Many of us have this notion that NP stands for “Non Polynomial”, the problems which can’t be solved in polynomial time. This is not true. First of all, NP consist of only decision problem (given any problem, the answer should be yes or no) solvable in polynomial time by a theoretical non-deterministic Turing machine. Well, I am not going to cover non-deterministic Turing machine in this blog, so I will give another verifier based definition.
Verifier Based Definition:
Consider a decision problem X. Let I be an instance of X for which the answer is “yes”. Now if we can indeed verify in polynomial time that the answer to I is “yes”, then we have a verifier for I. If there is a verifier for all such instances of X, then X is said to be in NP. Consider an example:
Subset sum problem: Given a set of natural numbers, is it possible to find a subset such that sum of all numbers in that subset is zero. Now for any instance I, I can simply add up all the numbers of the subset to verify if the sum is zero. So, I have a polynomial time Verifier. Therefore, the problem belong to NP.
Now, the next thing is whether we can find in polynomial time, the answer to that problem. Wait! Here by polynomial time, we mean polynomial in terms of input size. If my input is just a number, polynomial time implies polynomial in the number of bits required to store that number. So, the polynomial time in case of finding whether a number is prime or not will be log(n) (The binary representation will require log(n) bits).
If we can find the answer in polynomial time, the problem is in the class of ‘P’. So yeah, P is a subset of NP. Now, if you ask me whether it’s a proper subset or not, then you are asking me a million dollar question. Whether P = NP is one of the most famous question in Computer Science and nobody has been able to attack it.(You can try your hand!)
NP Hard
So, if it’s not a proper subset than what other problems does NP consist of? Well let me introduce one more class of problems - NP Hard.
The problems in NP hard are the set of problems which are “atleast” as hard as any other problem in NP. So, if you can find a polynomial time algorithm for a problem which is NP hard, then you can find a polynomial time solution for all the problems in NP. So, we can reduce any problem in NP to any problem in NP hard. This reduction will be done in polynomial time. But wait, although the class of problems is called “NP” hard, all the problems in NP hard need not belong to the class NP. Why? All NP hard problems are not decision problems. Now you will think that some NP hard problems must belong to NP and such problems are called NP complete(NPC) problems. So, NP complete is intersection of NP and NP hard as shown in the figure below.
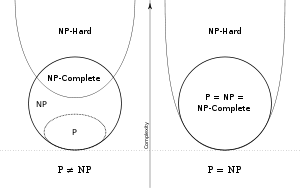
The above diagram is taken from wikipedia. It is widely believed that P != NP, but no proofs yet.
Resources:
You can follow the book ‘Algorithms’ by U.V. vazirani and ‘Introduction to Algorithms’ by Tardos for getting a better understanding.
