What is Cloud?
Simply put, cloud computing provides storage, computing resources, networking and other services without direct management by the user.
The existence of such user-accessible cloud resources is possible because of the presence of data centers.
A data center refers to the place where the servers/computers are located and the place of computation in the cloud. These servers communicate with each other using the local network.
Every cloud provider manages several data centers across the world. This kind of distribution of servers allows for reduced latency by routing the client requests to the geographically closest data center by determining his region and zone. Every region contains a certain number of zones. Users can use the cloud service through any of these regions.
Data centers will be working 24 x 7 so that the users of the cloud don’t have to worry about managing their own servers, scaling or failures since the servers are distributed. So the website will keep running even if one of the server instances goes down. Once the user buys a virtual machine by the cloud provider, he will be given an IP address of the virtual machine so that they can access it by SSHing into that virtual machine.
How does it work?
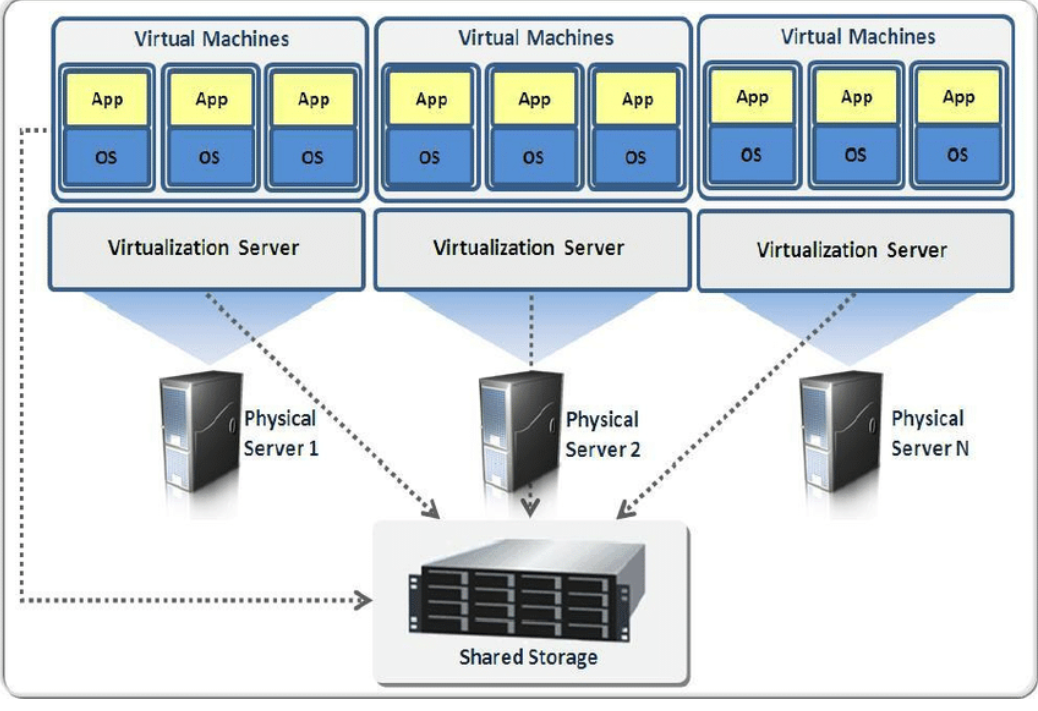
A virtual machine is an emulated computer system created using software(like virtual box). This is done by using hypervisors. Virtual machines use the resources of the physical system. They allow the user to run applications with various software dependencies in an isolated way so that developers don’t have to worry about managing dependencies. A single physical computer can run multiple VMs. They can be created using softwares like Virtual Box. Virtualization is one of the core ideas for the working of cloud computing. Each machine will have an hypervisor installed in them. Basically hypervisors are used to manage the virtualization in the machine. So to access a machine in the cloud, the user generally has to enter the hardware requirement they need and also the location of the machine they want (zone). Using this the cloud service provider will look up their data centers to find a suitable computer meeting the requirements of the request. This is done by an internal tool which is specific to the provider. The changes are continuously managed by the cloud providers. Once a particular machine is found, it will install the dependencies and the utilities user has specified and creates a connection for the user. Virtual space is allocated on the physical machine for the virtual machine and these user-specified applications.. This allows multiple users to access and utilize the resources of the same machine but have their activities completely isolated from each other on the hardware level. In this way, Virtual machines are really important for the functioning of the cloud. Cloud client/UI is basically where users select some of their software requirements. Everything else once they enter is done by the cloud provider.
Uses of cloud computing
Easy scaling/elasticity: When a company gets heavy traffic at some time, in the traditional developer-owned data center they need to scale their service horizontally to keep up with the traffic. In the cloud this is done easily using auto scaling features provided by the cloud. This makes the developers work on new ideas instead of managing servers.
Pay for what you use
The cloud service is elastic. The number of servers running in the cloud depends on the traffic. When there is usual traffic, the company doesn’t need a lot of servers. So, it is auto scaled down as required. This helps the client by cutting down on unnecessary server maintenance costs.
Performance
The servers will be upgraded to the latest generation of computing hardware when required by the cloud service provider. This is another layer of convenience to the client, since they don’t need to worry about operating on outdated hardware. Cloud has benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced network latency for the applications.
Easy and fast deployments
With the cloud, you can expand your application to new regions and deploy globally in minutes. It’s easier to expand the business all over the world with cloud instead of building data centers in all the regions and hiring people to manage them.
Cloud native apps
Cloud computing is used for building cloud native technologies and approaches like kubernetes for auto-scaling, microservices architecture, devOps etc. CI/CD : Whenever a developer commits and pushes changes to the repository, the CI system will rebuild the branch and run all related test cases to verify that new changes won’t break the existing application and functionalities. Cloud resources can automatically scale up and down based on CI/CD workloads.
DevOps
The set of practices that combines software development and operations. Sometimes the development team and operations team work together for the entire software development lifecycle from developing, deploying to operations. CI/CD is one of the best practices devops teams implement.
DevOps automation is becoming cloud-centric. Most cloud providers support DevOps systemically on their platform, including continuous integration and continuous development tools. This tight integration lowers the cost associated with on-premises DevOps automation technology, and provides centralized governance and control for a sound DevOps process.
Cloud Services
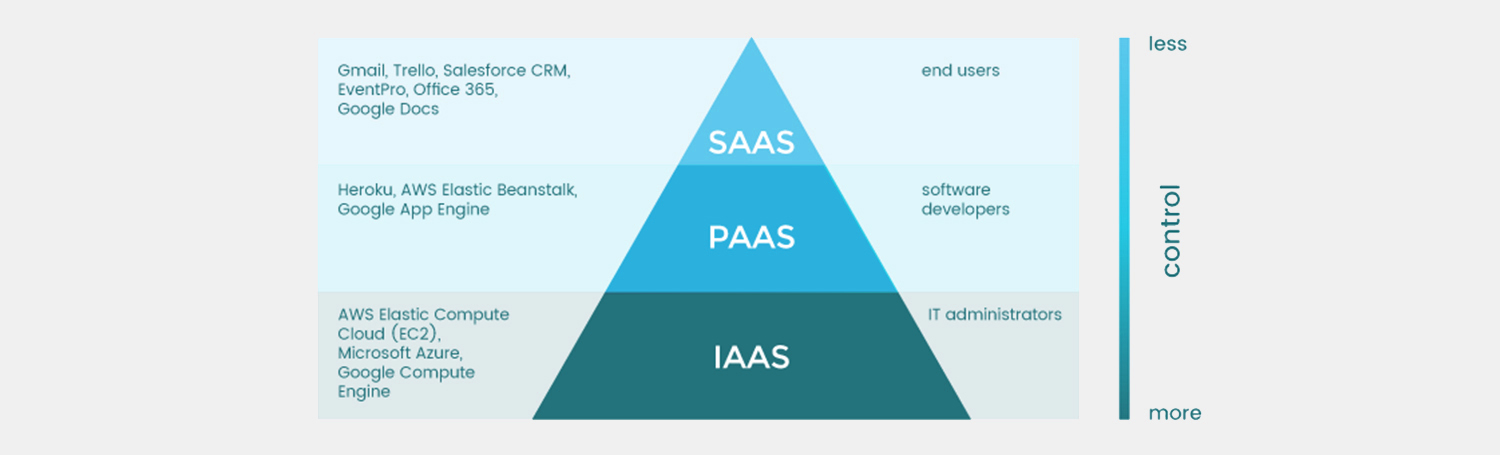
Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS)
This is the least abstracted service out of all the three. In this the user rents the resources, servers and then does the task of connecting the servers by themselves. IaaS users manage applications, runtime, OSes, middleware, and data. However, cloud providers manage the servers, networking, virtualization, and storage. Example: Google Cloud Platform
Platform as a Service(PaaS)
This is usually used by developers to code, build and run their code. This is done by using containerization/virtualization technology in the cloud. The servers, storage, and networking are managed by the cloud provider while the developers can maintain management of the applications. Developers can also use some of the APIs provided by the cloud. Example: Repl.it, Heroku
Software as a Service(SaaS)
SaaS eliminates the need of the IT staff to install applications and their dependencies on each individual computer. SaaS applications are hosted as web apps. Users of SaaS applications don’t have to install them in order to use it. Example: Salesforce, Google workspace
Conclusion
Cloud is really useful for startups by giving virtual data centres and a lot of other benefits mentioned above. It marked the beginning of a new era in the field of IT. Users are gradually moving from conventional computing to cloud computing. Using this technology, people with great business ideas will no longer need to spend a lot of money to buy computers but rather focus on building the business. Cloud computing is still at its beginning stage and there is still so much potential it can have owing to the ongoing research and development.
