Deep learning is progressing at a rapid pace and everyday there are some breakthroughs in the field of artificial intelligence. Recently, OpenAI came up with their DALL.E2 which creates realistic images and art from a description in natural language. It is all the talk right now. There are so many amazing models that it is hard to keep track of all of them. One particular neural network model changed the way common natural language processing tasks are done. It is called a Transformer which used the attention mechanism to do effective natural language processing tasks.
A brief introduction to sequence-to-sequence(seq2seq) models
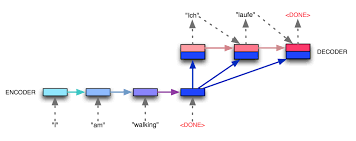
Seq2seq models convert one type of sequence to some other type of sequence. It may be converting sentence in one language to a sentence in some other language. They can also be converting audio to text. I will be focusing on the text2text sequence models in this blog. Generally, in seq2seq models, we use LSTM(long short term memory) models which keeps track of the sequence while remembering(or forgetting) the important(or unimportant) parts of the sequence. There are other models like GRU and RNN which can be used in specific usecases.
Seq2seq models consist of two components, the encoder and the decoder. The encoder operates on the input and converts it into encodings. The decoder takes these encodings and decode them to give an output. This output is then compared with the expected output and accordingly the parameters of encoder and decoder changes and the model learns. If the last few sentences seemed too complex to you, think of it this way, the encoder and decoder know a common language. The encoder converts the input into that common language and the decoder then converts this common language into the output language, sort of like translators.
Attention is all you need
The paper “Attention is all you need” introduced the novel architecture called Transformers. It uses attention mechanism for sequence transduction. But what exactly is attention mechanism? Let’s understand it.
Attention mechanism goes through an input and at each step decides which other parts of the sentence are important. Let me explain it with a real world example. While reading a sentence, you go through the entire sentence but hold on to the keywords to have the context of the sentence. Attention mechanism does something similar. It gives more attention to the words or parts of the sequence which gives context of the whole sequence.
Transformer is also a seq2seq model but it differs from the existing seq2seq models as it does not use recurrent neural networks. Let’s take a look at the transformer model architecture.
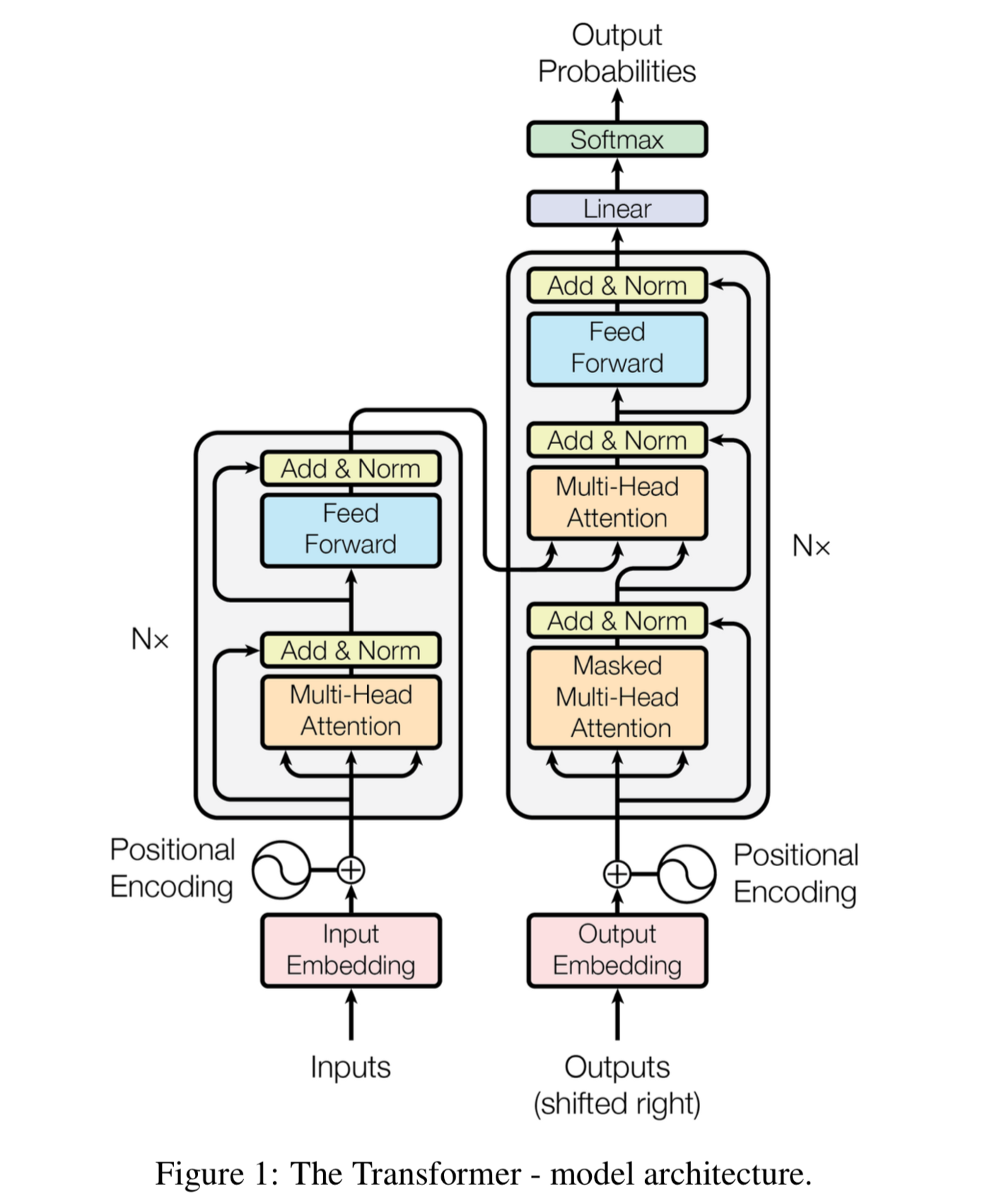
The encoder is made of modules that can be stacked on top of each other multiple times. Each module mainly consists of multi-head attention and feed forward layers. We can see a positional encoding at the bottom of both encoder and decoder. This is to give each word a relative position to remember the order of the sequence. The input and output sentences are first embedded into an n-dimensional space. Let’s define the attention equation first.
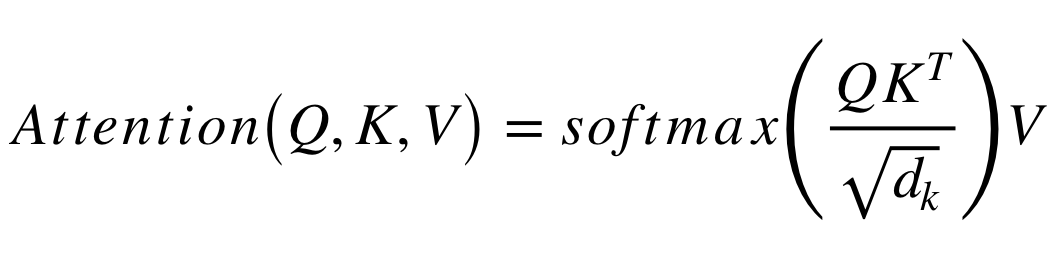
Here, Q is query matrix that contains the query (vector representation of one word in the sequence), K are all the keys (vector representations of all the words in the sequence) and V are the values, which are again the vector representations of all the words in the sequence. In simple terms, think of Q as asking a question for a particular word of the sentence as to how close or far is it from the other words of the sentence. K represents the words with which we are comparing our query word. Each word has a K vector. Now, once we have found out how close each word is with the query word, we multiply this similarity with the value(V) of each word to get a proper number. For the encoder and decoder, multi-head attention modules, V consists of the same word sequence than Q. However, for the attention module that is taking into account the encoder and the decoder sequences, V is different from the sequence represented by Q. Here, d_k is the dimension of the space into which the input and output are embedded.
Taking the analogy of linear regression, we can think that the values in V are multiplied and summed with weights which are defined as follows:
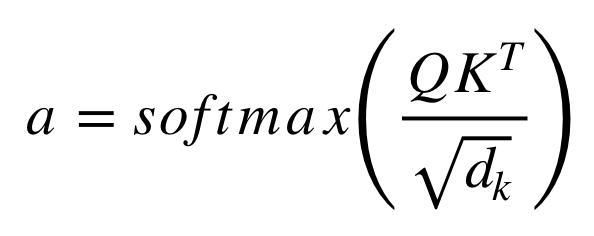
It means that weights a is defined as how each word (represented by Q) is influenced by all the other words in the sequence (represented by K). Because of the softmax function, the weights will have values from 0 to 1. These weights are then applied to all the words in the sequence that are introduced in V(same vectors than Q for encoder and decoder but different for the module that has encoder and decoder inputs).
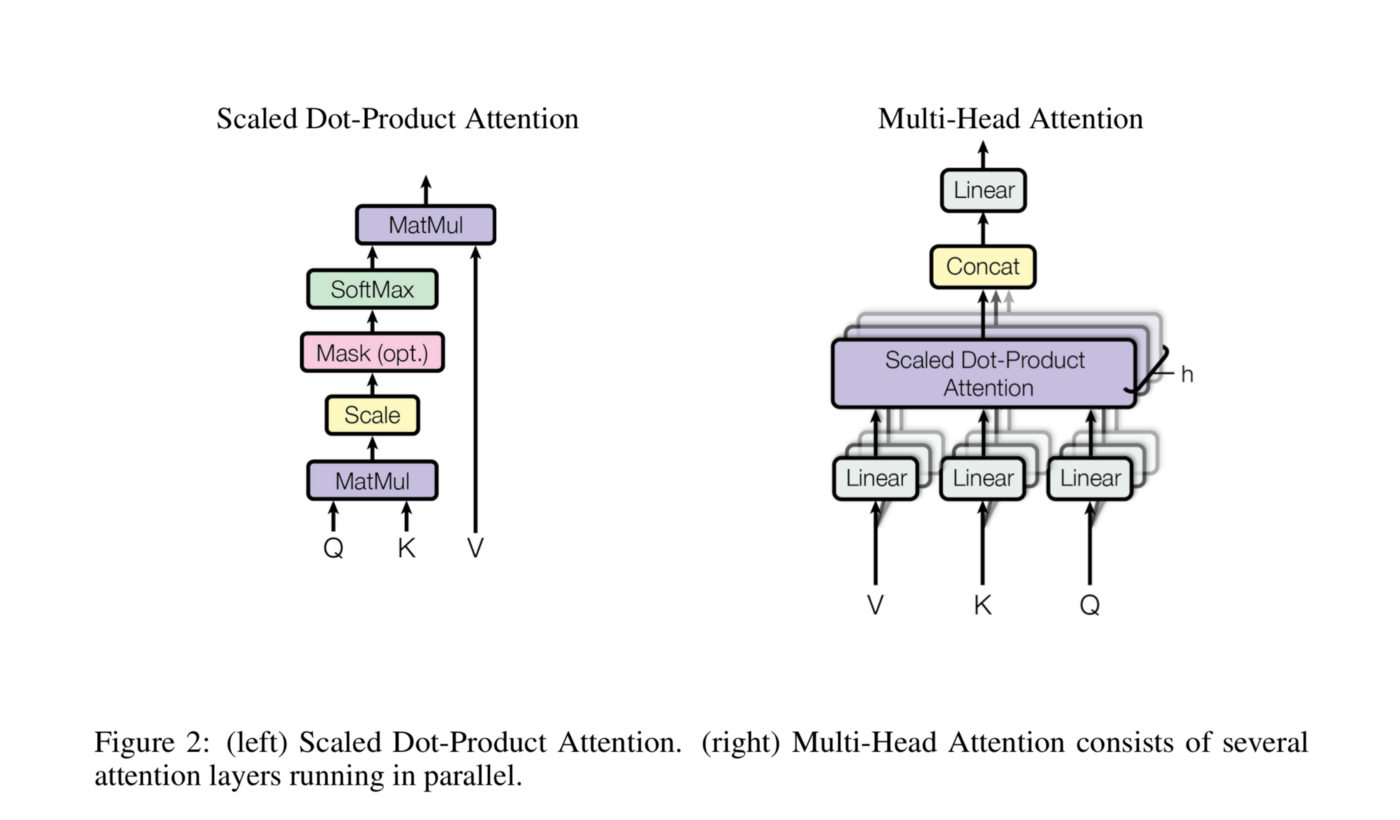
In the multi-head attention model, the attention mechanism is parallelized into multiple mechanisms. The attention mechanism is repeated multiple times with linear projections of Q, K and V. Hence the model learns with different values of Q,K,V which inceases the accuracy of the model.
Now, let’s see how the training of this big model takes place. We put the input into the encoder and it gives out the encodings. We then put the output into the decoder and it gives out the encodings too, but there is a catch here. It shift the positions of the words in the decoder layer by 1 to the right. This allows the model to learn the words on its own instead of just copying the output sentence’s words. It tries to guess what comes next based on the part of the sentence it has seen till now. Also, it applies a mask to the input in the first multi-head attention, the reason being that if we input all the words together, the model can see the possible future sequence elements and hence not learn properly. The training of this model is extremely fast because it does not go through the sentences sequentially, it puts all of them together and parallelizes learning. This parallelization speeds up the whole training process a lot.
This blog is just a small introduction to Transformers. There are many usecases and amazing models based on this architecture. I would encourage you to go and check them out and probably make a model of your own :)
