Project Guide
- Dr Bibhuti Bhusan Das
- Department of Civil Engineering
Mentors
- Pramod Sunil Parande
Members
- Rajeev Bhat
- Gaurav Kumar
Aim
To design 3d concrete printed models, perform and analyze characteristic tests on them using Fusion 360
Introduction
This project aims at understanding the 3D printing in civil engineering through design and analysis . 3D Printing technology has brought a remarkable change in the construction methods and speed. With this one can optimize construction time ,cost, design, flexibility, error reduction and it also reduces manual power. This process involves pre-set commands on which the robotic arms runs. Concrete is extruded through nozzle to build structural component layer by layer. In this project we design and draw 3d models and do analysis.
Literature Review
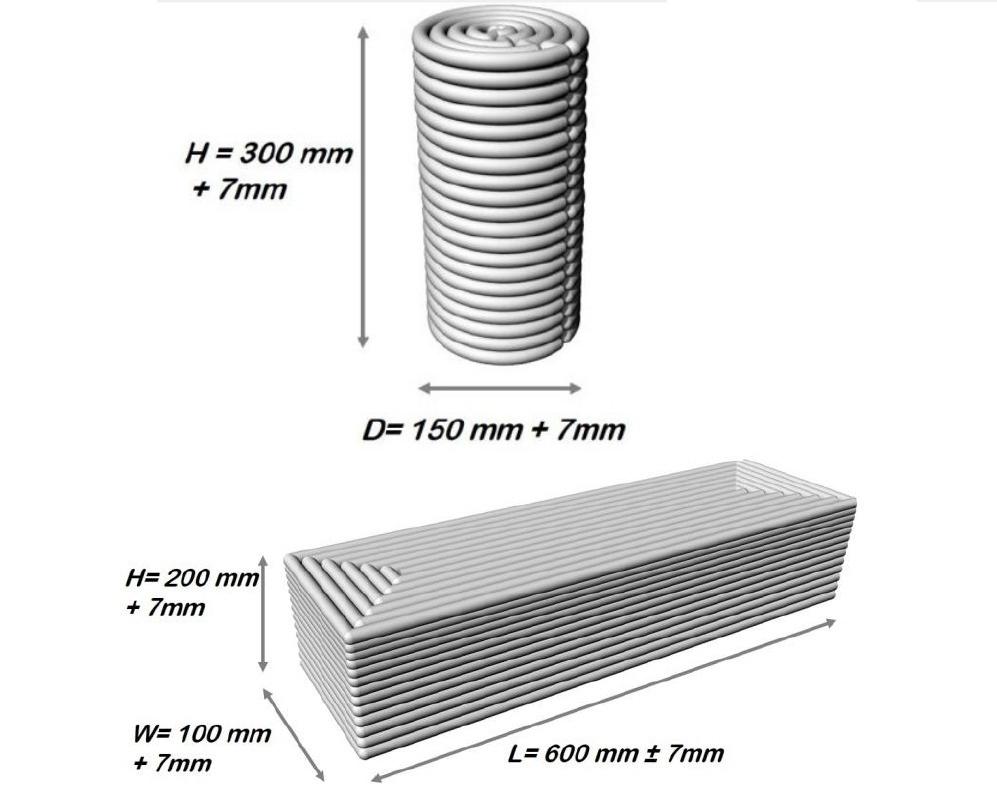
Before beginning the project ,we researched several sources such as research papers, journals , spoke with a 3D printing professional to have indepth overview of 3d printing. After completing literary review we finalized the models. DIMENSIONS OF 3D MODELS which were chosen are as follows #Nozzle dia- 15 mm #CYLINDER 1. Height- 300mm+7mm 2. Dia- 150mm+7mm
#BEAM 1.Length -600 mm +7mm 2. Width- 100 mm +7mm 3. Height- 200mm +7 mm
*For OPC mortar ….
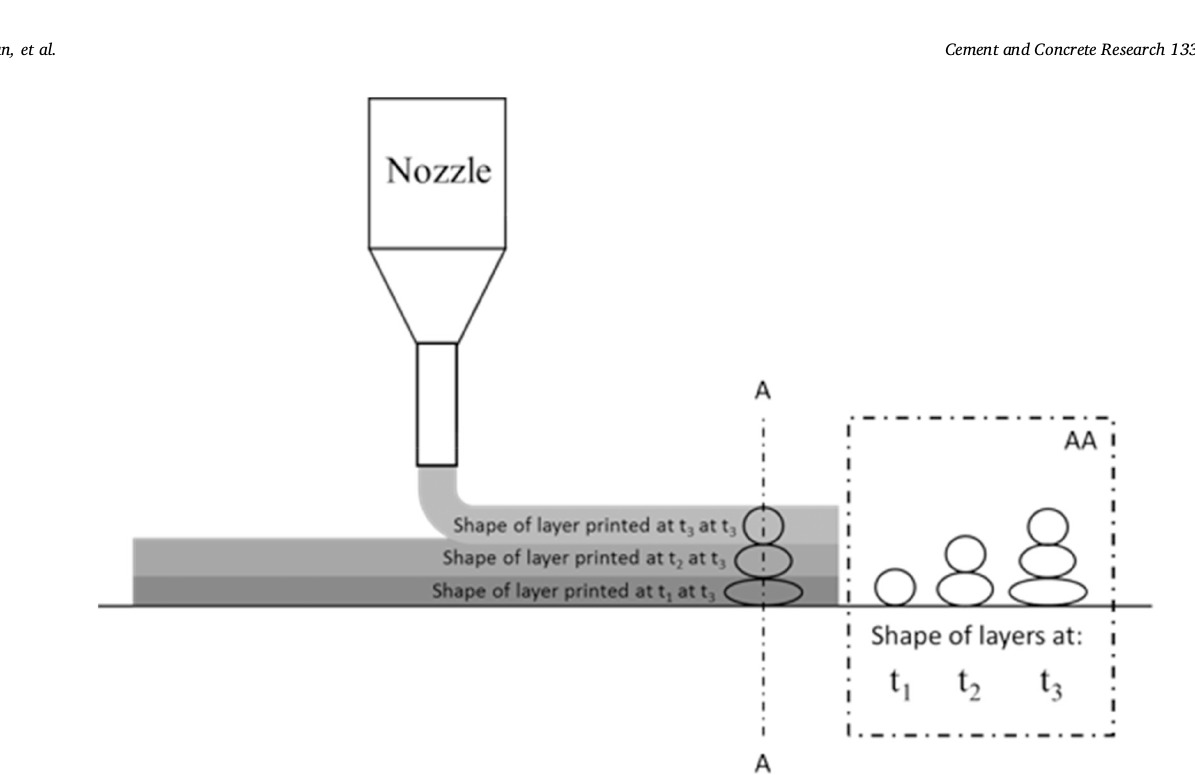
-> speed of robotic arm- 45 mm/ sec
 apart from these we also decided the tests which we were going to perform on these models.
apart from these we also decided the tests which we were going to perform on these models.
CAD work
Autocad
We learnt the basic concepts of autocad like 2d and 3d modelling since it was required for our project . We worked on several assignments to enrich our concepts. After completing this we were pretty much familiar with cad design.
Fusion 360
As this was the most essential cad where we were going to perform the tests related to these models. So here we again designed the models and conducted specific strength tests on the models.
-
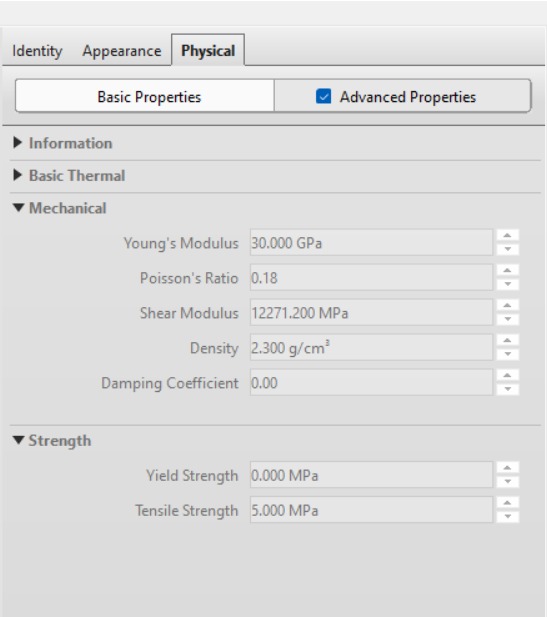
Compressive test- it helps us to know about the elastic and compressive behavior of materials . Compression tests are also used to determine the modulus of elasticity, proportional limit, compressive yield point, compressive yield strength, and ultimate compressive strength.
-
Split Tensile test- The splitting tensile strength test is performed on hardened concrete to determine its tensile strength, as true axial tensile load cannot be applied, since specimen might break at the point of holding. Hence such indirect methods are used to determine the tensile strength of concrete structures or objects. Marginal variations in water to cement ratio, ingredient proportioning, increase in a slump, etc impacts the desired concrete strength. This in turn affects the strength and stability of structures.
-
Following are the different tests and their effects on models are below
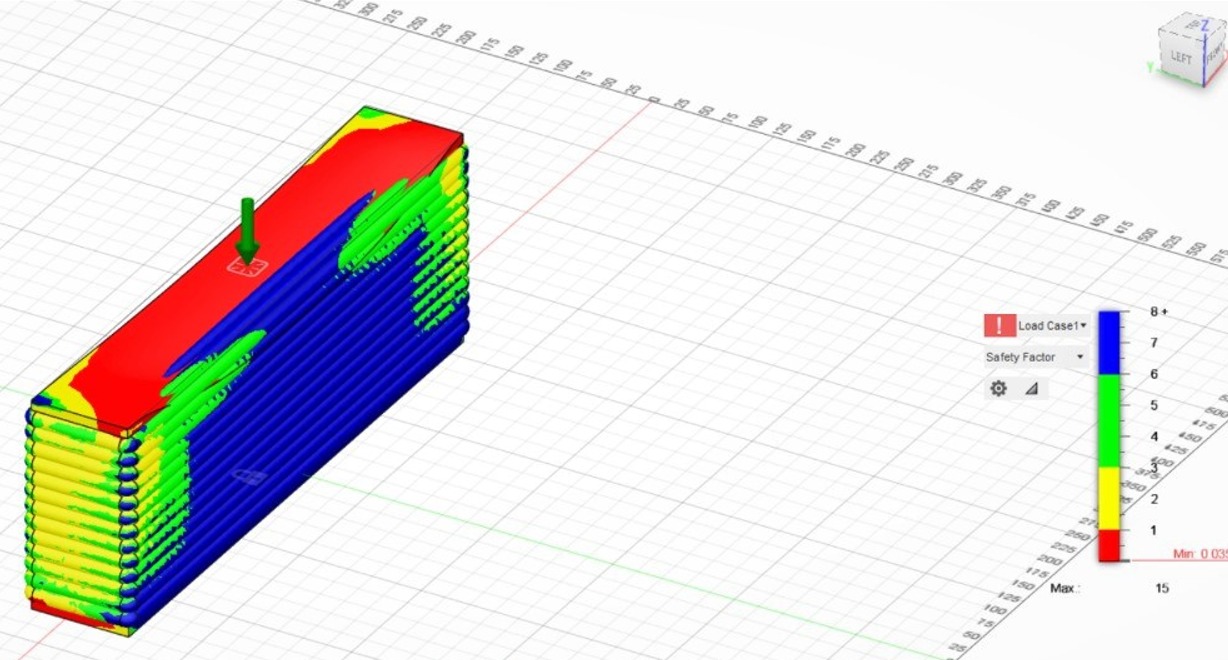
Result for static compressive stress on beam-
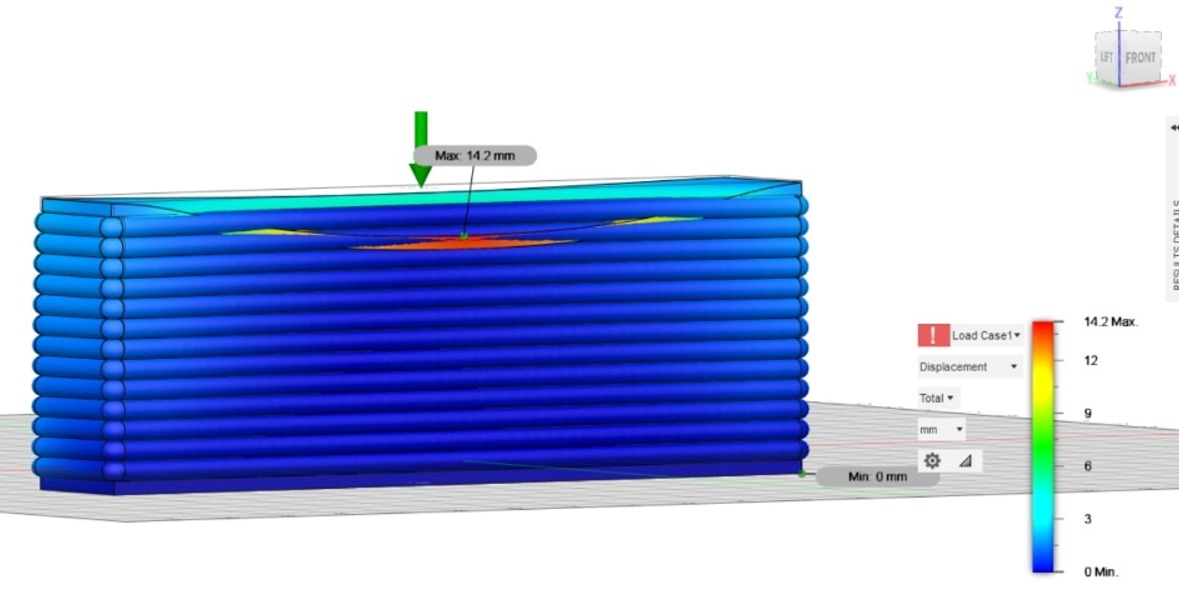
- Displacement- 9.47mm
- Reaction Force- 147.807kN
- Strain- .2191
- Contact pressure- 2411MPa
Result for static compressive stress on cylinder-
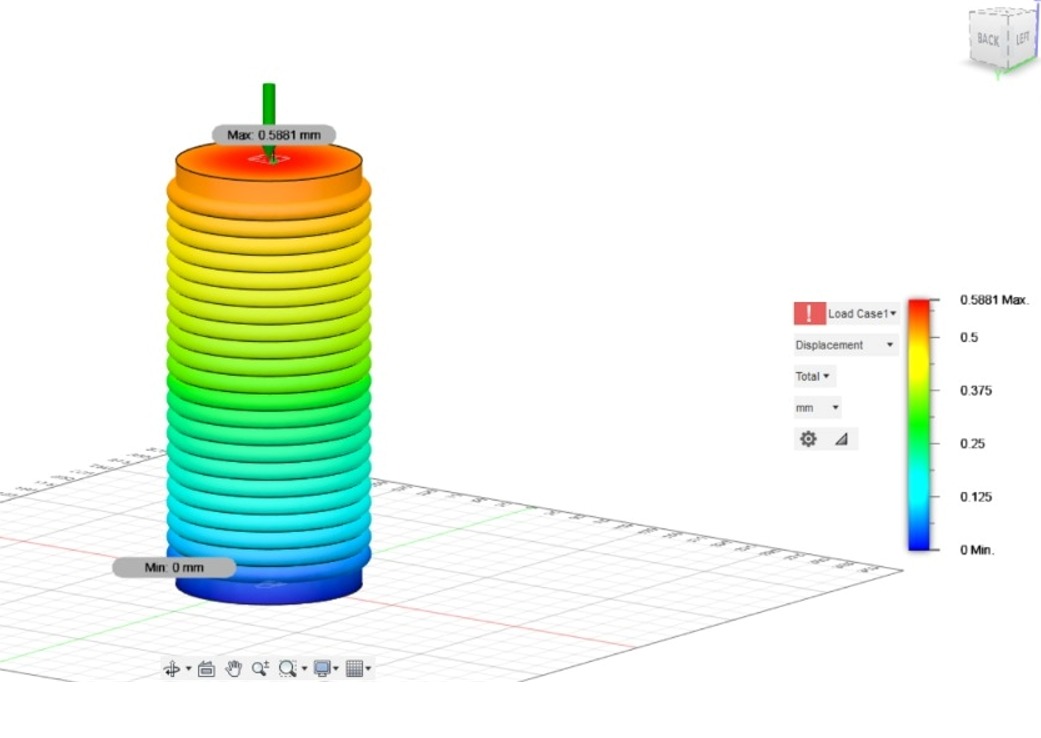
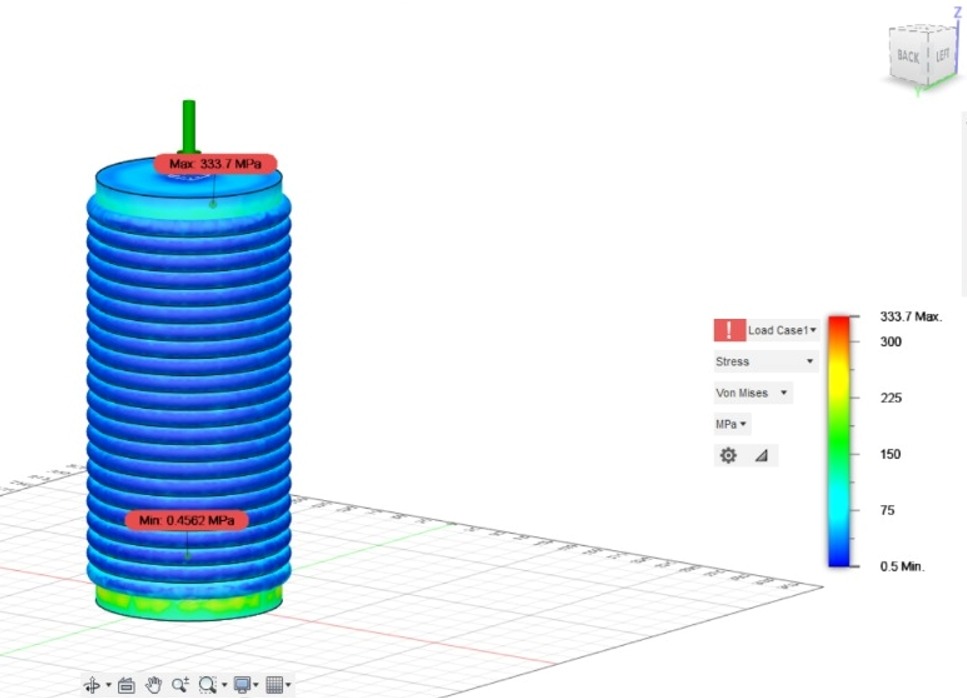
- Displacement- 0.5881mm
- Reaction Force- 12.875kN
- Strain- 0.01746
- Contact pressure- 155.2MPa
Result for split tensile stres: Load applied for split tensile stress is 5MPa
results for this test
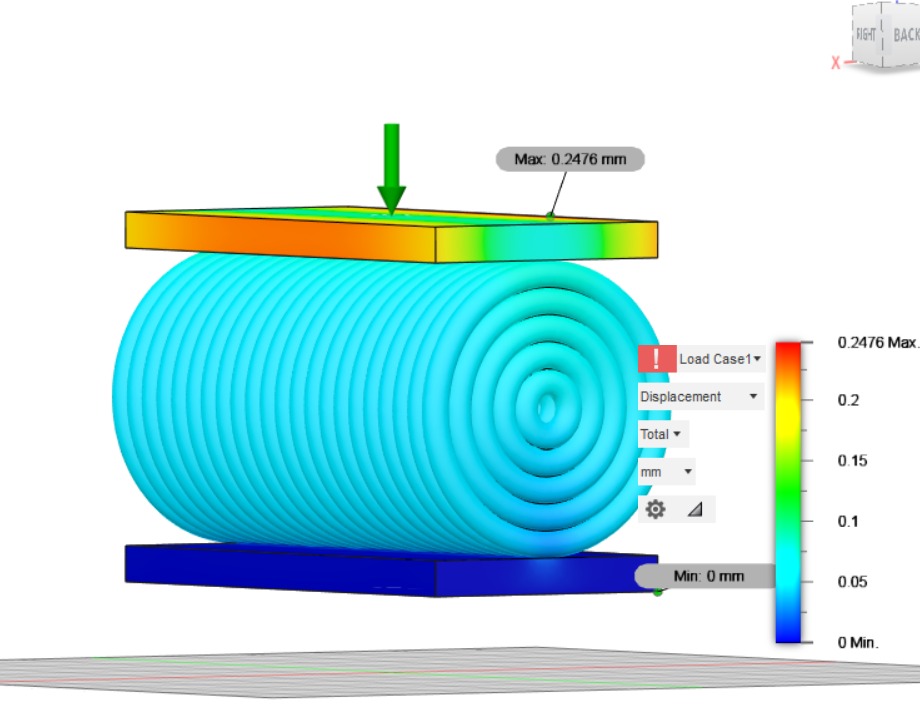
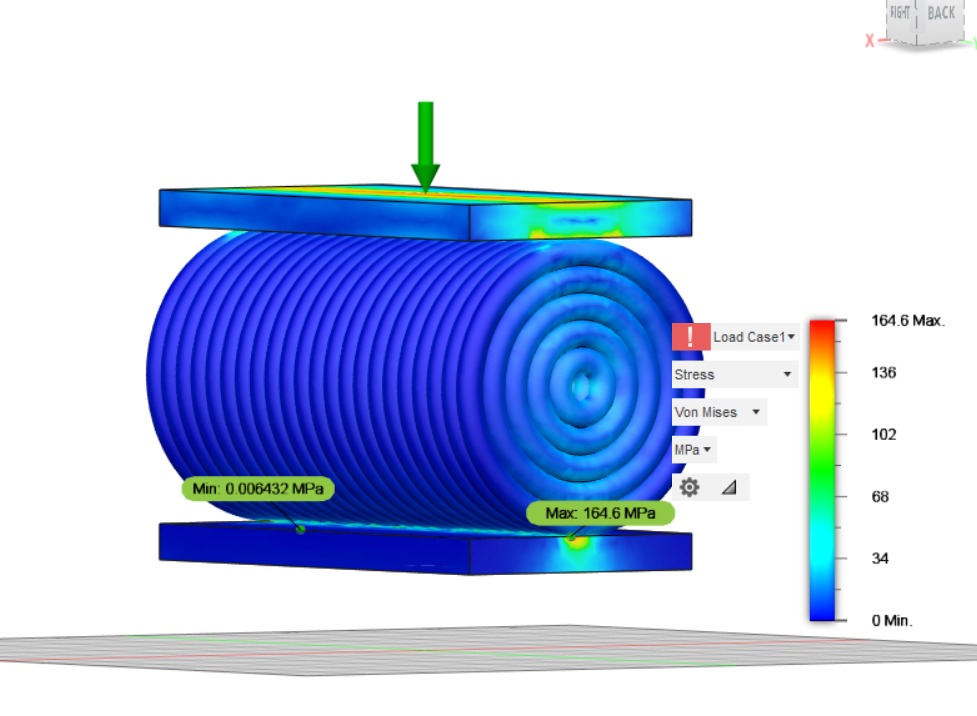
- Displacement- 0.2476mm
- Reaction Force (total)- 5511N
- Strain- .004969
- Contact Pressure - 171.1MPa
Conclusion
- After performing the analysis it was found that at 30 MPa compressive stress, the beam fails while the cylinder was able to sustain load so it is fine to go with cylinder.
- Layer must be bonded together while constructing a homogeneous structure, fast in comparison to conventional.
- Since we can alter the material ,the tensile stress was more better than concrete comparison to convention concrete ,compressive strength was also good.
- It can be used for creative structures, unique architectural and spatial experiences, innovative details, and full automation, informing a safer and more efficient use or resources in construction, particularly in harsh conditions on Earth, but also in future space colonies.