“Just torrent it!”
“You can torrent any type of file, its all there on the internet…”
These are just some of the common sentences one hears when it comes to downloading files from the internet. However, many people do not even know what BitTorrent is, much less know how it works.(It includes uploading files as well)
A simple introduction

BitTorrent is a communication protocol(set of rules) that is used for sharing all types of data and electronic files over the internet. This falls under the category of peer-to-peer file sharing.
Now, to implement this protocol, we need:
-
A device connected to the internet
-
A program known as a BitTorrent Client(Example- μTorrent,BitComet,etc.)
How it works
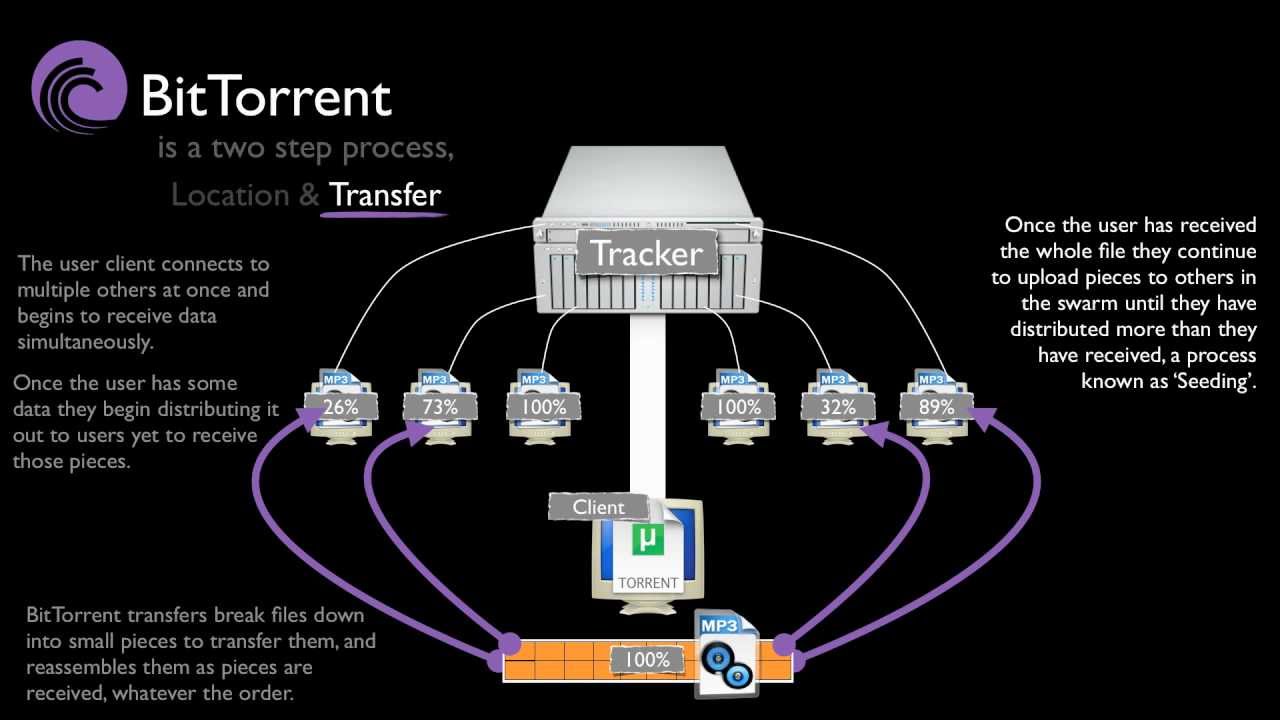
Using BitTorrent is different from any other common download or upload. Usually, users download from a single host server, but this protocol allows users to become a host , joining several other such user-hosts in the “swarm”, and upload as well as download files all at the same time. Consider the following simple example:
Several thousand users wish to download a large video file. The user responsible for uploading this file initially, becomes the seeder. The users who wish to download this file are known as leachers.
Now, each of the leachers begin to download segments/pieces of the file from the seeder. As they do so, they simultaneously begin to upload the pieces they receive to other users in need. Each of these pieces are downloaded non-sequentially, and this is where the client comes in. It rearranges the pieces so that they are in order, and determines what pieces are yet to be recieved.
Once the file is completely downloaded, the leacher becomes an additional seeder, and the greater the number of such transitions, the better the “health” of the file.
Why is this beneficial?
-
The data pieces are all of the same size. Hence, one can pause their download, and resume at any later point of time. There is no loss in information.
-
The bandwidth requirement is significantly reduced. This prevents an increase in internet traffic, and all users receive greater speed for data transfer.
Putting it all together
It is quite clear how using this protocol to transfer data is different than the orthodox method. The download in this case is in a random order, whereas it is sequential otherwise. There are security concerns that have been raised about the misuse of the technology, as it is harder to track down several different hosts rather than a single host.
For further reference, you can read up on Wikipedia or watch this video on YouTube
