We all know how infuriating it is when our devices drains battery when it uses wireless communication like wifi, bluetooth, infra-red. In every device we use, we are always concerned with the power consumption. A device which consumes less power is always favourable. So in this article, I am going to elucidate an effective solution to the power problem in wireless communication- Bluetooth Low Energy , also known as BLE.
Why BLE?
Historically, classic bluetooth (the bluetooth we are all aware of) was mainly designed to replace cable and it covers many protocols. And with speeds increasing with new versions, power consumption was not always the primary concern for this technology.
Hence, it was not suitable for wireless boards running on a battery that only needs to send a few bytes of information. Well this is where BLE comes in. It was contrived to consume as low power as possible. Devices using BLE can run on button cells for months or even years.
BLE Architecture
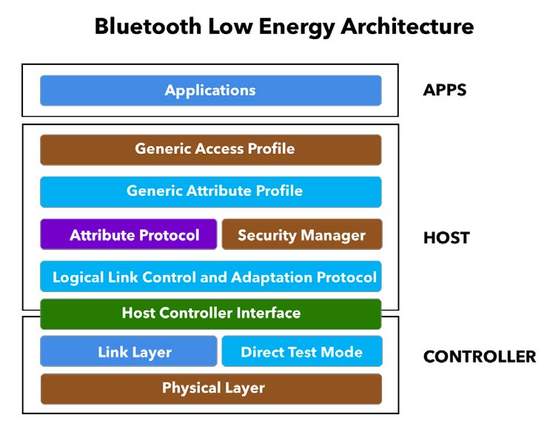
BLE architecture has the following stacks-
-
Physical layer -
This is the physical radio which transmits in the 2.4GHZ radio spectrum, which is the same spectrum used by classic bluetooth, wifi and zigbee.
-
Link layer -
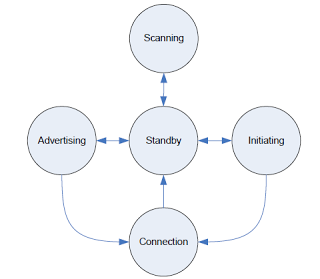
The link layer describes how two devices can use a radio link to transmit information from one to another. The link layer has a simple a state machine with only 5 states- - Standby mode: Device is in an idle state - Advertising mode: When the slave needs to make a connection. If it is sending data, it goes to anyone, its not specifically meant for any particular device. - Scanning mode: When a device wants to listen what other devices are advertising. - Initiating mode: This is sent from the future master to the device that is advertising and asked to make a specific connection. - Connected mode: This is when two devices are connectedand sending each other data packets purposefully, so it has a starting point and end point, not general advertising.
-
Host Controller Interface (HCI) -
It is the interface between the host and the controller. The HCI has 2 main functions- - It sends commands to the controller and receives events back. - And it sends and receives data from a peer device.
-
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) -
The L2CAP multiplexes 3 different channels and it enables segmentation and reassembly of the data packets that are larger than the radio can deliver.
-
Attribute Protocol -
This is where the data is stored and defines how the attribute is managed, the type of attribute, how to read or write data and much more.
-
The Generic Attribute Protocol (GATT) -
The GATT defines the format of the data exposed by a BLE device. It also defines the procedures needed to access the data exposed by a device.
-
Generic Access Protocol (GAP) -
This makes the device visible to the outside world and determines the role of the device in the network.
But why does BLE consume less power?
BLE uses less energy by keeping things simple. Instead of maintaining a constant connection, the BLE protocol only sends data as needed. And it does so with very little overhead. This allows the device to sleep for longer periods of time , turn off the radio and consume less power. Thus, it is great for periodic updates, like getting readings for a sensor. But its not so great for streaming audio or video. For now, that is a job left to classic bluetooth or wifi.
Advantages
- Ultra-low peak, average and idle mode power consumption
- Low power requirements
- Small size
- Low cost
- Compatibility with large base of mobile phones, computers and tablets
- Communication range(10-50m)
Applications
- Home Automation(Internet of Things)
- Fitness Devices
- Indoor Location(where GPS is not feasible)
- Medical and personal health devices
