Introduction to Deep Learning
Introduction?
What inspired me to write a blog on this topic was how popular the terms AI and ML were, compared to “Deep Learning” or “DL” which very few people had ever heard of, despite it making up a significant part of humanity’s journey toward achieving AI.
On an average in India, there are a higher number* of Google searches for “AI”, “ML” and “Cloud” than there is for “Deep Learning”.
DL is not an abstract concept that has not been implemented yet. Google is using deep learning in its voice and image recognition algorithms (such as face classification in Google Photos) whereas Netflix and Amazon are using it to understand the behavior of their customer. Now, imagine the potential DL has in revolutionizing the world.
Brief Summary of AI and ML
The term AI was coined in 1956 by John McCarthy, who is also referred to as Father of Artificial Intelligence. The idea behind AI is fairly simple, which is to make machines that can take decisions on its own i.e give them intelligence. Machine Learning was the first step towards AI. ML does not have a fixed definition and it is fairly common for researchers to have their own definitions. This is one such definition that is often used and most widely accepted:
“A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.” — Tom Mitchell, Carnegie Mellon University.
So, let us take the example where our program is playing chess. Then the variable definitions are as follows:
T = task of playing chess
E = experience of playing many games of chess
P = probability that the program will win the next game
So in ML, we are trying to get the program to learn without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Relationship between DL,ML,AI
Of course, the three terms are interlinked and the picture below summarizes their relationship.
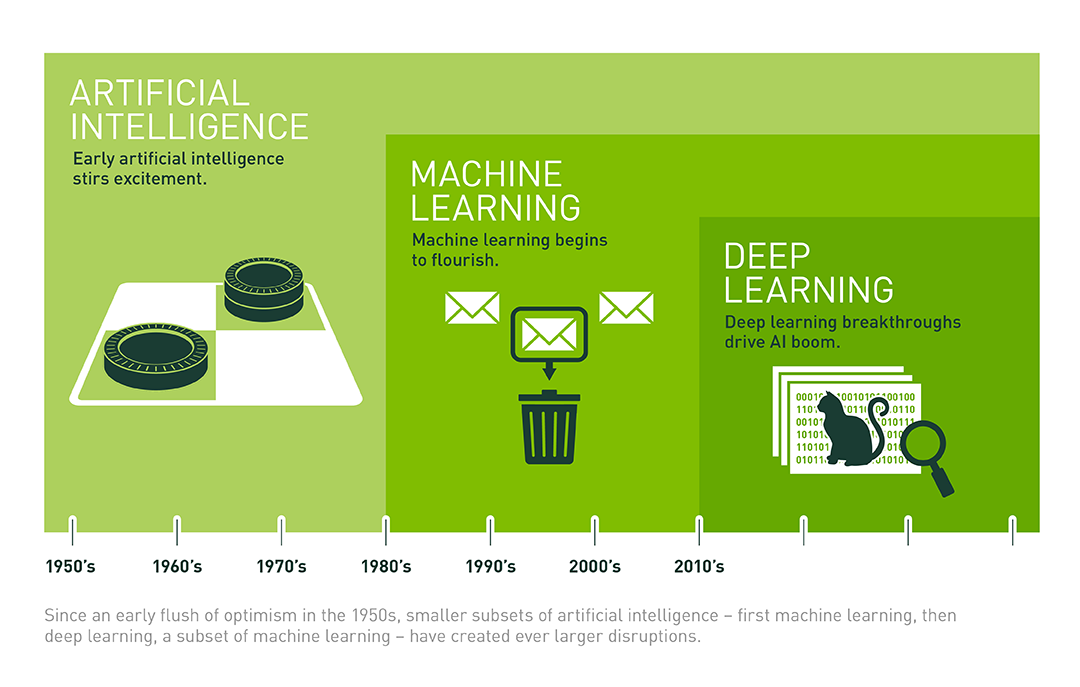
Source: Nvidia
Here, the expansion of AI is clearly outlined- where each domain takes precedence over the other in solving certain types of tasks.
Machine Learning is a subset of AI, where we provide a dataset which is often well structured to our model and it learns its craft based on that particular dataset. So if we provide the ML model a dataset of house prices in New Delhi,India, with the objective of predicting them then it will “learn” how to predict the prices specific to the dataset provided. Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning where similar Machine Learning Algorithms are used to train Deep Neural Networks so as to achieve better accuracy in those cases where former was not performing up to the mark. But why is ML not enough? This is discussed in the next section.
Drawbacks of the Machine Learning
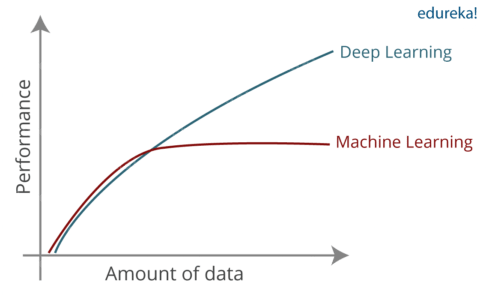
Souce: edureka
Traditional ML algorithms are not useful while working with high dimensional data, that is where we have a large number of inputs and outputs. For example, in the case of facial recognition, there are copious amounts of data that need to be dealt with. ML simply cannot provide a satisfactory result relative to the amount of data that is being provided to the program.
Another challenge is to extract the features or parameters in our data that play a vital role in predicting the outcome. This very process is referred to as feature extraction. ML does not seem to be able to efficiently extract features from the data we provide it. Let us take the example of image recognition, the patterns present in the image cannot be extracted satisfactorily with ML, and it fails to efficiently recognize important features in an image, like a face, scenery,etc…
How does DL work
Intuition
At the heart of deep learning lie Artificial Neural Networks(ANNs) or simply Neural Networks. These are the data structures or computational models that help us perform tasks such as feature extraction, as mentioned above. So why are they called Neural Networks? That is because they were inspired by the way information flows through a human- Neurons.
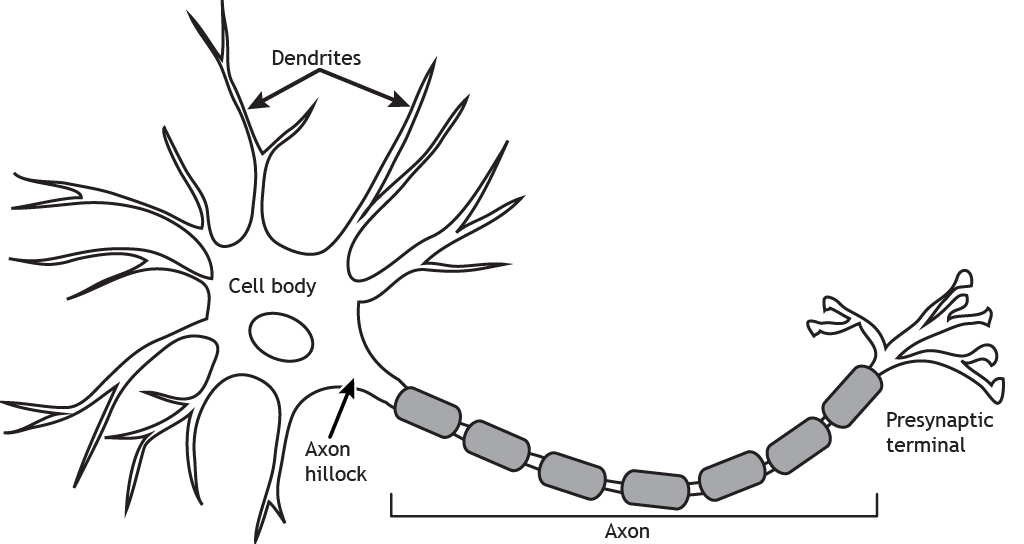
Source: openbooks.lib.msu.edu
Our human brain is a neural network, which is full of neurons and each neuron is connected to multiple neurons. Again, neurons have several Dendrites. Dendrites collect input signals which are summed up in the Cell body and later are transmitted to the next neuron through Axon.
Similarly, in an ANN, a perceptron(the basic computational unit in an ANN analogous to a human neuron) receives multiple inputs which are then processed through functions to get an output. But in the case of ANN, weights are assigned to various neurons. Then in the final layer everything is put together to come up with an answer.
Working
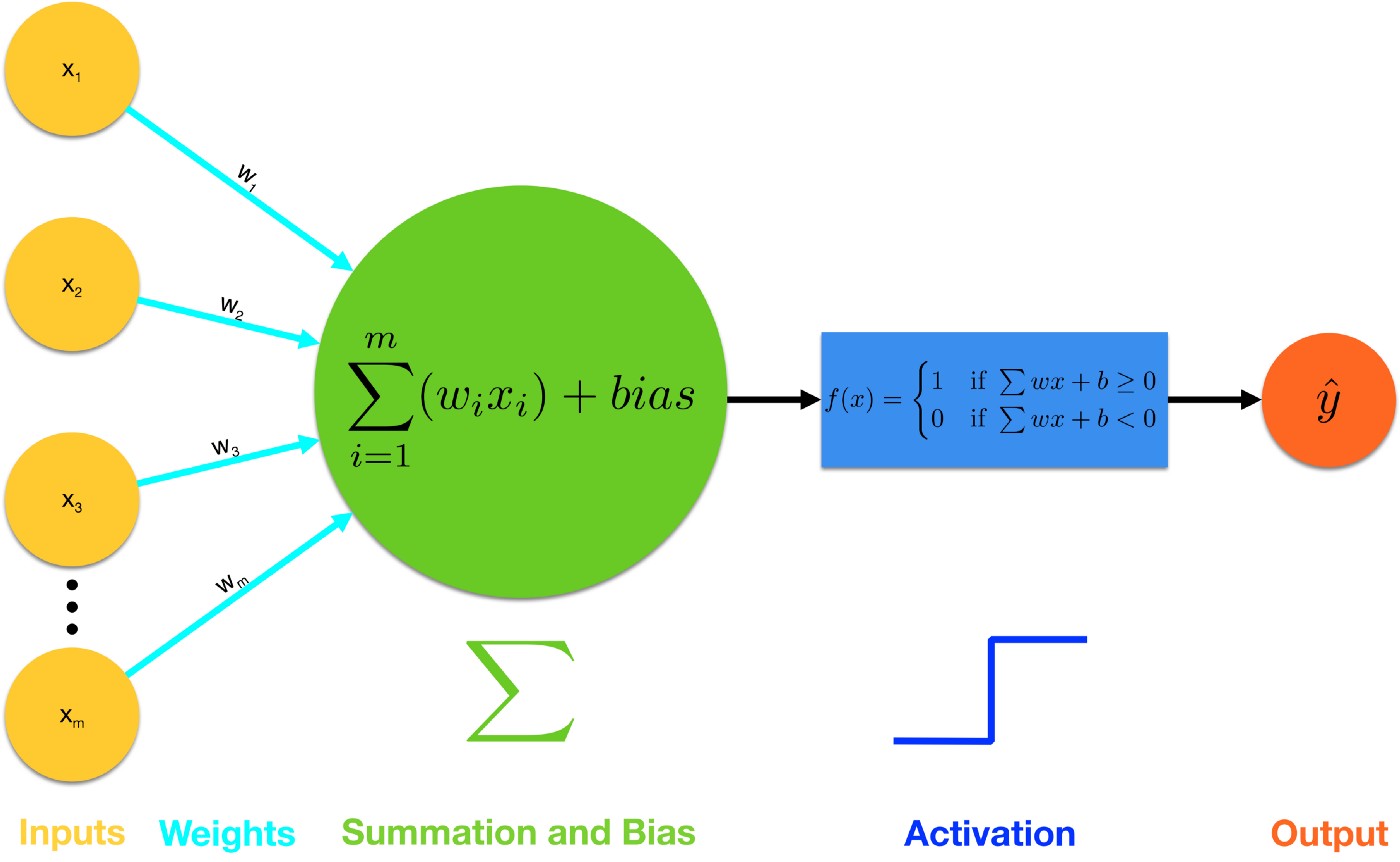
A single perceptron
Source: towardsdatascience
- On the left side data input represented by xi.
- We multiply each of the input by a weight wi, along the arrow (also called a synapse). So w1 * x1, w2 * x2, w3 * x3 and so on. The larger the weight, the more influential the corresponding input is.
- Once all the inputs are multiplied by a weight, we sum all of them up and add a bias to it bi.
- Now, we have an activation function. This particular activation f(x) outputs 1 if the sum obtained before is greater than or equal to zero. It outputs 0 otherwise.
Activation functions helps us map the input to a discrete output.
Say we are trying to recognize if the image of an animal is a dog, then we pass different pixel values of the image as input(x) and the activation function in the end tells us whether the animal is a dog(y=1) or not(y=0). Note how the results from each step moves towards the right, in a sort of forward direction. This type of flow of data is called forward propagation.
The working we saw just now is an example of a single-layer perceptron. Let us look at something a bit more complex
Multi-Layer Perceptron:
Neural networks with two or more layers are called multi-layer perceptron. This type of neural network has greater processing power. In this, the algorithm consists of two phases:
- Forward phase: Where the activations are propagated from the input to the output layer
- Backward phase: Where the error between the observed actual and the ideal value in the output layer is used to modify the weights and bias values.
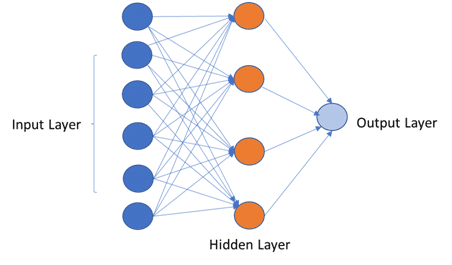
Source: edureka
Deep Neural Network:
Deep neural network refers to neural networks with multiple hidden layers and multiple non-linear transformations.
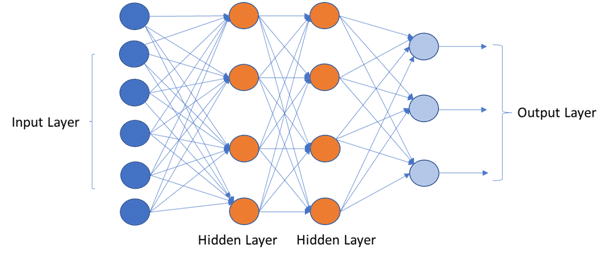
Source: edureka
As you can imagine, the power and capability of Deep Neural Networks are much higher than a single-layer Perceptron, and it has a wide range of applications.
Applications of Deep Learning:
Healthcare:
Deep Learning and its innovations are advancing the future of precision medicine and health management. Breast Cancer, Skin Cancer diagnostics are just a few examples of DL in Health Care.
In the coming years computer-aided diagnosis will play a major role in healthcare which not only speeds up the process but also may provide more accurate results than human diagnosis.
Computer vision and pattern recognition:
Computer vision has given rise to some very interesting applications such as autonomous driving. Mobileye is one such company. It is a global leader in the development of vision technology for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving.
Mobileye’s philosophy is that:
If a human can drive a car based on vision alone – so can a computer.
This philosophy reflects the culture of thinking that deep learning has developed among companies.
Their systems can identify an imminent collision and brake without any driver intervention, center the vehicles on the lane, and assist in traffic jam situations.
Note that none of these require human intervention!
Pixel restoration, automatic color-filling in B&W photos and videos are also creative applications of DL.
Voice-activated intelligent assistants:
Apple’s Siri, Google Now, Microsoft Cortana are a few examples of deep learning is voice search & voice-activated intelligent assistants.
Smart Advertising:
Publishers and ad networks can now leverage their content to create data-driven predictive advertising, precisely targeted advertising and much more. There have been ethical concerns about this such as privacy in the past few years.
Finance:
From predicting stock prices to analyzing trading strategy, and reviewing commercial loans- all come under the wings of DL.
Computer games:
Go
The standard Go board has a 19×19 grid of lines, containing 361 points. Despite its relatively simple rules, Go is extremely complex. Compared to chess, Go has both a larger board with more scope for play and longer games and, on average, many more alternatives to consider per move. The number of legal board positions in Go has been calculated to be approximately 2.1×10170, which is vastly greater than the number of atoms in the observable universe, estimated to be of the order of 1080.
DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated Lee Sedol, one of the best Go players in the world!
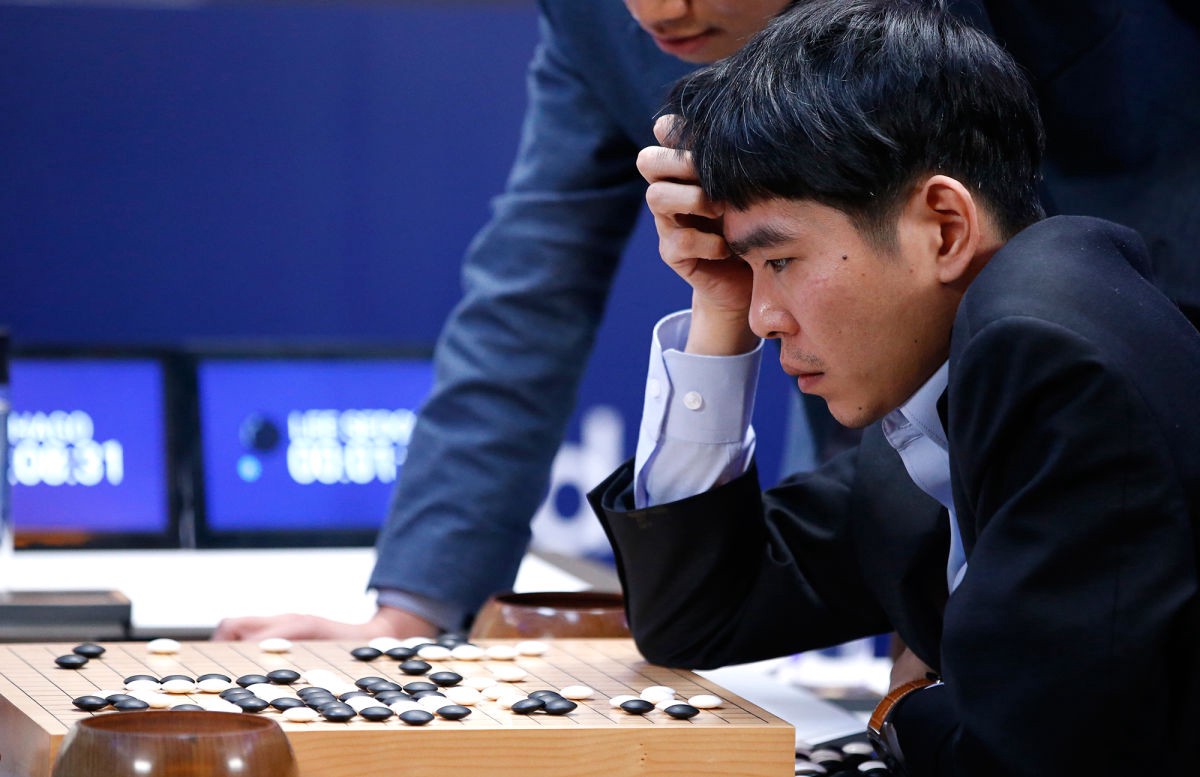

Lee Sedol vs. AlphaGo in 2016
Source: The New Yorker
Conclusion
Deep learning is not here to take part in the AI revolution, in fact it is taking over. The capabilities are limitless and its potential to help society progress is enormous.
Despite its positives, we must remember not to misuse AI such as this; to cause detrimental effects to the rest of humanity goes against the principles of why AI was pioneered in the first place- to help people.
I hope I inspired you to further pursue deep learning and use it to add something tangible to the community. With that, this is Harish Gumnur signing off.
_ _ _
According to Keyword Planner, a tool provided by Google to analyze the number of keyword searches on a monthly basis over a particular period of time. The time period referenced in this blog is April 2020 to March 2022.
