Introduction
Machine Learning is currently one of the world’s fastest-growing technologies with an increasingly broader range of applications. Apart from the evident Artificial Intelligence, ML has various applications ranging from procedural automation to language translation to data analysis. The advent of the digital age has further increased the use of ML in different fields of work.
But one of the more unexpected applications of ML has been its increasing use in video games.
Image Upscaling
Historically, video games have often used ML techniques to create AI-bots to compete against the players. This has been a common practice but has been replaced by more advanced techniques such as Reinforcement Learning.
However, in recent times, fans have discovered that machine learning is the perfect tool to improve the graphics of classic games. The technique is known as “AI Upscaling,” which uses GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) trained on millions of low-res and high-res images. This algorithm is then used to convert low-res to high-res images with minimum loss of accuracy. Upscaling, as a general technique, has been around for a long time, but AI has drastically improved the speed and quality of results.
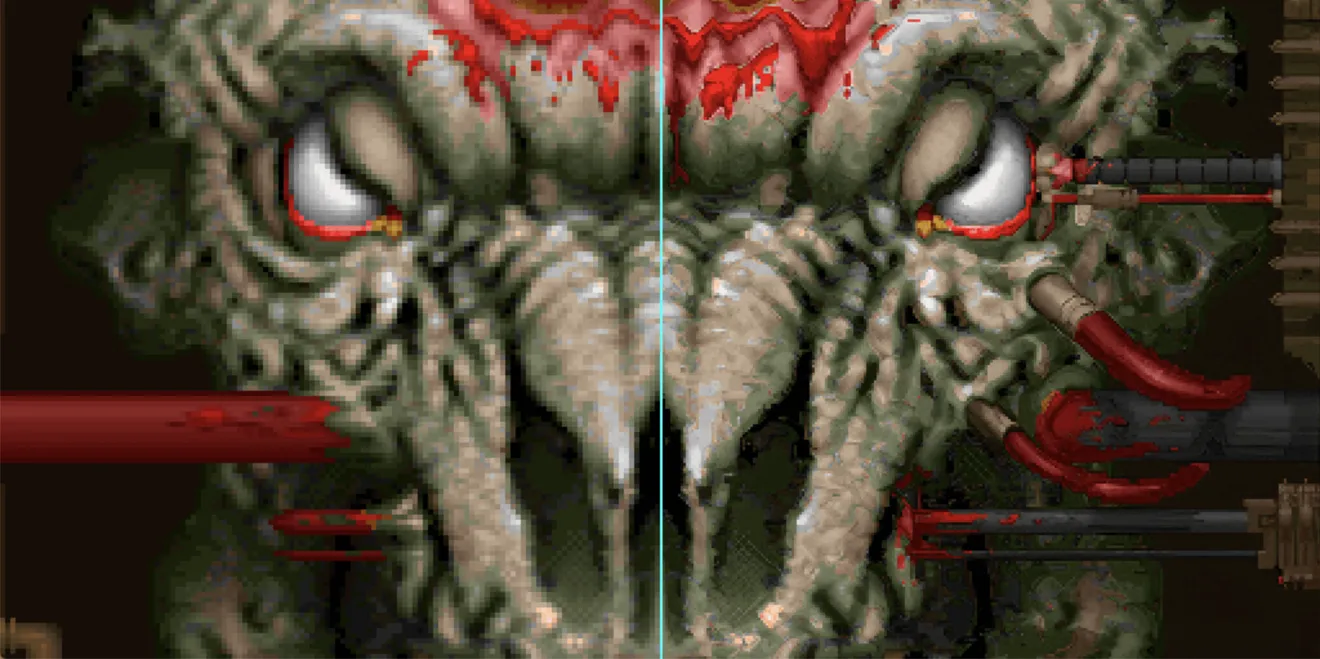
Case Study
The same can be seen in the case of the game Final Fantasy VII.
One of the big reasons a game like Final Fantasy VII looks so ugly today is because of its textures. Developers paint these JPG images on polygons so that a box looks like a wall of bricks instead. But when SquareSoft was trying to fit Final Fantasy VII on a handful of CDs, it squashed down the resolution of these assets and threw away the originals. And that posed a big problem for the prerendered background images in Final Fantasy VII.
Developers (and fan modders) have a lot of methods to improve the visuals of an old game. But nothing could make a 320-by-240 low-resolution CG background look better short of remaking them from scratch. That process is too time-consuming for fans to do for free. And Square Enix decided it was easier to remake the game instead of doing so.
This is where machine learning can make a difference. Fans used software AI Gigapixel which worked on the same principle to improve the resolution of Final Fantasy VII’s backdrops. The program works through a process of deep learning. Developers feed the system an extremely high resolution of an image and a low-resolution version of the same picture. The AI Gigapixel team then programs its neural network to attempt to make adjustments to the image.

Furthermore, big graphic-oriented companies like Square Enix have been using machine learning to improve the visuals of their games. <blockquote>“Nvidia has been inventing new ways to generate interactive graphics for 25 years, and this is the first time we can do so with a neural network,” said Bryan Catanzaro, who led the team and is also vice president of Nvidia’s deep learning research arm. “Neural networks — specifically generative models — will change how graphics are created. This will enable developers to create new scenes at a fraction of the traditional cost.”</blockquote>
To achieve this, the team based their approach on previous work like Pix2Pix, an open-source image-to-image translation tool that uses neural networks. In addition, the researchers utilized a particular type of unsupervised deep learning algorithm called generative adversarial networks (GANs), which designates one neural network as a “generator” and another neural network as a “discriminator.” These two networks play a zero-sum game — with the generator network aiming to produce a synthesized video that the discriminator network cannot ultimately determine as fake.
Training data was taken from videos of driving sequences, culled from autonomous vehicle research data in various cities, and segmented into multiple categories, such as buildings, cars, trees, etc. The GAN is then fed these data segments to synthesize a variety of fresh and different iterations of these objects to eliminate any perceived sense of déjà vu.
The team then used a conventional game engine to produce a virtual urban environment, using the GAN to generate and overlay the synthesized images in real-time. Moreover, to prevent the system from making a video where things might completely change appearance from one frame to the next, the team had to incorporate a kind of short-term memory that would enable the model to remember the attributes of objects consistently.
Future
With the advent of technologies and increasing processing power, machine learning in games has become a viable option. As a result, nowadays, game developers are looking toward ML to improve multiple facets of the games, such as-
- using AI to create a scenes a little different every time so that user feels that they are in reality which changes over time rather than a game which was created by someone and always look the same.
- reducing time to render 3D models and animations by using GANs and RL techniques.
- improving the graphics of the game by using AI Upscaling techniques.
Resources and Going Further
- AI Upscaling - A better understanding of AI Upscaling.
- Automating Model Rendering - A video about how GANs could potentially replace 3D desginers and introduction of procedural workflows.
