Varistor
The name itself might have given you some idea about what it is, varistor stands for variable resistor
What is a varistor?
Varistor is a varying resistor whose resistance depends on applied voltage,one of the special features of varistor is that it possesses non ohmic characteristics, which defines themselves as a non linear type of resistors
It has two semiconductor elements fixed in a particular fashion (i.e. anti-parallel to each other) as to provide same characteristics for both directions of traversing current
Its composition might have provided you with the insight that as it is made of semiconductor, it’s resistance will decrease as voltage across it increases
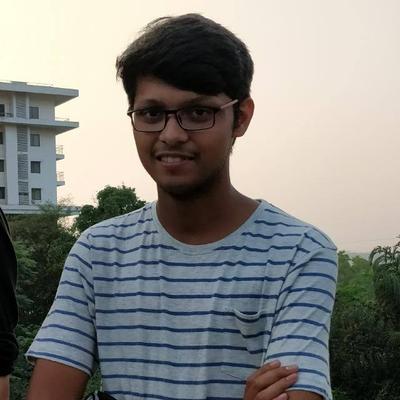
Its symbol is
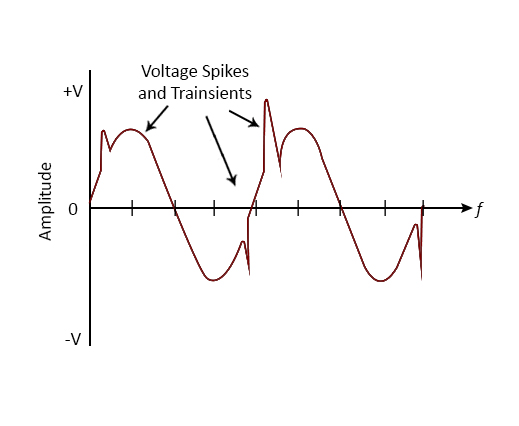
One of the major applications of varistors is its ability to suppress voltage transients in the cut
Voltage transient - short duration surges of electrical energy that are result of sudden release of energy that are previously stored or induced by other means, such as heavy inductive loads or lightning
Waveform of AC Transient
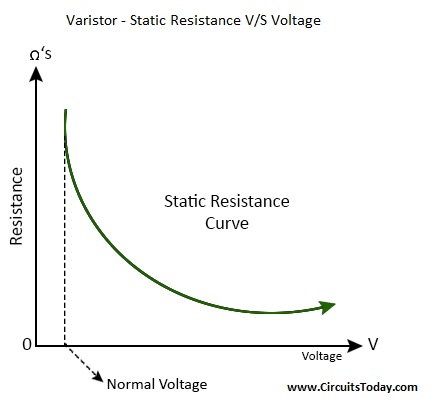
The above characteristics might actually lead you to think that varistor behaves like a potentiometer or a rheostat
Two characteristics that makes varistor a different entity is
i) resistance cannot be changed manually
ii) resistance decreases with increase in voltage
Varistor vs voltage graph
Working of a varistor
As I have already told that its characteristics are similar to that of Zener diode, its V-I characteristics are also similar to that Zener diode
V-I characteristics of varistor
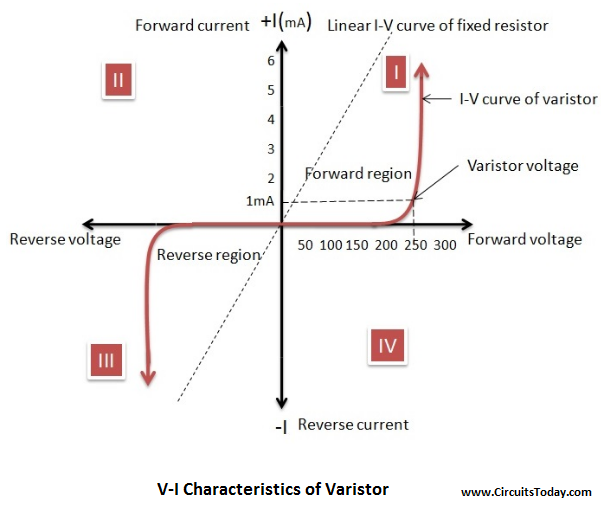
As the varistor operates in first and third quadrant, it makes it a suitable device to connect it in a circuit with AC or DC source
As the voltage increases above the clamping voltage, there is an abrupt increase in current
This helps during voltage transients, as when the circuit experiences high transient voltage, the voltage across the varistor increases, to a value greater than its clamping voltage, which in turn increases the current and acts as a conductor, it basically acts like a self-regulator at the event of voltage transient keeping the voltage input in check
Steep nonlinear curve indicates excessive currents can be passed through varistor over narrow range of voltage
Capacitance of varistor
A varistor in non-conducting state acts like a capacitor more than a resistor
Non-conducting state-the voltage applied across the varistor is less than the clamping voltage
Since the semiconductor body of the Varistor acts like an insulator during its insulating state, it can be regarded as the dielectric material, while the two terminals can be regarded as the two electrodes
Types of Varistor
Silicon carbide varistor
Metal oxide varistor
