Mentors
- Sahaj Saxena
- Nakshatra Gopi
Members
- Gayatri Kattimani
Aim
- To design a BMS for Li-ion battery packs of 24 cells in a 4s6p configuration.
Introduction
” With the increasing demand for Electronic Vehicles, it becomes important to have a Battery Management system to protect and increase the lifespan of the batteries. The BMS regulates the battery performance by constantly monitoring cell parameters. The BMS monitors and limits the cell voltages, currents, and temperatures whenever necessary. We are designing a BMS for 18650 Li-ion battery packs of 24 cells in a 4s6p configuration. The battery pack requires us to monitor all the cells for over-voltage and current protection, and at least 30% of the cells for over-temperature protection. To meet the design requirements, we made a master-slave type of BMS with four slave modules, and one slave module for each segment of the battery pack, which communicates with the master module. The master module will communicate with external systems like laptops, Vehicle Control Units, etc. “
Why do we need BMS?
- To monitor and indicate the life of a battery
- To make the battery pack less prone to accidents
- To increase the lifespan of the battery
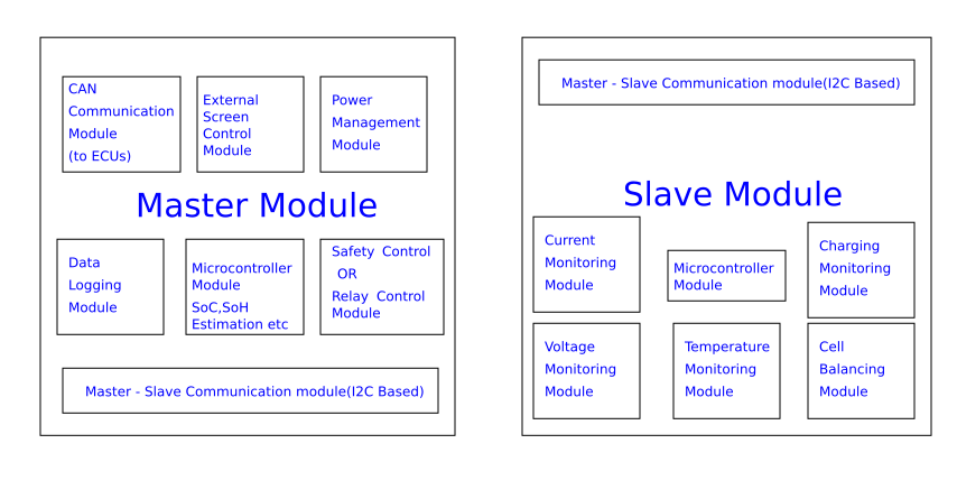
Overview
BMS will consist of 2 main modules, i.e the Master and Slave module. I2C Protocol is used to establish communication between both modules. Various different smaller modules are used inside each of the main modules. CAN Protocol is used as means of communication with external modules like the motor controller, vehicle control unit etc.
Modules inside Master Module.
- CAN Communication Module
- External screen control module
- Power management module
- Data logging module
- SoC, SoH estimation module
- Safety Control Module
Modules inside Slave Module
- Current Monitoring Module
- Microcontroller Module
- Charge Monitoring Module
- Voltage monitoring module
- Temperature monitoring module
- Cell balancing module
Various duties performed by BMS
Current Control
The BMS monitors the current going in and out of the battery. It can also regulate the current by disconnecting a particular slave module incase of a over current fault . So that the battery is protected.
Cell Balancing
When we used several cells grouped together to power a device, we need to use some sought of balancing. Cells get damaged if they are charged or discharged too much. In a battery pack with cells having different SoCs, the healthier cells will tend to overcharge. This will decrease the life of healthy batteries. So to ensure the charge balance between the cells we need Cell Balancing.
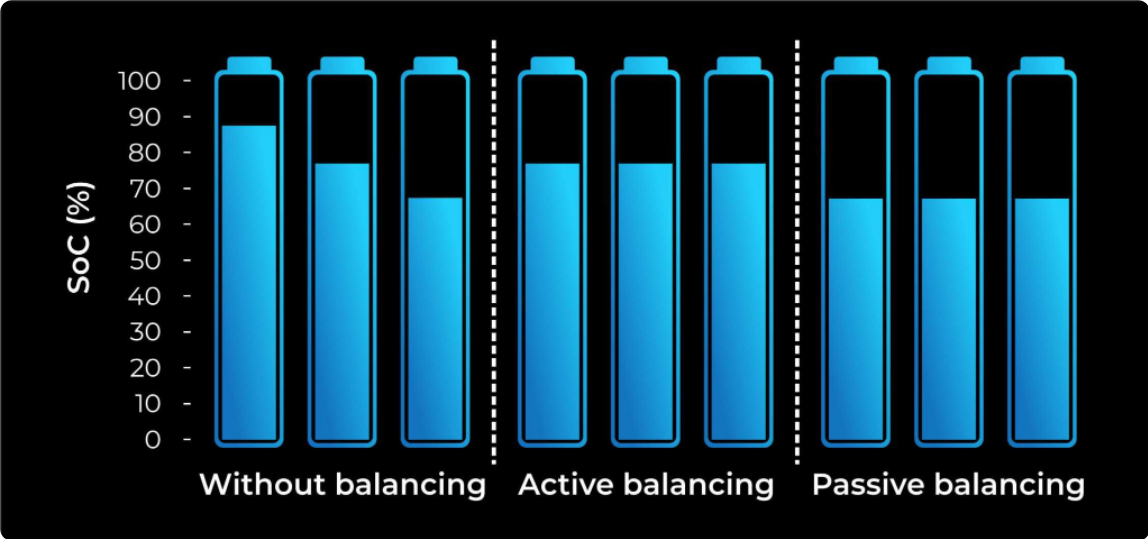
There are 2 types of cell balancing
- Active balancing
- Passive Balancing
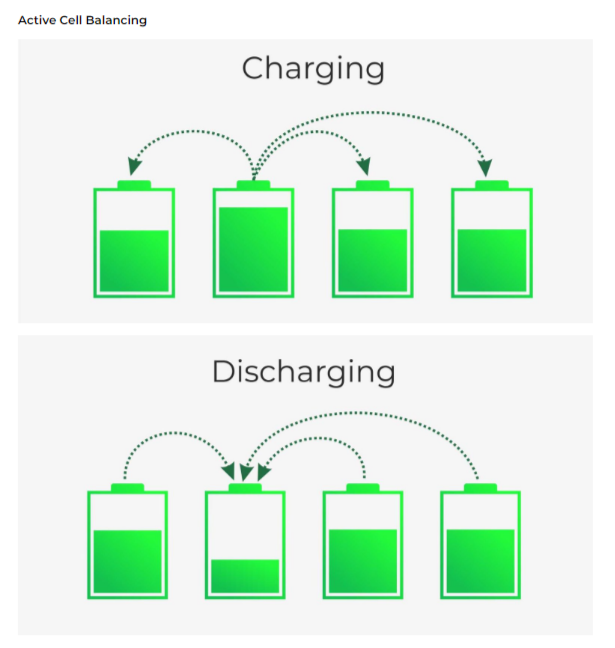
Active Balancing
An active cell balancer generally transfers energy from one cell to another. That is from high voltage/ high SoC to a cell with a lower SoC. The purpose of an active balancer is that if you have a pack of cells with lower capacity, you can extend the life or the SoC that you have on the pack by moving energy from one cell in the pack with more energy than the other cell. Instead of wasting all that energy as heat, an active cell balancer efficiently balances cells with tiny converter circuits that pass energy from the highest voltage cells to the lowest voltage cells.
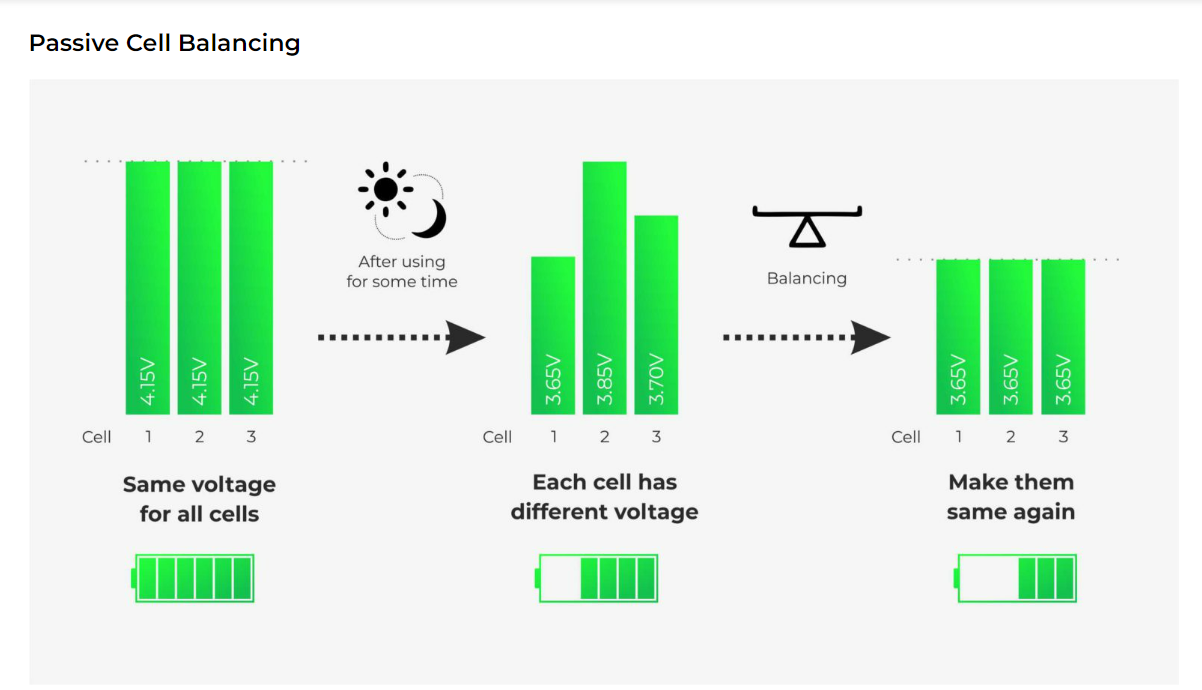
Passive Balancing
A passive system potentially burns off excess energy from the high cells through a resistive element until the charge matches the lower energy cells in the pack. If you have cells packed in series and you notice that some of the cells have higher energy than the other lower energy cells, you can balance the cells in burning energy of the top cells simply by attaching a resistor to the cells which release the energy into heat thereby equalizing the cell energy of the battery pack.
Voltage Control
An increase in Voltage can overcharge a battery, which can lead to degrading of the battery. If the battery is connected to a BMS, then it can’t overcharge the battery, since as soon as a cell reaches a critical voltage then the BMS will disconnect the charger from the pack.
Temperature Monitoring
The BMS consists of different ntc based temperature sensors, that will sense the heating of individual cells. The temperature of the battery pack is closely monitored to prevent overheating of the battery.
Soc and SoH estimation
The major task of a battery management system (BMS) is to provide security and longevity of the battery. This can be done through continuous monitoring and control of the battery’s state-of-charge (SOC) and state-of-health (SOH).
The SOC and SOH are the key metrics that describe the performance of the battery and help predict its future behavior. The state-of-charge shows the amount of electric charge left in the battery. It’s expressed as a percentage that ranges from 0% to 100% depending on the charge level. By looking at the state-of-charge indicator, a user knows the resources and understands when the battery needs to be recharged.The SOC is closely tied to the battery’s capacity and can also be determined as the ratio of the remaining capacity to the rated or maximum capacity specified by the manufacturer.
As time passes, every battery ages and degrades, as a result, the SOH goes below its initial level. Batteries with poor SOH discharge much faster than “healthier” batteries. This is the consequence of the decline in the rated capacity—an inevitable process that occurs over time. All this can serve as the evaluation criteria for finding out the SOH by battery management systems.The accurate state-of-health battery estimation can give early warning of deterioration and the need for battery replacement. Once you know the SOH, you gain access to useful information regarding the performance of your battery and the entire energy storage system, including their efficiency and reliability.Unlike with voltage or temperature, no special gauge could measure the battery state-of-health or state-of-charge. Neither SOH nor SOC has equivalents among physical quantities. You’ll have to consider a whole range of factors and parameters to assess these states most accurately.
Thus, calculating the SOH can rely on:
- Age
- Cycle life (number of charge/discharge cycles)
- Capacity
- Internal resistance
- Energy throughput
- Temperature
- Self-discharge rate
- Voltage
When evaluating the SOC, you can refer to the following parameters:
- Battery chemistry
- Voltage
- Current
- Capacity
- Impedance
- Charging/discharging rate
- Temperature
Methods for calculating the SoC and SoH
Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) Method
This method rests on the variation in the battery’s remaining capacity or SOC to the open-circuit voltage—voltage with the disconnected current load. The stronger the dependence between voltage and SOC, the higher level of measuring accuracy you can achieve. The relationship between these parameters is reflected in a look-up table as the discharge curve. Manufacturers can provide such a table in battery datasheets.
Coulomb counting (Current integration)
As the name suggests, this method is aimed at calculating coulombs or the quantity of electric charge, which is derived from current multiplied by the time necessary for the charge to flow. To measure the remaining capacity or SOC of a battery, you can add coulombs to the initial capacity in case of charging or take them away when you discharge the battery.
Current integration is a widespread method, but its accuracy depends on some factors. First off, you should know the correct measure of the initial SOC that serves as a reference point. You can get this by fully charging or discharging a battery. So if you want to use this technique, you need to allow for regular resetting of the battery SOC to 100% in your BMS design.
Kalman filtering
This method banks on the measurements and analysis of the battery’s input and output data, such as current, voltage, temperature, internal resistance, and other parameters. Based on this data, you can use the Kalman filtering algorithm to build an electrical model of a battery, simulate its behavior along with operating conditions, and estimate the state-of-charge.This method consists of two major steps. For starters, you enter the input data into the model and represent the physical processes running in a battery as mathematical equations. Thus, you predict the behavior of the battery and its output data by drawing on theoretical calculations. In the second step, you measure the actual battery parameters, such as voltage and current, and compare them with the predicted values. After that, the algorithm filters or corrects the model to reduce any possible deviations. Kalman filter can take the measurements every second throughout the entire discharge or charge cycle of a battery and predict the SOC at each iteration, every time minimizing the margin of error.
Conclusion
Now we know the main functions of any basic BMS. Various sensors and different control modules are put together to make the final modules. Finally, the 2 Modules are made to communicate using I2C communication protocol.