from Kaggle, face without masks includes faces with various skin colors, different angles, occlusion, etc. Faces with masks include a mask with hand, with masks and other objects that cover the face, that provides us an advantage to improve variants of the dataset.
Implementation
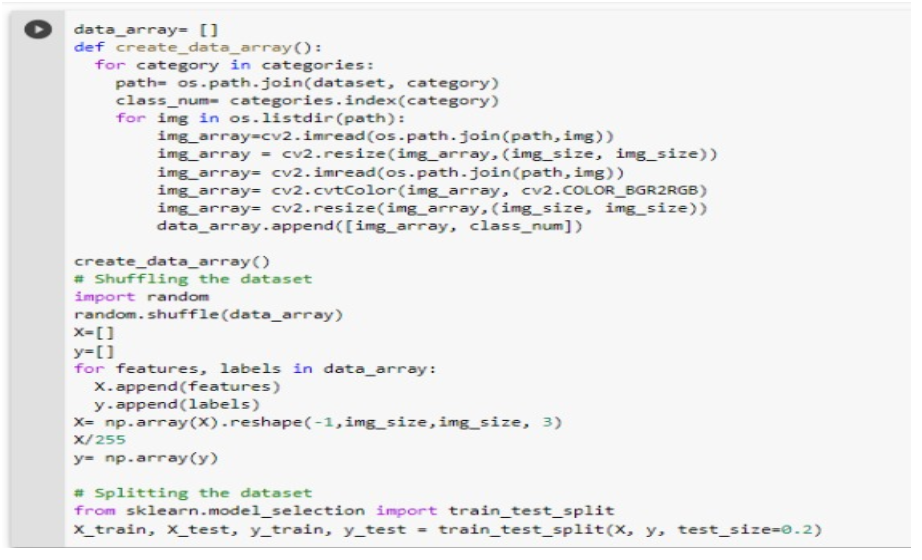
Firstly the images are resized to 240 X 240 pixels before feeding it to the model. The main reason for resizing is to maintain regularity in the input image size to the model. Then the images are appended in the list in a way that all the pics labelled with mask are in one single column and without mask are in another column. Then the list containing the dataset is shuffled. For getting the labelled data we append the images in a new list X[] and the corresponding labels in list y[].
Now we split the dataset into X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test using train_test_split() from sklearn library.
To reduce the model complexity and training time we convert the list into a more effective numpy array. And using feature scaling to normalize the pixel intensity from 0 to 1.
Now we move towards the interesting part of this project "CNN". Before moving lets know about tensorflow and keras.
Keras is a neural network library while TensorFlow is the open-source library for a number of various tasks in machine learning. TensorFlow provides both high-level and low-level APIs while Keras provides only high-level APIs.
In deep learning, the convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a phase of the deep neural network, which is widely used to analyze visual images.
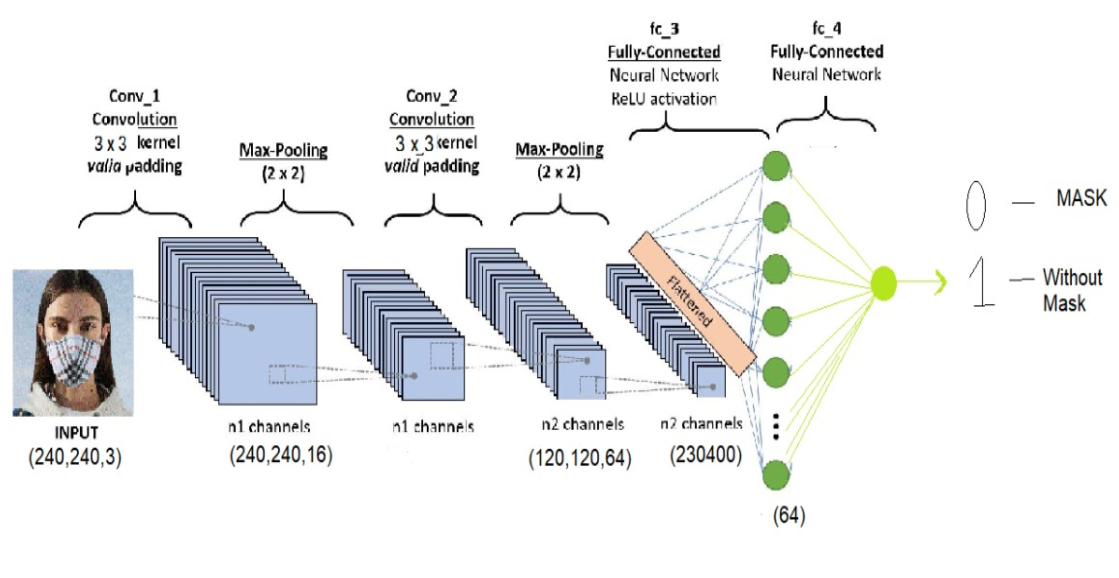
We built our Sequential CNN model and its architecture is as follows:- 1) We had 2 convolutional layers each followed by a Max pooling layer. Both of the convolutional layers have a 3 x 3 kernel (convolutional window) and ReLU activation function with 16 neurons in the first layer and 64 in the next. The Max- pooling layers have a pool size of 2 x 2. Then we flatten the layer and connect it to a dense layer. Dropout of 0.2 is also added to prevent overfitting. In the last Dense layer, we use the ' sigmoid' function which gives the output 0 or 1. A number close to 0 detects the mask in the input image whereas a number close to 1 outputs no mask in the input image . We use the ' adam' optimizer and ' binary_crossentropy' as our loss function as there are only two classes.
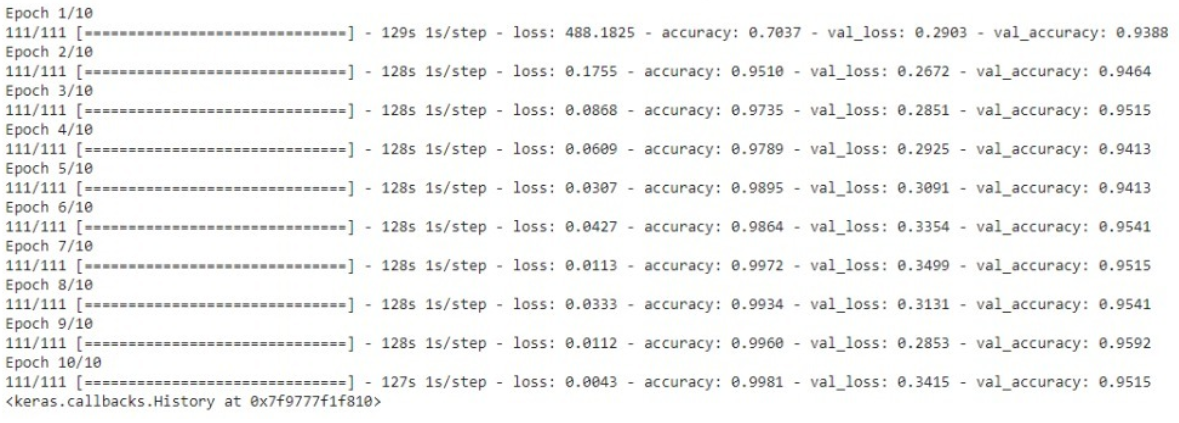
After building our model, let us train the model with the training set and use the validation split being 10% of the training data. We see that there are a total of 3135 images in the training set and 784 images in the test set.
I have trained the model for 10 epochs (iterations). However, we can train for more epochs to attain higher accuracy lest there occurs over-fitting.
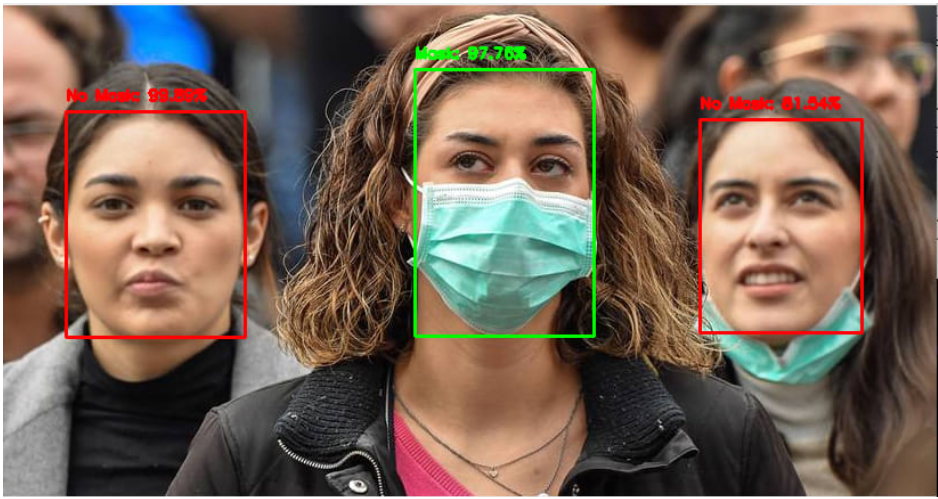
After building the model, we label two probabilities for our results. ['0' as 'with_mask' and '1' as 'without_mask'].
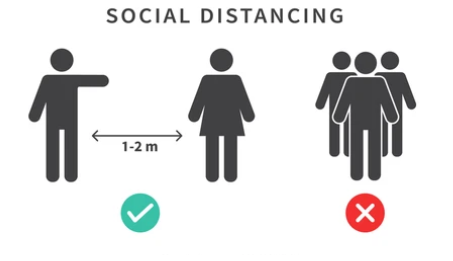
Now move on the next part of our project SOCIAL DISTANCING DETECTOR
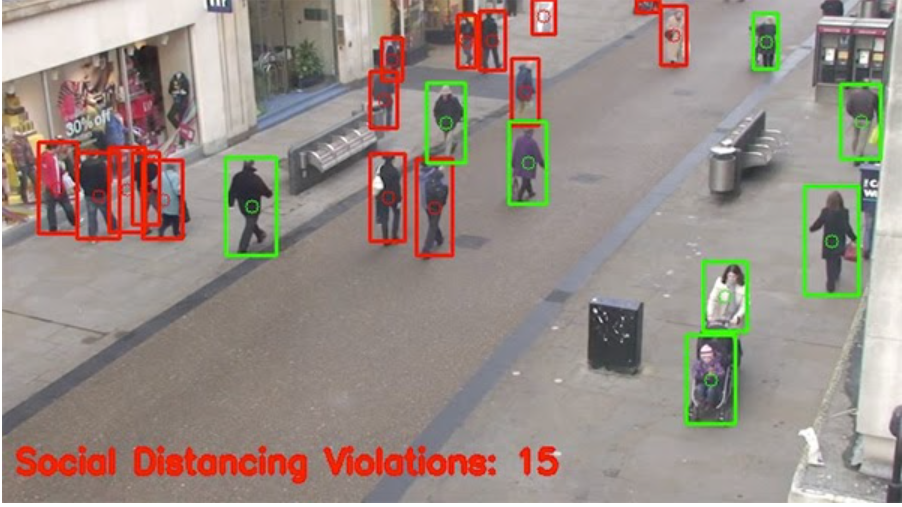
We used OpenCV, computer vision, and deep learning to implement social distancing detectors.
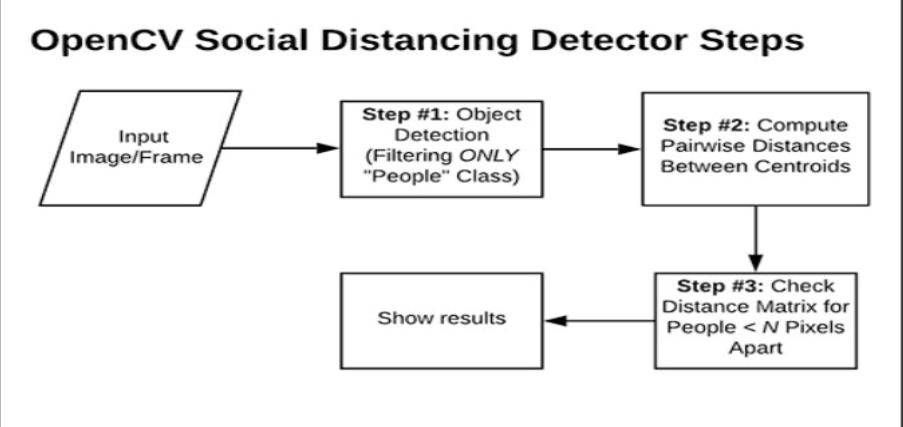
The steps to build a social distancing detector include:
- Apply object detection to detect all people (and only people) in a video stream
- We get a bounding box now we compute the pairwise distances between the centroids of all the bounding boxes
- Based on these distances, check if any two people are closer than a given threshold.
For the most accurate results,we should have calibrated our camera through intrinsic/extrinsic parameters so that we would have mapped pixels to measurable units.
An easier alternative (but less accurate) method would be to apply triangle similarity calibration.
Both of these methods can be used to map pixels to measurable units.
Finally,since applying camera calibration is a little complex, we utilized a social distancing detector, but we had to rely strictly on the pixel distances, which won't necessarily be as accurate.
For the sake of simplicity, our OpenCV social distancing detector implementation will rely on pixel distances
We'll be using the YOLO object detector to detect people in our video stream.
Result
After running the 10 epochs we get the following results:-
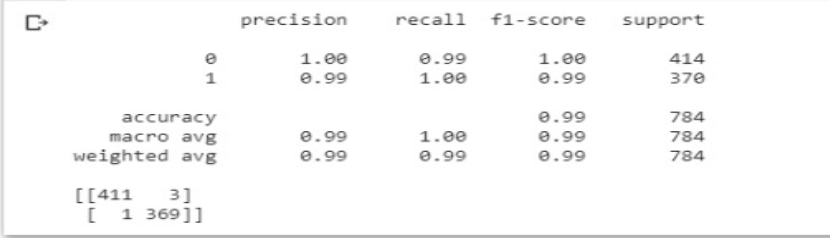
Now we check how our model performs on the testing set. We have plotted the classification report using the sklearn library. Further a confusion matrix is created.
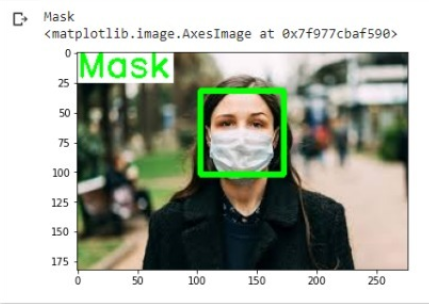
Now we finally use the model to predict on the images which were not in the dataset and the results are:-
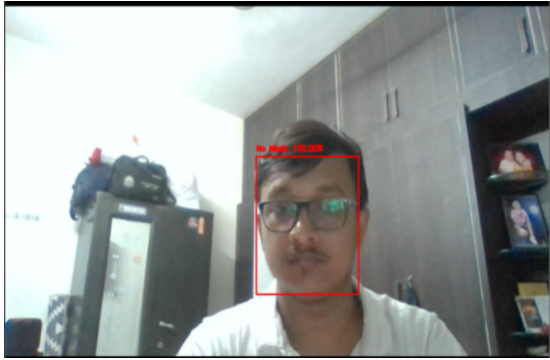
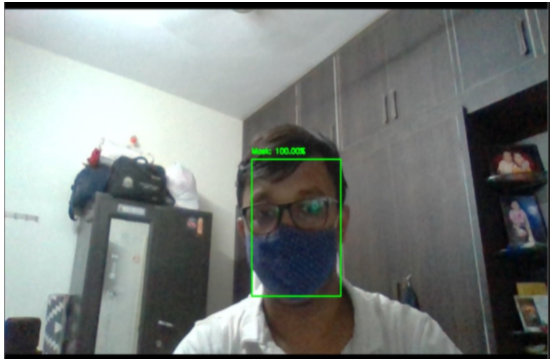
Now applying the model in real time mask detection using webcam or on a video camera the results are-
Now let's look how the social distancing feature works on a video clip:-