INTRODUCTION
Object detection, in simple terms, is a method that is used to recognize and detect different objects present in an image or video and label them to classify these objects. It provides a much better understanding of the object as a whole, rather than just basic object classification. The important difference is the “variable” part. In contrast with problems like classification, the output of object detection is variable in length, since the number of objects detected may change from image to image. All in all, it answers the question: “What object is where and how much of it is there?”.
Terminology
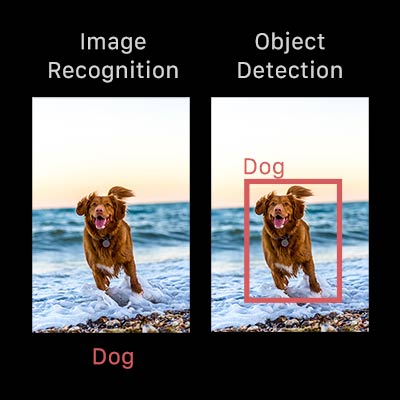
Object detection is commonly confused with image recognition, so before we proceed, it’s important that we clarify the distinctions between them.
Image recognition : It assigns a label to an image. A picture of a dog receives the label ‘dog’. A picture of two dogs, still receives the label ‘dog’.
Object detection : It draws a box around each dog and labels the box “dog”. The model predicts where each object is and what label should be applied. In that way, object detection provides more information about an image than recognition.
HOW OBJECT DETECTION WORKS?
The simplest approach is to pass the image to the series of convulation and pooling layer and we get object class as an output. But how we will do that for multiple objects? For multiple objects, we can divide the images into various regions and take different regions as different image. Pass all these regions (images) to the CNN and classify them into various classes. Once we have divided each region into its corresponding class, we can combine all these regions to get the original image with the detected objects. The problem with using this approach is that the objects in the image can have different aspect ratios and spatial locations. To overcome all these problems, there are multiple DL Algorithm. Some of them are discussed below:
DEEP LEARNING ALGORITHMS
1. R-CNN
In region convolution neural network, selective search algorithm is used to efficiently determine the region proposals. This selective search algorithm proposes approximately 2000 region proposals per image. These region proposals are then passed to the CNN model. This CNN model then outputs feature vector from each region proposal. This vector is passed to SVM model for classification of object and bounding box regressor for localization.
Disadvantage :
- In R-CNN we pass each region proposal one by one in the CNN architecture and selective search generated around 2000 region proposal for an image. So, it is computationally expensive to train and even test the image using R-CNN.
- It takes a large space to store feature map of each proposal.
- It takes enough time to detect object in image.
2. Fast R-CNN
To deal with the problem of R-CNN, Fast R-CNN was proposed, It takes the whole image and region proposals as input in its CNN architecture in one forward propagation. It also combines different parts of architecture (such as ConvNet, pooling, and classification layer) in one complete architecture. That also removes the requirement to store a feature map and saves disk space. It also uses the softmax layer instead of SVM in its classification of region proposal which proved to be faster and generate better accuracy than SVM.
DISADVANTAGES:
- Selective search algorithm takes a lot of time.
3. Faster R-CNN
After the Fast R-CNN, the bottleneck of the architecture is selective search. In Faster R-CNN, it was replaced by the region proposal network. RPN takes image feature maps as an input and generates a set of object proposals, each with an objectness score as output. RPN uses a sliding window over these feature maps, and at each window, it generates k Anchor boxes of different shapes and sizes. Anchor boxes are fixed sized boundary boxes that are placed throughout the image and have different shapes and sizes. For each anchor, RPN predicts two things:
- The probability that an anchor is an object
- The bounding box regressor for adjusting the anchors to better fit the object
DISADVANTAGES
- The algorithm requires many passes through a single image to extract all the objects
- As there are different systems working one after the other, the performance of the systems further ahead depends on how the previous systems performed
4. YOLO(YOU LOOK ONLY ONCE):
YOLO is a one-step process for object detection. It is a neural network model that requires just one pass of an image through its network to conduct object detection. An obvious benefit is that YOLO proposes greater efficiency when compared to RCNNs. YOLO algorithm works using the following three techniques:
- Residual blocks : First, the image is divided into various grids. Every grid cell will detect objects that appear within them. For example, if an object center appears within a certain grid cell, then this cell will be responsible for detecting it.

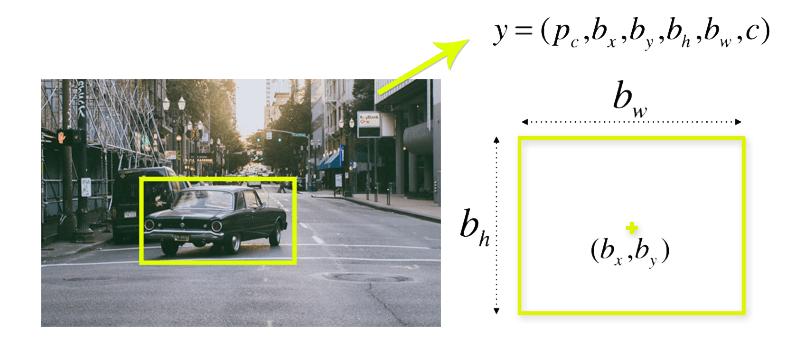
- Bounding box regression : A bounding box is an outline that highlights an object in an image. YOLO uses a single bounding box regression to predict the height, width, center, and class of objects.
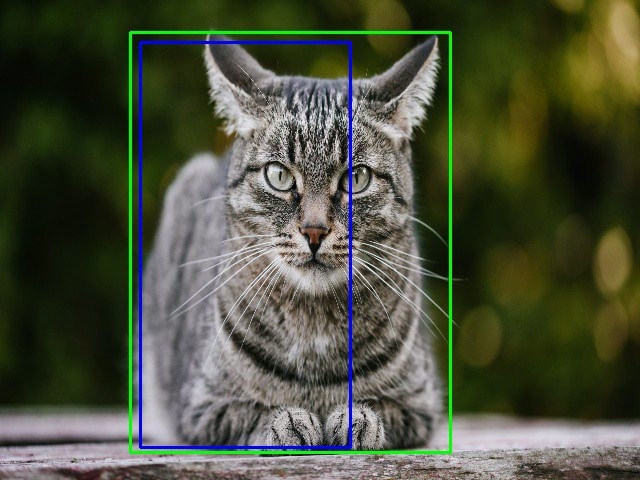
- Intersection over union (IOU) : Intersection over union (IOU) is a phenomenon in object detection that describes how boxes overlap. YOLO uses IOU to provide an output box that surrounds the objects perfectly. Each grid cell is responsible for predicting the bounding boxes and their confidence scores. The IOU is equal to 1 if the predicted bounding box is the same as the real box.
Object Detection Dataset
There are various dataset used for training the model
- The COCO Dataset
- Open Images
- Pascal VOC
APPLICATIONS
- FACE RECOGNITION : Most face recognition systems are powered by object detection. It can be used to detect faces, classify emotions or expressions, and feed the resulting box to an image-retrieval system to identify a specific person out of a group. It is also used in unlocking phone with face lock.
- AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES : Self-driving cars use object detection to spot pedestrians, other cars, and obstacles on the road in order to move around safely. For example, Tesla’s Autopilot AI heavily utilizes object detection to perceive environmental and surrounding threats such as oncoming vehicles or obstacles.
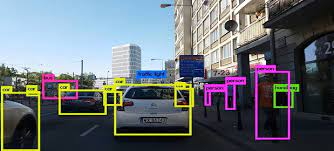
- People detection in Security : A wide range of security applications in video surveillance are based on object detection, for example, to detect people in restricted or dangerous areas, suicide prevention, or to automate inspection tasks on remote locations with computer vision.
- Pose Estimation : Finding the location of the main joints of a body from images, videos, or a sequence of images. Forms of pose estimation are present in applications such as Action recognition, Human interactions, creation of assets for virtual reality and 3D graphics games, robotics and more
- Crowd Counting : Crowd counting is another valuable application of object detection. For densely populated areas like theme parks, malls, and city squares, object detection can help businesses and municipalities more effectively measure different kinds of traffic—whether on foot, in vehicles, or otherwise.
REFERENCES
- https://github.com/amusi/awesome-object-detection
- https://towardsdatascience.com/beginners-guide-to-object-detection-algorithms-6620fb31c375”
- https://towardsdatascience.com/object-detection-with-10-lines-of-code-d6cb4d86f606
- https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2018/05/14/a-gentle-guide-to-deep-learning-object-detection/
- https://paperswithcode.com/task/object-detection
