How coronary stents work?
A Brief Breakdown On One Of The Most Frequented Surgeries.
Ever wondered how exactly stents are used during or after an angioplasty? Why did this method replace bypass surgeries for minor heart attacks ? Well, read on to comprehend.
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
CAD happens when a waxy substance called plaque builds up on the inner walls of the coronary arteries. This causes the arteries to harden and narrow, decreasing blood flow to the heart. As a result , the heart doesnt getthe blood, oxygen and nutrients it needs, which can lead to chest pain or a heart attack.
What are stents and how do they work?
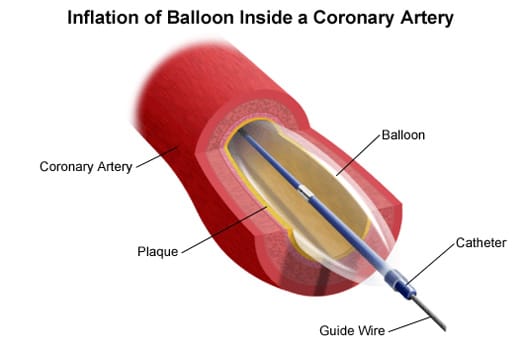
Coronary stents are small, wire, mesh tubes that help widen a clogged artery and restore adequate blood flow to the heart. during the procedure, the stent is placed over a thin, long tube with a balloon tip called a catheter and inserted into an artery in the thigh or arm. once the stent reaches the clogged artery, the balloon is inflated to expand the stent. when the stent reaches the desired size to widen the clogged artery, it is deflated and the balloon is removed.
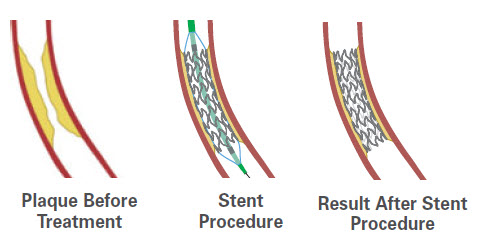
The stent will stay in place permanently to help prop open the artery and decreases its chance of narrowing agin. over time, the inner lining of the artery will grow over the surface of the stent, making it a permanent part of the artery.
Materials used
Stainless steel is the most widely used material.

But in balloon expandable stents, cobalt alloy is used.It is composed of cobalt, chromium and other metal elements . compared to stainless steel , cobalt alloy is stronger and has a higher radiocapcity. these properties make thinner struts (framework) possible. thinner struts make the device more flexible and reduce the stents cross-sectional diameter. Nitinol (fig 4) is another alloy used , which is composed mostly of nickel-titanium as well as cobalt and other metal elements. Nitinol alloy is the material most commonly used in self-expanding stents. Nitinol stents have 2 unique merits: super elasticity and shape-memory properties.
Advantages
In certain patients, stents reduce the re-narrowing that sometimes occurs after balloon angioplasty or other procedures that use catheters. patients who have angioplasty and stents recover from these procedures much faster than patients who have coronary artery bypass surgery. They have much less discomfort too.
Can stented arteries reclose?
In over a third of patients who have had angioplasty without a stent , the artery that was opened begins to become narrowed again within months of the procedure. Stents help prevent this by the use of drugs along with the them
You can watch the following video for a better visualization.
https://youtu.be/t-zCBKRg7Cs
