PIEZOELECTRICITY AND PIEZOELECTRIC SENSORS
Piezoelectricity
The accumulation of electric charge in solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress is called the piezoelectric effect or piezoelectricity, and those types of solid materials are called piezoelectric materials. Quartz, Berlinite (AlPO4), Sucrose (table sugar), Topaz, Tourmaline-group minerals, Lead titanate, etc. are some examples of naturally occurring piezoelectric materials. Some of the biological materials exhibiting piezoelectricity include silk, wood, enamel, tendon, etc. Barium titanate, Lead zirconate titanate, Potassium niobate, Sodium tungstate, Zinc oxide, etc., fall under the category of Synthetic ceramics that exhibit the piezoelectric effect. Piezoelectric effect is also exhibited by some polymers like polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyvinylidene chloride (PDVC), etc. The piezoelectric effect is a result of the linear electromechanical interaction between the electrical and mechanical states in crystalline materials. The internal generation of mechanical strain resulting from an applied electric field is called the reverse piezoelectric effect. The materials which exhibit the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect. We can say that a crystal can exhibit the piezoelectric effect if:
- The crystal lattice should contain polar bonds. For example, Quartz exhibits the piezoelectric effect because of the oxygen-sulfur bond which is a polar bond.
- The crystal structure should not have inversion symmetry/point symmetry. If point symmetry exists in the crystal then the center of charge will not be displaced even if there is some mechanical stress on the crystal, as a result, there would be no piezoelectric effect in this case.
Uses
Piezoelectricity has a number of useful applications. Piezoelectric materials are used in the detection and production of sound, high voltage power sources, sensors, actuators, piezoelectric motors, electronic frequency generation, etc. The piezoelectric material quartz is used as a time reference in Quartz watches. These materials also find some daily life applications such as acting as a source of ignition in lighters, for amplification pickups in some guitars.
Modes of operation of piezoelectric materials:
The piezoelectric material has three main modes of operation which depend on the way it has been cut.
1.Transverse Effect:
A force applied along a neutral axis(let’s say y-axis), displaces the charge along an axis perpendicular to the neutral axis(x-axis) and the amount of charge displaced is proportional to the applied force and the dimensions of the crystal along the respective axes. Qx = dxy * Fy * (b/a) Where ‘Qx’ is the charge displaced along the x-axis, ‘a’ is the dimension of the crystal parallel to the neutral axis(y-axis), ‘b’ is the dimension of the crystal along the x-axis and ‘dxy’ is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient in that plane(XY-plane).
2. Longitudinal Effect:
The amount of electric charge that gets displaced in the direction of the applied force(let’s say x-axis) is only proportional to the applied force and does not depend on any of the dimensions of the crystal.
Qx = dxx * Fx Where ‘Qx’ is the charge displaced along the x-axis, ‘Fx’ is the force applied along the x-axis and ‘dxx’ is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient along the x-axis3. Shear Effect:
The amount of charge produced in the plane(YZ-plane) normal to the direction of the applied force(along the x-axis) is only proportional to the applied force and does not depend on any of the dimensions of the crystal and is twice the amount of the charge produced in the direction of the force. Qyz = 2 * dxx * Fx Where ‘Qyz‘ is the amount of charge produced in the YZ-plane, ‘Fx’ is the force applied along the x-axis and ‘dxx’ is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient.
Piezoelectric Sensors
A piezoelectric sensor utilizes the piezoelectric effect to measure the change in physical quantities like acceleration, pressure, temperature, strain, force, etc by converting them into electric charge.
Equivalent circuit
The voltage produced at the source ‘V’ is directly proportional to the applied force, pressure, strain, or the magnitude of acceleration (in accelerometers). The Equivalent circuit of the piezoelectric sensor is as shown.
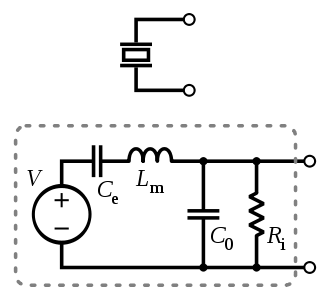
V - Voltage produced by piezoelectric material Ce - represents the mechanical elasticity of the material Lm - due to seismic mass and inertia of sensor Co - static capacitance of the sensor i.e. capacitance due to base plates Ri - insulation leakage reactance We attach a load(which depends on our application) parallel to the leakage reactance.Graph
The graph of the sensitivity i.e. ratio of the electric output and the applied force/acceleration denoted by s(w) and frequency(frequency of the crystal due to applied force, stress or acceleration ) will be as shown below.
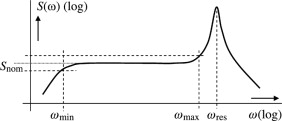
To make use of piezoelectric material as a sensor, the flat region of the frequency plot(the part of the graph which is in between wmin and wmax) is used. To accommodate low frequencies of interest the load resistance and leakage reactance should be quite large.
Working
So a typical piezoelectric sensor has a base plate, seismic mass, and the piezoelectric crystal. When the force/ stress is applied or the sensor experiences motion (this happens in accelerometers), the seismic mass loads up the elements. The voltage corresponding to the physical parameter is generated at the source as shown in the circuit above. This can be seen as if the voltage generated drives the equivalent circuit and we get an output signal (which is generally voltage across the load/current through the load), which is processed to determine the physical parameter.
Advantages and Disadvantages of piezoelectric sensors
Due to their inherent advantages, piezoelectric sensors are used in various fields. They have a high modulus of elasticity and high natural frequency. They are insensitive to electromagnetic fields and radiation, enabling measurements even under harsh conditions. One major disadvantage of piezoelectric sensors is that they cannot be used for truly static measurements because a static force causes a fixed amount of charge, so there would not be any output signal.
Applications of piezoelectric sensors
The piezoelectric sensors are used to measure physical parameters, for example, they are used in accelerometers, etc. They are used as touch sensors and tilt sensors in mobile phones and other consumer electronics. Piezoelectric sensors are used to measure inside internal combustion engines to monitor combustion inside them. Piezoelectric sensors also find applications in aerospace, medical, nuclear instrumentation.
