Mentors
- Pranav DV
- Sanjkeet Jena
- Harshwardhan Singh Rathore
Members
- Amandeep Singh
- RS Muthukumar
- Mohan Nayak
- Anirudh Prabhakaran
Aim
The goal of this project is to build a web app to diagnose lung diseases from chest x-ray images using deep learning.
Introduction
Deep learning, also known as hierarchical learning or deep structured learning, is a type of machine learning that uses a layered algorithmic architecture to analyze data. Unlike other types of machine learning, deep learning has the added advantage of being able to make decisions with significantly less human intervention. While basic machine learning requires a programmer to identify whether a conclusion is correct or not, deep learning can gauge the accuracy of its answers on its own due to the nature of its multi-layered structure.
With technological advancements, the earlier identification of diseases, particularly lung disease, we can be helped to detect earlier and more accurately, which can save many many people as well as reduce the pressure on the system.
dataset:
- Test set - 234 normal and 390 pneumonia
- Validation set - 344 normal and 964 pneumonia
- Train - 1005 normal and 2919 pneumonia
Description
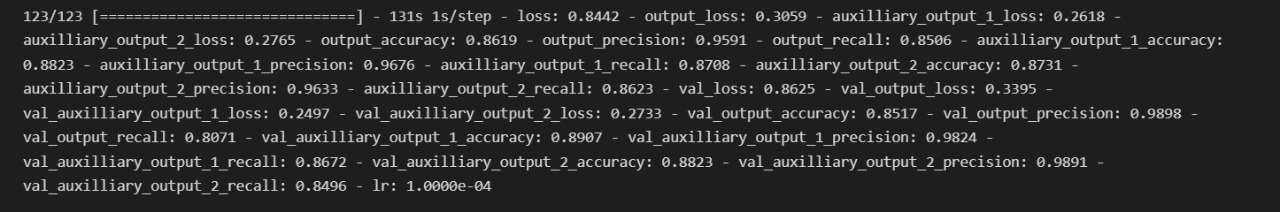
In this project, we conducted a study and analyzed the data set, then applied Deep Learning using convolutional neural networks to predict whether the patient has a lung disease. This project involves binary classification with input as patient data and output is whether disease is found or not.
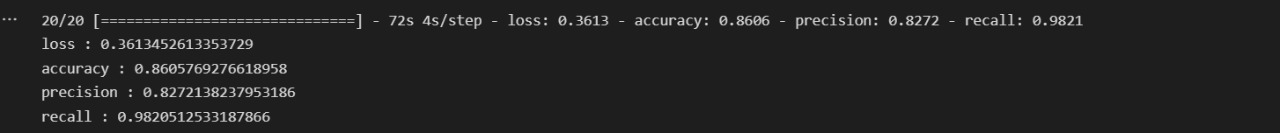
Libraries/framewroks used: keras, pandas, matplotlib,scikit-learn, tensor-flow, numpy, flask(for website).
The dataset was highly imbalanced, we updated the train and validation datasets.
Model
Convolutional Neural Networks are inherently designed for image processing, and this sets them up for handling and gathering insights from large images more efficiently.
The CNN architectures used include:
AlexNet
Alexnet has eight layers with learnable parameters. The model consists of five layers with a combination of max pooling followed by 3 fully connected layers using Relu activation except the output layer.
The input to this model is the images of size 227X227X3.
VGG16
VGG16 is a simple and widely used Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Architecture used for ImageNet, a large visual database project used in visual object recognition software research. The VGG16 Architecture was developed and introduced by Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman from the University of Oxford, in the year 2014, through their article “Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition.”
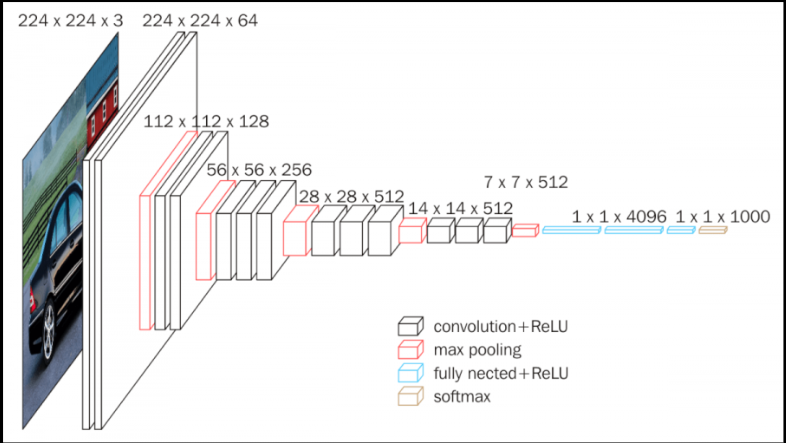
The input to the network is image of dimensions (224, 224, 3). The first two layers have 64 channels of 3x3 filter size and same padding. Then after a max pool layer of stride (2, 2), two layers which have convolution layers of 256 filter size and filter size (3, 3). This followed by a max pooling layer of stride (2, 2) which is same as previous layer. Then there are 2 convolution layers of filter size (3, 3) and 256 filter. After that there are 2 sets of 3 convolution layer and a max pool layer. Each have 512 filters of (3, 3) size with same padding.This image is then passed to the stack of two convolution layers. In these convolution and max pooling layers, the filters we use is of the size 3x3.
ResNet
Residual Network (ResNet) is one of the famous deep learning models that was introduced by Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Jian Sun, and Xiangyu Zhang in their paper.
The architecture of ResNet-34:
- The first layer is a convolutional layer with a kernel of 7x7 and 64 filters. This is followed by a max-pooling layer.
- After that, there are several layers (in pairs because of the skip connections) with 3x3 kernel sizes and a different number of filters (64, 128, 256, 512).
- Finally, there is average pooling and the softmax function.
We used transfer learning to implement further models.
Transfer learning is a technique to transfer what has been learned previously to new related tasks. Generally, traditional models work in isolation. Transfer learning overcomes the isolated learning paradigm and utilizes knowledge acquired for one problem to solve related ones.
Transfer learning is usually expressed through the use of pre-trained models. A pre-trained model is a model that was trained on a large benchmark dataset(like ImageNet) to solve a problem similar to the one that we want to solve.
MobileNet
MobileNet uses depth-wise separable convolutions. It significantly reduces the number of parameters when compared to the network with regular convolutions with the same depth in the nets. This results in lightweight deep neural networks.
InceptionNet
An inception network is a deep neural network with an architectural design that consists of repeating components referred to as Inception modules.
An Inception Module consists of the following components:
- Input layer
- 1x1 convolution layer
- 3x3 convolution layer
- 5x5 convolution layer
- Max pooling layer
- Concatenation layer
Website
Flask is an open-source microframework written in the Python language. It allows users to quickly and easily build powerful web applications. It is a favorite of developers due to its simplicity, and its insane scalability. Some of the biggest companies, like Reddit, Netflix and Uber use APIs built using Flask.
For our project, the web application shouldn’t be a very process-intensive one. The major processing that the app does is applying the ML model to the input and giving us the output. This leads us to choose to make out web applications in Flask.
The website facilitates the user to upload a chest x-ray image and when the user asks for predictions, each of the pneumonia models displays a probability. They are compared using a bar chart. If the user selects multiple models, a piechart showing how many models predict pneumonia and how many predict normal is.
Conclusion
In this project, we proposed the diagnosis of lung disease from the patient’s X-ray data plus some additional information. We did this by :
- Testing multiple architectures, optimizing and testing on a sample dataset.
- Using good architects to test the full dataset, continue optimizing and statistics.
The results of this project have achieved our initial expectations, but to be able to apply in hospitals, more improvements are needed to increase the precision of the model.
References
- Notebooks and datasets,
- Courses used,
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks-deep-learning
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks-deep-learning
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/introduction-tensorflow?specialization=tensorflow-in-practice
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/convolutional-neural-networks-tensorflow
- https://www.kaggle.com/learn/intro-to-deep-learnin
- https://www.kaggle.com/learn/computer-vision
- Research Papers,