PSLV to Mars
(Mars Orbiter Mission)
Marking the series of events in the world history, November 5,2013 is recognized to be a day of great significance all over the world. On this day, ISRO launched MOM(Mars Orbiter Mission) also called Mangalyaan,a space probe orbiting Mars since September 24,2014.This made India the first Asian nation to reach Martian Orbit and the first nation in the world to do so in its first attempt.The launch took place from Satish Dhawan Space centre in Sriharikota.Indian scientists in ISRO proposed to launch the Mars satellite using PSLV(Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) rocket. First, they thought to launch MOM with GSLV but it failed twice in 2010 and was continuing to experience issues with cryogenic engine.It was planned to launch MOM when Mars is closest to the Earth which happens once in about 26 months.Only few months were left to launch and in such a short time they couldn’t make a new rocket for MOM launch.They decided to launch MOM using PSLV-XL C-25 rocket knowing that it has low fuel capacity.
Challenges involved :
- The PSLV has low load and fuel capacity which was insufficient to reach Mars. So they had to reduce the fuel and overall weight.
- To overcome earth’s gravitational force to move satellite away from earth’s orbit.
- To cover a large distance with less fuel.
Objectives:
- To develop technologies required for design,Mars orbit insertion and on orbit phase around Mars.
- Deep space communication and navigation.
- Incorporate autonomous features to handle contingency situations.
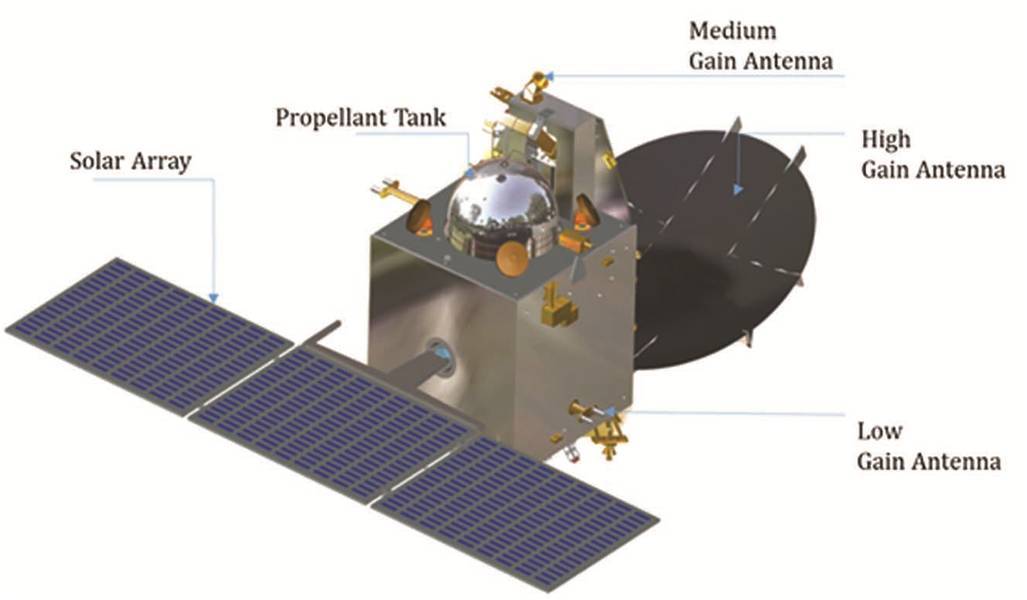
The total load was of 1350 kg including 850 kg of fuel. The satellite weighed 15 kg with 5 instruments to study Martian surface, morphology, mineralogy and Martian atmosphere. One of the instrument used was Methane detector since specific research of methane could tell the possibility and past existence life on Mars.
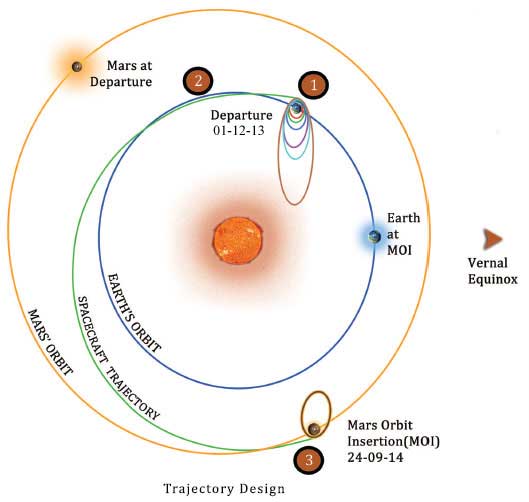
Trajectory
There were three phases involved:
1)Geo centric phase
The basic idea was based on Hohmann Transfer Orbit, a minimum energy transfer orbit. Since PSLV couldn’t take the satellite all the way but could leave satellite in earth’s orbit easily. When satellite reached the perigee, they fired the satellite engine with a little fuel then switched off the engine.The firing force increased the speed of the satellite and propelled it further away from the Earth into a higher orbit.When it came back at perigee, they kept doing the same and at last when the satellite was at perigee again, the speed of the satellite was so much that a final strong firing force threw it out of the Earth’s gravitational sphere.
2)Helio centric phase
The satellite left the Earth’s orbit tangentially and met Mars tangentially to its orbit.
3)Martian phase
The satellite arrived at the Mars sphere of influence in a hyperbolic trajectory and finally captured into planned orbit around Mars on September 24,2014.