Mentors
- Soma Anil Kumar
Members
- Anannya Rao
- Vasanth M
Aim
The aim is to use an Android smartphone, ROS, and Gazebo to simulate the motion of a robot that can be controlled through the use of sensors
Introduction
Sensors are increasingly being utilized for a variety of purposes in today’s environment, one of which is controlling a device using the motion of another device, part of a technology called telepresence. This project controls the motion of a robot using a sensor on an Android smartphone known as the accelerometer. The robot’s mobility in the surroundings is determined by the motion of the smartphone.
Working/Implementation
The implementation of this project was carried out in 3 parts.
Part I : Android Smartphone Using Android studios, we created an application (written in Java) to read the accelerometer data. The accelerometer data contains the value of acceleration of the phone in each of the x, y and z axes. The data was then sent over a private wireless network.
Part II: ROS The accelerometer data sent over the private wireless network was received by a computer running ROS and was a part of the wireless network. A ROS node was created retrieve the data. ROS checks the value of the acceleration received. If the acceleration is positive, then ROS set a variable to +2. If the acceleration was negative, then ROS set a variable to -2. This variable is the velocity value of the robot.
Part III: Gazebo Gazebo is an open-source 3-D simulator that was used to simulate a robot. The velocity variable value of the robot was varied by ROS and then sent to Gazebo using the ROS framework. The robot thus moved according to the motion of the Android smartphone.
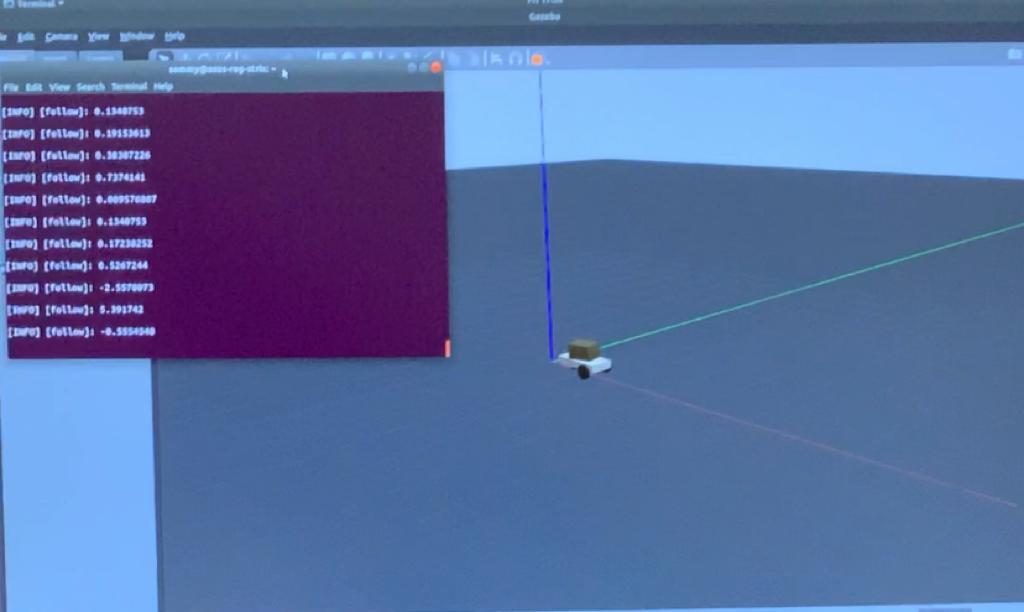 This image shows the robot on Gazebo being controlled by the velocity values (on the terminal)
This image shows the robot on Gazebo being controlled by the velocity values (on the terminal)