What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a school of computer science that focuses on programming machines to improve their performance through data and iteration. The machine can learn without being explicitly programmed. Yes, you read it right. This is called Artificial intelligence, where we feed in data into the machine, and it learns the data and predicts the output for any other input given. Machine learning is broadly classified into
- Supervised Learning In supervised learning, we have an idea of the relationship between the inputs and the outputs from the dataset given. It is further classified into - Regression: Output can take continuous values (e.g., If the picture of a vehicle is given and it is asked to predict how old the vehicle is. ) - Classification: Output is discrete(binary) (e.g., If the age of a person is given and the machine is asked to predict if they have a particular disease.)
-
Unsupervised Learning Unsupervised learning is the training of an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm using information that is neither classified nor labeled. Hence the algorithm acts on the data without any previous guidance.
- Reinforced Learning Unlike the other types, there is no data set given, and the machine is bound to learn from experience (e.g., In a chess game the machine rains itself with all possible moves) Now we shall move ahead and understand the algorithms used for learning
The Learning Algorithms
Before proceeding with the learning algorithms, we can first have a look at the variables we shall be using. x(i) -The input y(i)-The output (x(i),y1(i))-Training example h(θ(x(i)) - Hypothesis function using which values can be predicted, and θ(i) are the weights
J(θ0,θ1)=(1/2m)*∑(i=1 to m) (y(i)−y1(i))^2 = (1/2m)*∑(i=1 to m)(hθ(x(i))−y(i))^ 2
In the given equation, the variable J is called the cost function, which calculates the error and aids in calculating the accuracy of the hypothesis, which is measured. The error term is the difference between the hypothesis and the original output y. The error term is squared and divided by two as while we calculate the gradient descent (a method of reducing the error ), it will be easier for calculation.
Gradient Descent
The purpose of finding the cost function is to reduce the error in the hypothesis and improve the accuracy. Gradient Descent is an iterative algorithm used to optimize and find the minimum value for the cost function in this case. The gradient descent algorithm is as follows:
θj:=θj−α(∂/∂θ(j))J(θ0,θ1)
Here the value of θ the weight is updated so that the slope of the cost function reduces, and it becomes optimized. This concept can be clearly understood with the image shown below.
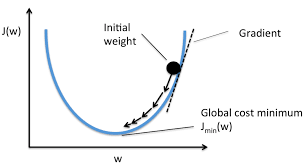
This iterative process is continued until J reaches its minimum value. This process can be imagined in 3-D as the two weights θ0 and θ1 as the x and y axes and the function J as the z-axes, then the lowermost point(like the lowermost pint of a basin) can be found using this algorithm.
Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression is the appropriate analysis to conduct when there are only two possibilities(binary). Logistic Regression is a predictive analysis. Logistic Regression is used to describe data and to explain the relationship between one binary variable and one or more nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio-level independent variables.
Take an example where we need to classify whether an email is a spam or not. If we use linear Regression for this problem, there is a need for setting up a threshold around which the classification can be done. Say if the actual email is spam; if the predicted continuous value 0.4, and the threshold value is 0.5, the data point will be classified as not spam.
The hypothesis, instead of being the weighted sum of inputs is the sigmoid function with the input as the weighted sum of inputs.
The sigmoid function also called the logistic function gives an ‘S’ shaped curve that can take any real-valued number and map it into a value between 0 and 1. If the curve goes to positive infinity, y predicted will become 1, and if the curve goes to negative infinity, y predicted will become 0. If the output of the sigmoid function is more than 0.5, we can classify the outcome as 1 or YES, and if it is less than 0.5, we can classify it like 0 or NO. Using the sigmoid function we are squashing the output of the linear function into the range [0,1]. Now the threshold value can be applied and the predction can be done.

1/1+(e^(-x)).
Regularization
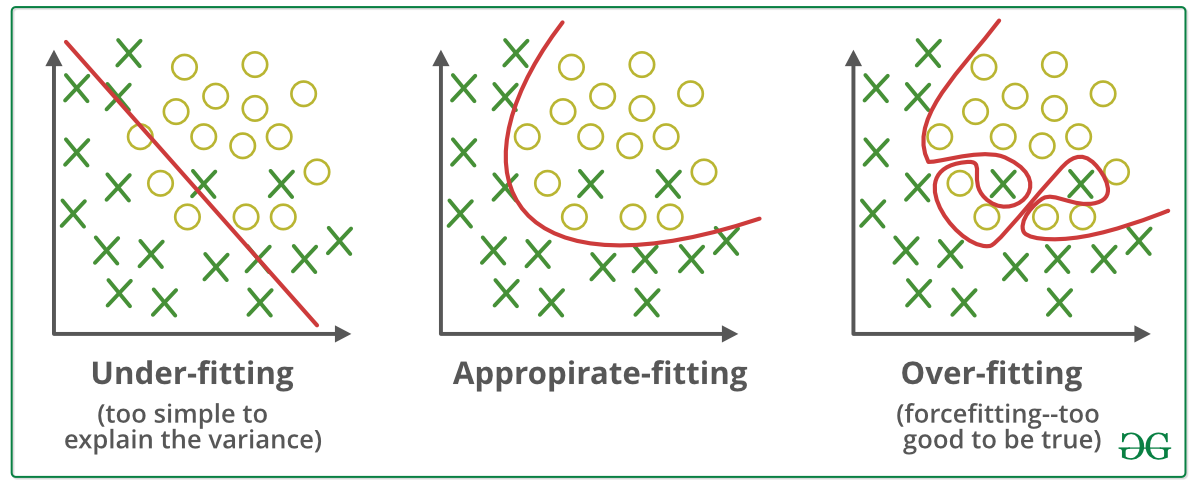
Sometimes when we try to reduce errors a lot, we end up with a function that fits the training data set correctly, but it may not be correct for predicting the output for new data(overfitting). This overfitting happens due to larger weights and more input variables, and by using regularization, it can be avoided. This is a form of Regression that regularizes or shrinks the coefficient estimates towards zero. In other words, this technique discourages learning a more complex or flexible model to avoid the risk of overfitting.In simple terms, if we utilize a curve with higher powers, we can get an equation that fits the training set but might have significant errors during prediction. Hence regularization is used.
There is a regularization parameter(λ) multiplied with the sum of the square of the weights. This λ inflates the weights, and hence while using gradient descent, the curve is smoothened, and overfitting is avoided. Too large a value of λ can also cause problems like underfitting, so an optimum value of λ should be taken.
Neural Networks
A neural network is a type of machine learning which models itself after the human brain. This type creates an artificial neural network that, via an algorithm, allows the computer to learn by incorporating new data. So far, we were calculating the hypothesis from various inputs directly. However, in neural networks, there are several layers, and the hypothesis output for the previous layer acts as the input for the next layer. It is analogous to the brain and the nerves. The dendrites take in the input and processes it. Then it is passed to the axon, which is, in turn, connected to the dendrites of another neuron.
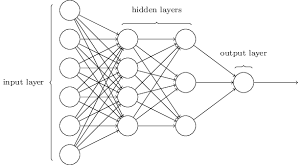 This is the figurative representation of the neural network. Where layer 1 acts as input, and it is processed by layer two whose output is in turn processed by layer three and is finally given out as the final output. The layers 2 and 3 are called hidden layers.
Usually, you set to buy something, but you end up buying a lot more than planned. This is due to the recommendations on the online websites.
Yes, neural networks do play a role in that. By making use of neural networks and its learnings, the e-commerce giants are creating Artificial Intelligence systems that know you better than yourself. Data is collected from online searches.
Social Media platforms instantly identify which of your friends is in the photo Artificial Intelligence research, discusses the applications of Neural Networks to power their facial recognition software. The image is passed through various levels of the network.
This is the figurative representation of the neural network. Where layer 1 acts as input, and it is processed by layer two whose output is in turn processed by layer three and is finally given out as the final output. The layers 2 and 3 are called hidden layers.
Usually, you set to buy something, but you end up buying a lot more than planned. This is due to the recommendations on the online websites.
Yes, neural networks do play a role in that. By making use of neural networks and its learnings, the e-commerce giants are creating Artificial Intelligence systems that know you better than yourself. Data is collected from online searches.
Social Media platforms instantly identify which of your friends is in the photo Artificial Intelligence research, discusses the applications of Neural Networks to power their facial recognition software. The image is passed through various levels of the network.
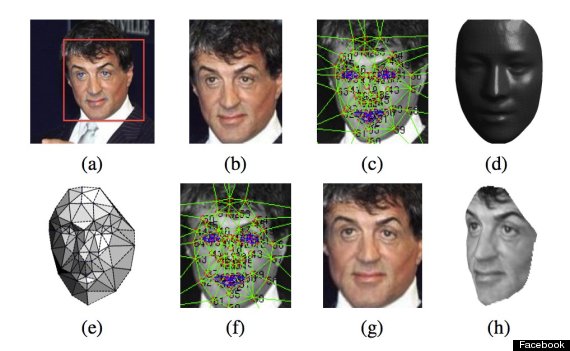 To determine which weight is better to modify, a particular process, called “backpropagation” is done.
To determine which weight is better to modify, a particular process, called “backpropagation” is done.
Backpropogation
In neural networks also, the accuracy can be improved. Backpropagation algorithms are a group of methods used to train artificial neural networks following a gradient-based optimization algorithm appropriately. The critical feature of backpropagation is its iterative, recursive, and efficient method for calculating the weights updates to improve the network until it can perform the task for which it is being trained. In machine learning, backpropagation is commonly used by the gradient optimization algorithm to adjust the weight of neurons by calculating the gradient of the loss function. For the algorithm refer:https://towardsdatascience.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-neural-networks-and-backpropagation-machine-learning-made-easy-e5285bc2be3a
The Types of Neural Networks
-
Feed Forward Neural Network:
A feedforward neural network is an artificial neural network in which connections between the node are not cyclic. The feedforward neural network was the first and most straightforward type of artificial neural network. In the feedforward network, the information moves in only one direction, forward, from the input layer, through the hidden layers, and to the output nodes.
-
Multilayer Perceptron:
A multilayer perceptron has one more hidden layer between the input and output layers. It is used to separate data into classes that cannot be separated by linear methods. This is a type of artificial neural network that has connections from every single node in a layer to each node in the following layer.
-
Convolution Neural Network(CNN):
CNN, like all neural networks, are made up of neurons with weights and biases. Each neuron receives inputs, takes a weighted sum over them, passes it through an activation function, and responds with an output. The whole network has a loss function, and all the tips and tricks that are applicable for neural networks still apply on CNNs.
-
Recurrent Neural Network(RNN):
A Recurrent Neural Network is a type of ANN(Artificial Neural Network) in which the output from a particular layer is saved and given as feedback to the input. This feedback helps predict the outcome of the layer. The first layer is formed in the same way as it is in the feedforward network. That is, with the product of the sum of the weights and features. However, in subsequent layers, the recurrent neural network process begins.
