AI IN MEDICINE
Artificial intelligence finds application in many fields and is now being increasingly used in healthcare. A large percentage of healthcare companies have already deployed AI technologies and are satisfied with the results
Why do you think AI is becoming so popular in the healthcare industry?
Vast amounts of medical data is available but how do we process all the data efficiently without the risk of missing out information which is vital for quality of patient care. This is where Artificial intelligence comes to the rescue. Artificial intelligence(AI) in medicine is the use of machine learning models to search medical data and uncover insights. AI, machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning (DL) enable medical professionals and healthcare stakeholders to identify healthcare needs and solutions faster with more accuracy. This helps to improve health outcomes and patient experience.
In this blog, I would like to explore 4 main applications of AI in medicine
1. Diagnosing diseases
Radiological imaging is of paramount importance as doctors often use them to confirm the diagnosis of a health condition and start the required treatment. With megapixels of data packed into the various scans like X-rays, CAT scans, MRIs, and other testing modalities, combing through very high-resolution images is often challenging even for very experienced clinicians. Studies have shown that AI tools can perform just as well, if not better, than human clinicians at analyzing features in scans.
Some examples of AI used in Radiological Imaging are:
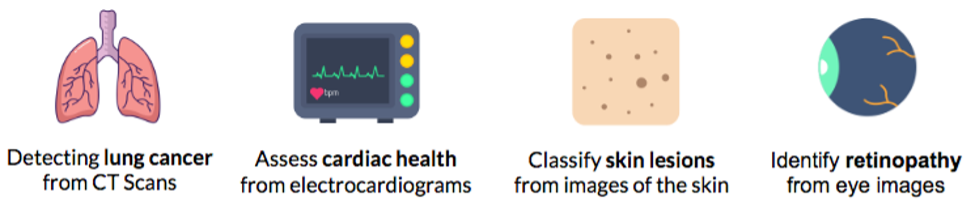
- Detecting lung and breast cancer based on CT scans - Lung and breast cancer is known to be two of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. Hence, advancements in screening processes are of utmost importance. So, AI has been implemented in nodule identification from scan images and has shown promising results in terms of sensitivity and specificity compared to radiologist performance without AI.
- Assessing cardiac health from Electrocardiograms - Researchers found that by combining AI with imaging techniques like electrocardiograms and cardiac MRI images, physicians could improve predictive models indicating a patient’s risk for heart attacks.
- Classifying skin lesions from images of the skin - AI is making progress in the field of dermatology, particularly in improving the sensitivity and accuracy of screening of skin lesions including malignancies.
- Finding indicators of diabetic retinopathy in eye images
Now let us take a quick dive into how AI is actually used in detection of lung cancer from CT scans.
Which ML technique is used for this? Deep Learning.
Deep Learning is a technique that is inspired by our brain’s own network of neurons. In this specific situation, we’ll be using the deep learning algorithm called Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).
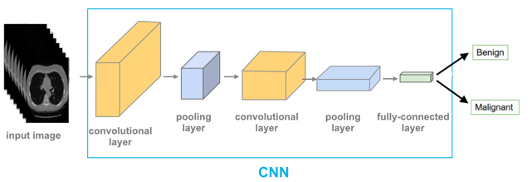
The CNN architecture generally consists of 3 main types of layers: convolutional layers, pooling layers, and a fully connected layer.
A dataset consisting of a large number of images (matrix of pixel values) of lung CT scans, both benign and malignant, is fed as input into a series of convolutional and pooling. The convolutional layers are responsible for eventually detecting objects like nodules in the lung in the images. The pooling layers are responsible for reducing the spatial size of the matrices outputted by each convolutional layer before it is sent as input into the next convolutional layer. This will help to reduce the amount of computation performed in the network.
Based on the activation values of the final convolutional layer, the fully connected layer outputs a set of confidence scores (probability) that specify how likely the image is to belong to the ‘benign’ class or the ‘malignant’ class.
2. Developing drugs faster
Developing drugs is a very laborious process involving years of work and huge amounts of investment.
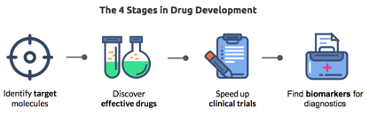
There are 4 main stages in drug development and AI is used in all the stages.
Stage 1: Identify targets for intervention
The first step is to identify the biological molecules with which potential drugs may interact to alter disease activity. Traditionally targets were discovered through experiments, however you wouldn’t know whether there is better target out there because you are limited by the targets that you have screened for. This is where ML can help.
Stage 2: Discover drug candidates
Next, you need to identify a compound that can interact with the identified target molecule in the desired manner. This often involves screening many thousands or even millions of potential compounds for to observe their effect on the target which can be done easily with the help of ML models.
Stage 3: Speed up clinical trials
It’s quite hard to select suitable candidates for clinical trials and if you choose the wrong candidates, it prolongs the trial, costing a lot of time and resources. ML can speed up the process by automatically identifying suitable candidates They also act as an early warning system for a clinical trial that is not producing conclusive results.
Stage 4: Find Biomarkers for diagnosing the disease
Biomarkers are molecules that are found in bodily fluids which can be used to diagnose a disease, to assess disease progression, disease risk and disease prognosis. AI algorithms classify molecules into good and bad candidates – which helps clinicians focus on analyzing the best prospects.
3. Personalized disease treatment
No patient is the same. Sounds obvious, yet often doctors treat patients with the same diagnosis in a similar way. ML models can help doctors to personalize treatments for different patients with the exact same diagnosis.
4. Improve gene editing
Gene editing has been gaining popularity as potential treatment for genetic diseases. CRISPR-Cas9 system for gene editing is a big revolution in gene editing as it uses single guide RNA (sgRNA) to target and edit a specific location on the DNA. However, the limitation is that the sgRNA can fit multiple DNA locations which can lead to off target effects. ML models can reliably predict the degree of both sgRNA – target interactions and off target effects for a given sgRNA. This helps to develop appropriate shRNA for all regions of human DNA with precision.
What are the challenges of AI in healthcare?
In order for an AI solution to be successful, it requires a vast amount of patient data to train and optimise the performance of the algorithms. In healthcare, getting access to these datasets poses a wide range of issues such as:
- Patient privacy and the ethics of data ownership – accessing personal medical records is strictly protected.
- Quality and usability of data – in other industries, vast amounts of data are generally reliable and accurately measured – for example, aircraft engine sensors or car location and velocity data to predict highway traffic. However, in the healthcare industry, data can be subjective, and often inaccurate.
The future outlook for AI
Over the next few years, hybrid models will be adopted, where clinicians are supported in diagnosis, treatment planning, and identifying risk factors, but retain ultimate responsibility for the patient’s care. This will result in faster adoption by healthcare providers by mitigating perceived risk and start to deliver measurable improvements in patient outcomes and operational efficiency at scale.