Liquid Crystal Display
Abstract
Liquid Crystal Display(LCD) is a flat panel display which is used in almost every screen which we are currently using. LCDs were a big leap in terms of the technology they replaced, which include light emitting diodes(LED) and gas-plasma displays. LCDs allowed displays to be much thinner than cathode ray tube technology. LCDs consume much less power than LED and gas-display displays. In short, LCDs are much more efficient than any of the previous generation inventions.
How does Liquid Crystal Display work?
A display is made up of millions of pixels. The quality of a display commonly refers to the number of pixels; for example, a 4K display is made up of 3840 x2160 or 4096 x2160 pixels. A pixel is made up of three subpixels; a red, blue and green commonly called RGB. When the subpixels in a pixel change color combinations, a different color can be produced.
With all the pixels on a display working together, the display can make millions of different colors. When the pixels are rapidly switched on and off, a picture is created.
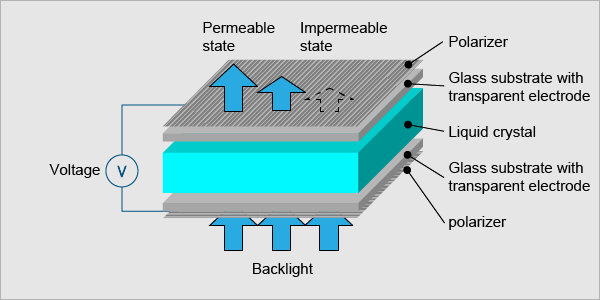
The way a pixel is controlled is different in each type of display. In short, LCDs are lit by a backlight, and pixels are switched on and off electrically while using liquid crystals to rotate polarized light. A polarized glass filter is placed in front and behind all the pixels, the front filter is placed at 90 degree. In between both filters are the liquid crystals, which can be electrically switched on and off.
Types of LCDs:
- Twisted Nematic (TN) : which are inexpensive while having high response times. However, TN displays have low contrast ratios, viewing angles and color contrasts.
- In Panel Switching Displays (IPS Panels) : which boast much better contrast ratios, viewing angles and color contract when compared to TN LCDs.
- Vertical Alignment Panels (VA Panels) : which are seen as a medium quality between TN and IPS displays.
- Advanced Fringe Field Switching (AFFS) : which is a top performance compared IPS display in color reproduction range.

Advantages of LCDs
- Energy Efficient : LCDs are known for their energy-efficient properties. When compared to cathode ray tubes, for example, a typical LCD will use about 25% less power. As a result, LCDs offer cost saving benefits in the form of cheaper utility bills.
- Long Lasting : LCDs have a longer lifespan than that of other display devices. A typical LCD may last for up to 60,000 hours.
- LED Backlighting : LED is the most common type of backlighting used in their construction.
- NO Screen Burn-In : screen burn-in is a phenomenon that occurs in display devices with phosphor-based pixels. Traditional cathode ray tubes fall under this category because their pixels are made of phosphor compounds. LCDs, however, use pixels made of organic materials.
- Supports Small and Low-Profile sizes : LCD devices come in all shapes and sizes. While some of them are large, others are small with a narrow and low-profile design. Smartphones and tablets, for example, often use LCD technology. It allows for small and low-profile designs that isn’t possible with other, older display technology.
Disadvantages of LCDs
- For an LCD the aspect ratio and resolution are fixed and cant be changed.
- Viewing Angle : Restricted viewing angles affect the brightness, contract and colors shown. Wide angles can lead to contrast and color reversal.
- Cost : Considerably more expensive purchase price than comparable cathode ray tubes.
- White Saturation : Saturation and compression can occur due to the bright-end of the intensity scale becoming overloaded. Contract control must be carefully adjusted.
Some facts on LCDs
To say LCDs have a lot of pixels would be an understatement. While the exact number varies, most LCDs are now made with over 6 million pixels. You may discover display devices marketed and sold as light-emitting diodes (LED). Based on the name alone, conventional wisdom should lead you to believe they are powered LED display technology. However, LED displays are actually LCD displays. They are only called LEDs because they use LEDs for backlighting.
According to Statista, over 200 million LCD TVs are sold each year and that’s just one type of LCD device. Others include tablets, smartphones,watches, alarm clocks, smart appliances, human machine interfaces (HMis) and more.
And moreover the LCD displays are not affected by the magnets. So, you don’t have to worry about magnets damaging your LCD.

Conclusion
From TVs and computer monitors to smartphones, tablets and more, Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is used to power countless display devices. LCD has become an indispensable part of your life.
